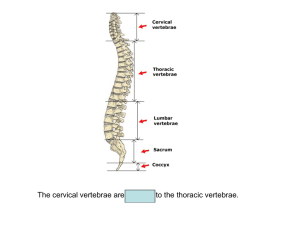
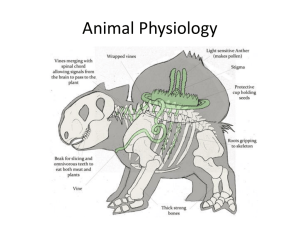
Body Notes Fill In
... 1. Sperm is produced in the __________________ which are located in the _______________. 2. Sperm moves from the seminiferous tubules to the ______________________ to mature. 3. From the epididymis the sperm travels up a tube called the ___________________. 4. The sperm mixes with fluid from the ___ ...
... 1. Sperm is produced in the __________________ which are located in the _______________. 2. Sperm moves from the seminiferous tubules to the ______________________ to mature. 3. From the epididymis the sperm travels up a tube called the ___________________. 4. The sperm mixes with fluid from the ___ ...
9/25 SI A Ecl 365 Test Review 1. Name 4 characteristics of a
... 13. This fish is eel-like, jawless, has slime glands, has no stomach, is a decomposer and deep marine species. a. Hagfish or Myxini b. Follow up question!! Are these true vertebrates? NO 14. This fish is jawless, scaleless, has no paired fins, and filter feed as larvae; adults either do not feed or ...
... 13. This fish is eel-like, jawless, has slime glands, has no stomach, is a decomposer and deep marine species. a. Hagfish or Myxini b. Follow up question!! Are these true vertebrates? NO 14. This fish is jawless, scaleless, has no paired fins, and filter feed as larvae; adults either do not feed or ...
Nerve Supply of the Upper Limb
... • Describe the basic anatomy and course of the brachial plexus • Describe the distribution of all branches of the plexus • Describe the course of the major nerves and identify where each is vulnerable to injury • Identify the dermatomes of the upper limb • Predict the effects of damage to nerve root ...
... • Describe the basic anatomy and course of the brachial plexus • Describe the distribution of all branches of the plexus • Describe the course of the major nerves and identify where each is vulnerable to injury • Identify the dermatomes of the upper limb • Predict the effects of damage to nerve root ...
What Is an Animal?
... • More complex animals have a reproductive system that functions in all reproductive ...
... • More complex animals have a reproductive system that functions in all reproductive ...
The Human Body workforce planning
... Purpose: works with the skeletal and nervous system to produce movement, also helps to circulate blood through the human body ...
... Purpose: works with the skeletal and nervous system to produce movement, also helps to circulate blood through the human body ...
Crayfish Physiology
... the mouth. Also used in defending itself from predators. Uropod and Telson – These flippers aid the crayfish in backward swimming to escape from danger. Walking Legs – Used for locomotion. Swimmerets – Used for backward locomotion. Digestive System Mouth - The opening to the digestive system. 1st, 2 ...
... the mouth. Also used in defending itself from predators. Uropod and Telson – These flippers aid the crayfish in backward swimming to escape from danger. Walking Legs – Used for locomotion. Swimmerets – Used for backward locomotion. Digestive System Mouth - The opening to the digestive system. 1st, 2 ...
Systems of the Human Body Study Guide
... 2. Air enters your body through your ________________ and your ______________. 3. Another name for the trachea is the _________________. 4. The trachea divides into two branches called the ________________ ______________. 5. Our bodies use oxygen, and gives off ___________________ __________________ ...
... 2. Air enters your body through your ________________ and your ______________. 3. Another name for the trachea is the _________________. 4. The trachea divides into two branches called the ________________ ______________. 5. Our bodies use oxygen, and gives off ___________________ __________________ ...
The Human Body workforce planning
... Purpose: works with the skeletal and nervous system to produce movement, also helps to circulate blood through the human body ...
... Purpose: works with the skeletal and nervous system to produce movement, also helps to circulate blood through the human body ...
ZOOLOGY 101 SECTION 1 LECTURE NOTES
... (segments) fused to form tagmata 2. Three body regions: head, thorax, abdomen 3. Appendages jointed and often specialized 4. Exoskeleton (cuticle) made chiefly of chitin; some proteins and lipids also 5. Muscular system complex, no cilia 6. Coelom reduced and filled with blood to form hemocoel 7. Co ...
... (segments) fused to form tagmata 2. Three body regions: head, thorax, abdomen 3. Appendages jointed and often specialized 4. Exoskeleton (cuticle) made chiefly of chitin; some proteins and lipids also 5. Muscular system complex, no cilia 6. Coelom reduced and filled with blood to form hemocoel 7. Co ...
Body System Structures Function
... neurons. In the running example, the brain sent a message to muscles to contract. This message was sent through neurons. A reflex arc is another example of regulation by the nervous system. Reflexes include the detection of a stimulus such as a hot object by a sensory neuron. The impulse travels dow ...
... neurons. In the running example, the brain sent a message to muscles to contract. This message was sent through neurons. A reflex arc is another example of regulation by the nervous system. Reflexes include the detection of a stimulus such as a hot object by a sensory neuron. The impulse travels dow ...
The Kingdom Animalia is in the domain Eukarya and in the
... and the anus. Two variations of this body plan-the polyp and medusa. The polyp is a cylinder form that is sessile and adheres to the bottom of the water. The medusa is a "flattenedversion of the polyp upside-down". It moves in the water by drifting and contracting its bell shaped body. Some species ...
