Introduction to Animals
... Ganglia are clusters of nerve cells found in more complex animals Nerve cells may specialize to detect, light, sound, etc. Brain interprets nerve impulses & sends a response ...
... Ganglia are clusters of nerve cells found in more complex animals Nerve cells may specialize to detect, light, sound, etc. Brain interprets nerve impulses & sends a response ...
7system of the body
... cells. Air enters the body through our nose or mouth and goes to the trachea .Next it goes into bronchial tubes in the lungs .The diaphragm is the muscle that makes the air go in and out. The system has 6 parts: lungs, diaphragm, trachea, air sacs, bronchial tubes and blood vessels. The respiratory ...
... cells. Air enters the body through our nose or mouth and goes to the trachea .Next it goes into bronchial tubes in the lungs .The diaphragm is the muscle that makes the air go in and out. The system has 6 parts: lungs, diaphragm, trachea, air sacs, bronchial tubes and blood vessels. The respiratory ...
Phylum Chordata Subphylum Vertebrata Class Amphibia
... Origins of Amphibians • Most likely, amphibians arose as their ability to breathe air through well-developed lungs evolved. • The success of inhabiting the land depended on adaptations that would provide support, protect membranes involved in respiration, and provide efficient circulation. ...
... Origins of Amphibians • Most likely, amphibians arose as their ability to breathe air through well-developed lungs evolved. • The success of inhabiting the land depended on adaptations that would provide support, protect membranes involved in respiration, and provide efficient circulation. ...
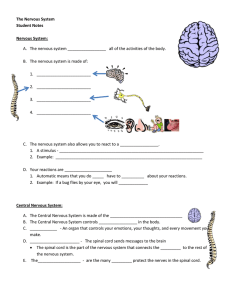
The Nervous System Student Notes Nervous System: The nervous
... 1. Automatic means that you do _____ have to __________ about your reactions. 2. Example: If a bug flies by your eye, you will _____________ ...
... 1. Automatic means that you do _____ have to __________ about your reactions. 2. Example: If a bug flies by your eye, you will _____________ ...
An Introduction to Animal Diversity
... • Animals are heterotrophs that ingest their food • Animals are multicellular eukaryotes – Their cells lack cell walls – Their bodies are held together by structural proteins such as collagen ...
... • Animals are heterotrophs that ingest their food • Animals are multicellular eukaryotes – Their cells lack cell walls – Their bodies are held together by structural proteins such as collagen ...
BIOLOGY NOTES: THE ANIMAL KINGDOM I. Overview of the
... B. Existing Amphibians 1. Several characteristics are common: a. All have bony endoskeletons and usually four legs. b. Most shed their eggs into water, which is also home to a free-swimming larval stage. c. Depending on their habitat, amphibians can respire by use of gills, lungs, skin, and pharynge ...
... B. Existing Amphibians 1. Several characteristics are common: a. All have bony endoskeletons and usually four legs. b. Most shed their eggs into water, which is also home to a free-swimming larval stage. c. Depending on their habitat, amphibians can respire by use of gills, lungs, skin, and pharynge ...
ECOLOGY SPRING 2009 - Florida International University
... -Larval sponges use cilia for swimming -Settle down on a substrate -Transform into adults ...
... -Larval sponges use cilia for swimming -Settle down on a substrate -Transform into adults ...
Animals
... and name each one individually. Although species can be very different from each other, many of them have similar features that allow us to put them into groups. • Putting different species into different groups according to their features is called classification. ...
... and name each one individually. Although species can be very different from each other, many of them have similar features that allow us to put them into groups. • Putting different species into different groups according to their features is called classification. ...
The Human Body workforce planning
... Function: works with the skeletal and nervous system to produce movement, also helps to circulate blood through the human body ...
... Function: works with the skeletal and nervous system to produce movement, also helps to circulate blood through the human body ...
Human Body Article - New World Preparatory
... Your body has many different parts. You have hard bones. You have muscle. You have a brain, a stomach, and a heart. Your body needs all these parts to work properly. Think about the different parts of your body. Your eyes, arms, and toes are very different from each other. Yet they are all alike in ...
... Your body has many different parts. You have hard bones. You have muscle. You have a brain, a stomach, and a heart. Your body needs all these parts to work properly. Think about the different parts of your body. Your eyes, arms, and toes are very different from each other. Yet they are all alike in ...
The Respiratory System.
... tendon that serves as the main muscle of respiration and plays a vital role in the breathing process 6) Trachea-The trachea, commonly known as the windpipe, is a tube about 4 inches long and less than an inch in diameter in most people. The trachea begins just under the larynx (voice box) and runs d ...
... tendon that serves as the main muscle of respiration and plays a vital role in the breathing process 6) Trachea-The trachea, commonly known as the windpipe, is a tube about 4 inches long and less than an inch in diameter in most people. The trachea begins just under the larynx (voice box) and runs d ...
