Kingdom animalia
... Blastula – A hollow ball of cells surrounding a cavity called the blastocoel Gastrula – form that begins to feature embryonic tissue layers (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm) Ectoderm – Outer tissue layer Endoderm – Inner tissue layer Blastophore – opening into the gastrula Archenteron – pou ...
... Blastula – A hollow ball of cells surrounding a cavity called the blastocoel Gastrula – form that begins to feature embryonic tissue layers (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm) Ectoderm – Outer tissue layer Endoderm – Inner tissue layer Blastophore – opening into the gastrula Archenteron – pou ...
Chapter 8A The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton
... – Short: most carpal and tarsal bones – Flat: some cranial bones, sternum, ribs, scapula – Irregular: vertabrae, os coxae, most facial bones – Sesamoid: patella ...
... – Short: most carpal and tarsal bones – Flat: some cranial bones, sternum, ribs, scapula – Irregular: vertabrae, os coxae, most facial bones – Sesamoid: patella ...
Interrelationship of the Body Systems
... systems. Each living cell in the body carries out all of the processes that allow us to live and to grow. Similar cells group together to form special tissues (e.g. muscle tissue, nerve tissue, bone tissue) that group together to form organs (e.g. heart, lungs, brain). Organs group together to creat ...
... systems. Each living cell in the body carries out all of the processes that allow us to live and to grow. Similar cells group together to form special tissues (e.g. muscle tissue, nerve tissue, bone tissue) that group together to form organs (e.g. heart, lungs, brain). Organs group together to creat ...
Third head of sternocleidomastoid muscle
... lesser supraclavicular fossa. The muscle is vascularized by and additional clavicular heads were blending into a thick, the branches of suprascapular, superior thyroid and occipital rounded muscle belly which was inserted by a tendon onto arteries and innervated by accessory nerve along with the lat ...
... lesser supraclavicular fossa. The muscle is vascularized by and additional clavicular heads were blending into a thick, the branches of suprascapular, superior thyroid and occipital rounded muscle belly which was inserted by a tendon onto arteries and innervated by accessory nerve along with the lat ...
Surgical Anatomy and Approaches to the Anterior Thoracolumbar
... include standard laminectomy, transpedicular decompressions, posterolateral costotransversectomy and the lateral extracavitary approach. The main anterior-based approaches to the thoracolumbar junction are performed antero-laterally, which can be performed via a thoracotomy or, more recently, by tho ...
... include standard laminectomy, transpedicular decompressions, posterolateral costotransversectomy and the lateral extracavitary approach. The main anterior-based approaches to the thoracolumbar junction are performed antero-laterally, which can be performed via a thoracotomy or, more recently, by tho ...
Anatomy and Physiology Name: Chapter 6 DRO Period: Bones
... (2): found below the parietal bones- contains many anatomical features such as the external acoustic meatus, eardrum, mandibular fossa, mastoid and styloid processes. ...
... (2): found below the parietal bones- contains many anatomical features such as the external acoustic meatus, eardrum, mandibular fossa, mastoid and styloid processes. ...
"atlas and axis" through the eyes of the transoral surgeon
... anteror arch forms about one-fifth of the ring: Its anterior surface is convex. and presents about its centre a tubercle for the attachment of the Longus Colli muscles. The posterior arch is convex backward. and has a median posterior tubercle and a groove on the lateral part of upper-outer surface ...
... anteror arch forms about one-fifth of the ring: Its anterior surface is convex. and presents about its centre a tubercle for the attachment of the Longus Colli muscles. The posterior arch is convex backward. and has a median posterior tubercle and a groove on the lateral part of upper-outer surface ...
Introduction
... e. Each thoracic vertebra has articulated facets for the ________________________ 5. Vertebral column as a whole articulated with the head, ribs, and iliac ________________________ 6. Individual vertebrae articulate with each other in ________________________ between their bodies and between their a ...
... e. Each thoracic vertebra has articulated facets for the ________________________ 5. Vertebral column as a whole articulated with the head, ribs, and iliac ________________________ 6. Individual vertebrae articulate with each other in ________________________ between their bodies and between their a ...
Functions of Our Organ Systems
... cells called osteoblasts • Types of bone tissue compact (no visible open spaces) and spongy (many open spaces) • Marrow-soft tissue the fills the core of larger bones where the production of blood cells take place • Found in sternum, skull, pelvis, humerus, and femur ...
... cells called osteoblasts • Types of bone tissue compact (no visible open spaces) and spongy (many open spaces) • Marrow-soft tissue the fills the core of larger bones where the production of blood cells take place • Found in sternum, skull, pelvis, humerus, and femur ...
