* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Respiratory System.
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
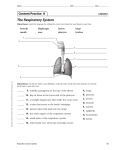
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. WHAT IS THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM •The human respiratory system is a series of organs responsible for taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide. ORGANS THAT MAKES UP THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. • The primary organs of the respiratory system are lungs, which carry out this exchange of gases as we breathe. • According the America Lungs association red blood cells collect the oxygen from the lungs and carry it to the parts of the body where it is needed. During this process, the red blood cells collect the carbon dioxide and transport it back to the lungs, where it leaves the body when we exhale. ORGANS THAT MAKES UP THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. • Other organs that makes up the respiratory system include: 1. Nasal Cavity-The nasal cavity (or nasal fossa) is a large air filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils.2. Mouth- also known as the oral cavity, the mouth is the hollow cavity that allows food and air to enter the body. 3. Alveoli- any of the many tiny air sacs in the lungs where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place. 4. Bronchi- major air passages of the lungs that diverge from the windpipe. ORGANS THAT MAKES UP THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 5) Diaphragm-The diaphragm is the dome-shaped sheet of muscle and tendon that serves as the main muscle of respiration and plays a vital role in the breathing process 6) Trachea-The trachea, commonly known as the windpipe, is a tube about 4 inches long and less than an inch in diameter in most people. The trachea begins just under the larynx (voice box) and runs down behind the breastbone (sternum) 7) Larynx- The larynx (voice box) is part of the respiratory system that holds the vocal cords. It is responsible for producing voice, helping us swallow and breathe. Air passes in and out of the larynx each time the body inhales or exhales 8) Pharynx - The pharynx, or throat, is the passageway leading from the mouth and nose to the esophagus and larynx. FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM • The primarily function of the respiratory system is to deliver air to the lungs. Oxygen in the air diffuses out of the lungs and into the blood, while carbon dioxide diffuses in the opposite direction, out of the blood and into the lungs. TYPES OF THE RESPIRATIONS. Respiration includes the following processes: • External respiration is the process of gas exchange between the atmosphere and the body tissues. In order to accomplish this task, the following events occur: • Pulmonary ventilation is the process of breathing—inspiration (inhaling air) and expiration (exhaling air). • Gas transport, carried out by the cardiovascular system, is the process of distributing the oxygen throughout the body and collecting CO 2 and returning it to the lungs. TYPES OF RESPIRATION CONTD. • Internal respiration is the process of gas exchange between the blood, the interstitial fluids (fluids surrounding the cells), and the cells. Inside the cell, cellular respiration generates energy (ATP), using O 2 and glucose and producing waste CO 2.