Invertebrates and Vertebrates
... longitudinal fibres rather than a net. 7)Generally dorsoventrally flattened. 8)Reproduction mostly sexual as hermaphrodites. 9)Mostly they feed on animals and other smaller life forms. 10)Some species occur in all major habitats, including many as parasites of other animals. ...
... longitudinal fibres rather than a net. 7)Generally dorsoventrally flattened. 8)Reproduction mostly sexual as hermaphrodites. 9)Mostly they feed on animals and other smaller life forms. 10)Some species occur in all major habitats, including many as parasites of other animals. ...
ORAL MUCOSA
... • occur as complete (soft and hard palate, possibly including a gap in the jaw) or incomplete (a 'hole' in the roof of the mouth, usually as a cleft soft palate) • a direct result of an open connection between the oral cavity and nasal cavity is velopharyngeal insufficiency • corrected by surgery us ...
... • occur as complete (soft and hard palate, possibly including a gap in the jaw) or incomplete (a 'hole' in the roof of the mouth, usually as a cleft soft palate) • a direct result of an open connection between the oral cavity and nasal cavity is velopharyngeal insufficiency • corrected by surgery us ...
Name Human Body Study Guide Lesson 1 1. homeostasis: the
... 12. Circle the correct word from each pair of words to complete the sentence. a. Arteries / Veins carry oxygen-rich / oxygen poor blood away from the heart. It contains more oxygen because it delivers oxygen from the lungs / heart to the valves / capillaries. b. Arteries / Veins carry oxygen-rich / ...
... 12. Circle the correct word from each pair of words to complete the sentence. a. Arteries / Veins carry oxygen-rich / oxygen poor blood away from the heart. It contains more oxygen because it delivers oxygen from the lungs / heart to the valves / capillaries. b. Arteries / Veins carry oxygen-rich / ...
Name Human Body Study Guide Lesson 1 MC #14: 1. homeostasis
... a. Arteries / Veins carry oxygen-rich / oxygen poor blood away from the heart. It contains more oxygen because it delivers oxygen from the lungs / heart to the valves / capillaries. b. Arteries / Veins carry oxygen-rich / oxygen poor blood back to the heart. The blood with less oxygen is taken from ...
... a. Arteries / Veins carry oxygen-rich / oxygen poor blood away from the heart. It contains more oxygen because it delivers oxygen from the lungs / heart to the valves / capillaries. b. Arteries / Veins carry oxygen-rich / oxygen poor blood back to the heart. The blood with less oxygen is taken from ...
Kingdom Animalia
... exit from the same opening 2. complete digestive system- two openings; food enters the mouth and wastes exit the anus Skeletal System FUNCTION: Provides protection 1. exoskeleton: Rigid outer covering to protect the animal’s soft tissue Limits size & impedes movement Does not grow; must be she ...
... exit from the same opening 2. complete digestive system- two openings; food enters the mouth and wastes exit the anus Skeletal System FUNCTION: Provides protection 1. exoskeleton: Rigid outer covering to protect the animal’s soft tissue Limits size & impedes movement Does not grow; must be she ...
7-3.3 Notes
... function. Circulatory System The main function of the circulatory system is to transport blood to all parts of the body so that gases, nutrients, and waste products are transported to and from the cells. The white blood cells within the circulatory system help to fight infection in the body. Res ...
... function. Circulatory System The main function of the circulatory system is to transport blood to all parts of the body so that gases, nutrients, and waste products are transported to and from the cells. The white blood cells within the circulatory system help to fight infection in the body. Res ...
... The xylem resulted remarkably homogeneous in these six species; only the presence of crystals allowed to separate them in two groups: those with crystal inclusions (F. benjamina, F. insipida, F. maitin, F. velutina) and those lacking of crystals (F. elastica, F. tonduzii). Perforated ray cells (F. t ...
PLATYHELMINTHES THE FLATWORMS
... PHARYNX – comes out of body to feed MOUTH – on ventral surface ...
... PHARYNX – comes out of body to feed MOUTH – on ventral surface ...
Musculoskeletal notes (Human Body I)
... Terms of reference for human biology: Master these words, as they will be used throughout the unit! Coelom: body cavity Thoracic: refers to the chest cavity containing the heart and lungs (aka, “trunk” or “torso”) Abdominal: refers to the lower body cavity; separated from the thoracic cavity by the ...
... Terms of reference for human biology: Master these words, as they will be used throughout the unit! Coelom: body cavity Thoracic: refers to the chest cavity containing the heart and lungs (aka, “trunk” or “torso”) Abdominal: refers to the lower body cavity; separated from the thoracic cavity by the ...