Skeletal System
... Rheumatoid arthritis – synovial membrane inflamed & grows thicker • autoimmune cause (immune system mistakenly attacks synovial membrane) ...
... Rheumatoid arthritis – synovial membrane inflamed & grows thicker • autoimmune cause (immune system mistakenly attacks synovial membrane) ...
Zoology – Arthropod Unit
... number of functions: • Walking legs • Mouth parts • Antennae • Claws • Organs for mating • Holding eggs ...
... number of functions: • Walking legs • Mouth parts • Antennae • Claws • Organs for mating • Holding eggs ...
midterm review packet _2 skeletal and muscular systems student
... -What happens to the sarcomere during muscle contraction? ______________________________________________________ - What makes up a motor unit? ______________________________________________________________ -Why are you out of breath after a hard workout? Why do your muscles burn? How does this help ...
... -What happens to the sarcomere during muscle contraction? ______________________________________________________ - What makes up a motor unit? ______________________________________________________________ -Why are you out of breath after a hard workout? Why do your muscles burn? How does this help ...
Introduction to Anatomy-HHAP
... You may have heard of an umbilical bulge or an inguinal hernia, and now you know exactly where such hernias are located. A hernia is a tear in the muscle wall that allows a structure (usually an organ) to protrude through it. ...
... You may have heard of an umbilical bulge or an inguinal hernia, and now you know exactly where such hernias are located. A hernia is a tear in the muscle wall that allows a structure (usually an organ) to protrude through it. ...
5/15/12 Mollusks - Solon City Schools
... • Modified Foot: – Muscular foot and/or tentacles • Mantle: fold that wraps around visceral mass & secretes the shell • Most have shell (internal or external) – Or remnants of a shell ...
... • Modified Foot: – Muscular foot and/or tentacles • Mantle: fold that wraps around visceral mass & secretes the shell • Most have shell (internal or external) – Or remnants of a shell ...
Functional Anatomy Review for Coding Professionals
... The participants will be able to identify Anatomical Directional Terms and Planes ...
... The participants will be able to identify Anatomical Directional Terms and Planes ...
ABDOMEN 1
... Pyramidalis muscle – anatomy, atachments, actions, innervation Functions and actions of anterolateral abdominal muscles Nerves of anterolateral abdominal wall, dermatomes of anterolateral abdominal wall Vessels of anterolateral abdominal wall Internal surface of anterolateral abdominal wall – umbili ...
... Pyramidalis muscle – anatomy, atachments, actions, innervation Functions and actions of anterolateral abdominal muscles Nerves of anterolateral abdominal wall, dermatomes of anterolateral abdominal wall Vessels of anterolateral abdominal wall Internal surface of anterolateral abdominal wall – umbili ...
The-Human-Body-Overview
... with feet parallel and the arms hanging at the sides with palms facing forward. HOMEOSTASISpp. 2, 11 ...
... with feet parallel and the arms hanging at the sides with palms facing forward. HOMEOSTASISpp. 2, 11 ...
Human Body Systems The human body consists of several systems
... internal organs, and allows us to move. ...
... internal organs, and allows us to move. ...
PHYLUM MOLLUSCA
... Excretion All animals must remove waste products An open circulatory system will work well for slow moving animals. Why is an open circulatory system not adequate for ...
... Excretion All animals must remove waste products An open circulatory system will work well for slow moving animals. Why is an open circulatory system not adequate for ...
BIOL 2015 – Evolution and Diversity
... of steroids appropriately called ecdysteroids. If you have ever seen an insect crawl out of its old skin or a butterfly leaving its chrysalis then you have seen ecdysis take place. The ability to shed the cuticle has opened up options for ecdysozoans that are not available to animals with skeleton ...
... of steroids appropriately called ecdysteroids. If you have ever seen an insect crawl out of its old skin or a butterfly leaving its chrysalis then you have seen ecdysis take place. The ability to shed the cuticle has opened up options for ecdysozoans that are not available to animals with skeleton ...
Body Planes, Sections, and Cavitites
... Plane which splits body into anterior and posterior section ...
... Plane which splits body into anterior and posterior section ...
Circulatory System and Respiratory System Notes
... 9. Your lungs get bigger as you breathe in air, and they get smaller as you breathe out air. 10. The air travels through a system of tubes in your lungs that end in tiny air sacs. 11. Oxygen passes from the air sacs into your bloodstream, which delivers it to all of the cells in your body. 12. Carbo ...
... 9. Your lungs get bigger as you breathe in air, and they get smaller as you breathe out air. 10. The air travels through a system of tubes in your lungs that end in tiny air sacs. 11. Oxygen passes from the air sacs into your bloodstream, which delivers it to all of the cells in your body. 12. Carbo ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.