... and the anus. Two variations of this body plan-the polyp and medusa. The polyp is a cylinder form that is sessile and adheres to the bottom of the water. The medusa is a "flattenedversion of the polyp upside-down". It moves in the water by drifting and contracting its bell shaped body. Some species ...
Study Guide
... c. Some animals are multicellular, all are heterotrophic, and all lack cell walls. d. Some animals are multicellular, some are heterotrophic, and some lack cell walls. _____ 2. An animal’s ability to move results from the interrelationship between a. dermal tissue and vascular tissue. c. nervous tis ...
... c. Some animals are multicellular, all are heterotrophic, and all lack cell walls. d. Some animals are multicellular, some are heterotrophic, and some lack cell walls. _____ 2. An animal’s ability to move results from the interrelationship between a. dermal tissue and vascular tissue. c. nervous tis ...
BDS 101
... Select the best answer for each question: (2x5=10) All the following muscles adduct the vocal folds except: a) Lateral cricoarytenoid b) Posterior cricoarytenoid c) Thyroarytenoid d) Interarytenoid ii) The most abundant papillae on the dorsum of tongue is: a) Filiform b) Fungiform c) Foliate d) Vall ...
... Select the best answer for each question: (2x5=10) All the following muscles adduct the vocal folds except: a) Lateral cricoarytenoid b) Posterior cricoarytenoid c) Thyroarytenoid d) Interarytenoid ii) The most abundant papillae on the dorsum of tongue is: a) Filiform b) Fungiform c) Foliate d) Vall ...
Ch 13 Test review
... Eat more green vegetables and red meats. skeletal muscle d. Get plenty of bedrest. cardiac muscle How do pairs of skeletal muscles work together? At the start of 400 m run your body releases adrenaline Both muscles contract at the same time. and carries more oxygen to the body cells. Both muscles ex ...
... Eat more green vegetables and red meats. skeletal muscle d. Get plenty of bedrest. cardiac muscle How do pairs of skeletal muscles work together? At the start of 400 m run your body releases adrenaline Both muscles contract at the same time. and carries more oxygen to the body cells. Both muscles ex ...
Animal Physiology Powerpoint
... Circulation in Echinodermata • Echinoderms are similar to early chordates but have developed radial symmetry • Like sponges and unlike more advanced invertebrates, they use seawater as their circulatory system – They use a water vascular system to nourish their body ...
... Circulation in Echinodermata • Echinoderms are similar to early chordates but have developed radial symmetry • Like sponges and unlike more advanced invertebrates, they use seawater as their circulatory system – They use a water vascular system to nourish their body ...
Anatomy and Physiology of Poultry
... Feathers Lack teeth Lay eggs Float and fly Waste excreted from only one orifice ...
... Feathers Lack teeth Lay eggs Float and fly Waste excreted from only one orifice ...
Name Period ______ Table of Contents Body System Page
... 11. __________________________ - much absorption of H 2O occurs here 12. ________________ - bottom portion of large intestine 13. ___________________ - finger-like projections found in small intestine to increase surface area for more absorption Functions/Roles: 1. __________________________________ ...
... 11. __________________________ - much absorption of H 2O occurs here 12. ________________ - bottom portion of large intestine 13. ___________________ - finger-like projections found in small intestine to increase surface area for more absorption Functions/Roles: 1. __________________________________ ...
Body Systems Review and Quiz
... 3. Which system in the frog produces chemicals that regulate functions in different parts of its body? A) respiratory system B) excretory system C) endocrine system D)circulatory system ...
... 3. Which system in the frog produces chemicals that regulate functions in different parts of its body? A) respiratory system B) excretory system C) endocrine system D)circulatory system ...
Class - carterbiology2-12-1809
... scales to allow quick body movement and ability to swim faster than most fish Preferred Living Conditions: large streams/rivers, lakes, back waters; near vegetation ...
... scales to allow quick body movement and ability to swim faster than most fish Preferred Living Conditions: large streams/rivers, lakes, back waters; near vegetation ...
Lab handout
... pinpoint to separate each tergum from the underlying tissues so that only the sclerites and intersegmental membranes are removed. Leave the last abdominal tergum intact. The thoracic terga are more securely fastened by dorso-ventral muscles, which may have to be cut. What is the function of these mu ...
... pinpoint to separate each tergum from the underlying tissues so that only the sclerites and intersegmental membranes are removed. Leave the last abdominal tergum intact. The thoracic terga are more securely fastened by dorso-ventral muscles, which may have to be cut. What is the function of these mu ...
Name Class Date SECTION 32-1 Study Guide THE NATURE OF
... c. Some animals are multicellular, all are heterotrophic, and all lack cell walls. d. Some animals are multicellular, some are heterotrophic, and some lack cell walls. _____ 2. An animal’s ability to move results from the interrelationship between a. dermal tissue and vascular tissue. c. nervous tis ...
... c. Some animals are multicellular, all are heterotrophic, and all lack cell walls. d. Some animals are multicellular, some are heterotrophic, and some lack cell walls. _____ 2. An animal’s ability to move results from the interrelationship between a. dermal tissue and vascular tissue. c. nervous tis ...
Anatomy

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. In some of its facets, anatomy is related to embryology and comparative anatomy, which itself is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny. Human anatomy is one of the basic essential sciences of medicine.The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic anatomy. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal’s body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology and also in the study of cells.The history of anatomy is characterized by a progressive understanding of the functions of the organs and structures of the human body. Methods have also improved dramatically, advancing from the examination of animals by dissection of carcasses and cadavers (corpses) to 20th century medical imaging techniques including X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.