Survey of the Phyla
... and the anus. Two variations of this body plan-the polyp and medusa. The polyp is a cylinder form that is sessile and adheres to the bottom of the water. The medusa is a "flattenedversion of the polyp upside-down". It moves in the water by drifting and contracting its bell shaped body. Some species ...
... and the anus. Two variations of this body plan-the polyp and medusa. The polyp is a cylinder form that is sessile and adheres to the bottom of the water. The medusa is a "flattenedversion of the polyp upside-down". It moves in the water by drifting and contracting its bell shaped body. Some species ...
upper limb - Fisiokinesiterapia
... Sensory from limb (dermatomes/sensory skin segments from spine) • Dermatomes extend over limbs • Twisted orientation reflects twisting of limb during development • Named nerves generally innervate skin over muscles that they innervate ...
... Sensory from limb (dermatomes/sensory skin segments from spine) • Dermatomes extend over limbs • Twisted orientation reflects twisting of limb during development • Named nerves generally innervate skin over muscles that they innervate ...
UPPER LIMB
... Sensory from limb (dermatomes/sensory skin segments from spine) • Dermatomes extend over limbs • Twisted orientation reflects twisting of limb during development • Named nerves generally innervate skin over muscles that they innervate ...
... Sensory from limb (dermatomes/sensory skin segments from spine) • Dermatomes extend over limbs • Twisted orientation reflects twisting of limb during development • Named nerves generally innervate skin over muscles that they innervate ...
Arthropods - Cloudfront.net
... • -all have 8 legs • -all spiders produce silk, but may NOT spin a web • -venom can be injected by fangs by spiders • -scorpions use claws & inject venom w/ stingers in their tail • -spiders can get O2 from book lungs & air tubes • -ticks can be parasitic, sucking blood from animals and thereby spre ...
... • -all have 8 legs • -all spiders produce silk, but may NOT spin a web • -venom can be injected by fangs by spiders • -scorpions use claws & inject venom w/ stingers in their tail • -spiders can get O2 from book lungs & air tubes • -ticks can be parasitic, sucking blood from animals and thereby spre ...
Chapter 10 The Digestive System Overview Animals use energy
... Body cells need a constant supply of oxygen to carry out metabolic functions. The respiratory system is responsible for bringing oxygen into the body, delivering it to cells in all parts of the body, and carrying carbon dioxide away from the cells and out of the body. Animals in different environmen ...
... Body cells need a constant supply of oxygen to carry out metabolic functions. The respiratory system is responsible for bringing oxygen into the body, delivering it to cells in all parts of the body, and carrying carbon dioxide away from the cells and out of the body. Animals in different environmen ...
The Animal kingdom
... Backbone – a column of several bones called as vertebrae Backbone is a part of endoskeleton Muscles are attached to bones – movement Divided into five groups – Fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals • Live on land or in water • Herbivore, carnivore or omnivore • Separate genders (one gender p ...
... Backbone – a column of several bones called as vertebrae Backbone is a part of endoskeleton Muscles are attached to bones – movement Divided into five groups – Fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals • Live on land or in water • Herbivore, carnivore or omnivore • Separate genders (one gender p ...
Tissues
... ▫ Lines exposed surfaces of body ▫ Forms inner lining of body cavities ▫ Covers organs ...
... ▫ Lines exposed surfaces of body ▫ Forms inner lining of body cavities ▫ Covers organs ...
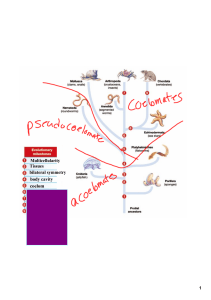
Multicellularity Tissues bilateral symmetry body cavity coelom
... Multicellularity Tissues bilateral symmetry body cavity coelom segmentation jointed appendaes deuterostomes notochord ...
... Multicellularity Tissues bilateral symmetry body cavity coelom segmentation jointed appendaes deuterostomes notochord ...
1 Notes for Friday September 13, 2002 Outline • Body cavities
... Notes for Friday September 13, 2002 Outline ...
... Notes for Friday September 13, 2002 Outline ...
Arthropods
... • Insects – reason for evolutionary success is: – Ability to fly allows insects to colonize new habitats. – They may use many sense organs to respond to stimuli. – Many have a life cycle in which the young are very different from adults. – The body is divided into a head, thorax, and abdomen. – Sens ...
... • Insects – reason for evolutionary success is: – Ability to fly allows insects to colonize new habitats. – They may use many sense organs to respond to stimuli. – Many have a life cycle in which the young are very different from adults. – The body is divided into a head, thorax, and abdomen. – Sens ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.