Human Biology
... List the levels of organization in humans. What are the four basic types of human tissue? List the organ systems of the human body. Using any type of machine as an example, explain how each part of the machine works together with every other part so that the machine can do its job. Compare this with ...
... List the levels of organization in humans. What are the four basic types of human tissue? List the organ systems of the human body. Using any type of machine as an example, explain how each part of the machine works together with every other part so that the machine can do its job. Compare this with ...
Thoracolumbar Spine
... a combination of vertebrae, intervertebral joints, ligaments/tendons, muscles, nerves and vascular supply. • The thoracic region consists of 12 vertebrae. Due to its articulations with rib cage, the thoracic spine is more rigid than the cervical and lumbar regions. • The lumbar spine is made up of 5 ...
... a combination of vertebrae, intervertebral joints, ligaments/tendons, muscles, nerves and vascular supply. • The thoracic region consists of 12 vertebrae. Due to its articulations with rib cage, the thoracic spine is more rigid than the cervical and lumbar regions. • The lumbar spine is made up of 5 ...
Porifera and Cnidaria
... b. Note the structure of the body wall. You should be able to observe 3 kinds of cells. i. One cell type that is unique to sponges is the choanocyte (or collar cell). These cells line the spongocoel and the channels leading to it. Each collar cell has a flagellum extending from its surface. The coll ...
... b. Note the structure of the body wall. You should be able to observe 3 kinds of cells. i. One cell type that is unique to sponges is the choanocyte (or collar cell). These cells line the spongocoel and the channels leading to it. Each collar cell has a flagellum extending from its surface. The coll ...
Handout 6
... Allows movement of neck, thoracic and lumbar regions. Makeup: extends from base of skull to the coccyx. Serves as axial support for the body and provides protection for spinal cord. Vertebral column 33 bones called vertebrae. divided into 5 segments: 7 cervical, ...
... Allows movement of neck, thoracic and lumbar regions. Makeup: extends from base of skull to the coccyx. Serves as axial support for the body and provides protection for spinal cord. Vertebral column 33 bones called vertebrae. divided into 5 segments: 7 cervical, ...
a rare case report
... variations of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The SCM shows a great variation in its clavicular origin. The clavicular head can be as narrow as the sternal head, or it can be up to 8 cm of width. When the clavicular origin is wide, it is occasionally subdivided in various slips, separated by narrow ...
... variations of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The SCM shows a great variation in its clavicular origin. The clavicular head can be as narrow as the sternal head, or it can be up to 8 cm of width. When the clavicular origin is wide, it is occasionally subdivided in various slips, separated by narrow ...
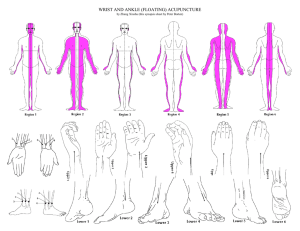
wrist and ankle (floating) acupuncture
... passing down to the lumbus. The diseases related to this region include posterio-temporal headache, pain in the scapula, and disorders of the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae. Upper 5 is located in the centre of the dorsal side of the forearm, between the radius and ulna. Ask the patient ...
... passing down to the lumbus. The diseases related to this region include posterio-temporal headache, pain in the scapula, and disorders of the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae. Upper 5 is located in the centre of the dorsal side of the forearm, between the radius and ulna. Ask the patient ...
The Hip
... The area inferior to the ligament is supplied by the subcostal nerve, the femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve, and the iliolingual nerve ...
... The area inferior to the ligament is supplied by the subcostal nerve, the femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve, and the iliolingual nerve ...
Respiratory System – A
... Start your PC and open A.D.A.M Interactive Anatomy. From the dialog select Dissectible Anatomy, Male and Anterior Position the image so that the head is in the center of the screen. On the left of the screen position the slide to level 35. Placing your cursor over the nose identify the four distinct ...
... Start your PC and open A.D.A.M Interactive Anatomy. From the dialog select Dissectible Anatomy, Male and Anterior Position the image so that the head is in the center of the screen. On the left of the screen position the slide to level 35. Placing your cursor over the nose identify the four distinct ...
BDS Ist YEAR EXAMINATION 2008-09
... Note: 1. Attempt all questions and return this part of the question paper to the invigilator after 20 Minutes. 2. Please tick (√) correct one only. Cutting, overwriting or any other marking are not allowed. 3. For answering please use Ball- pen only. Q.1 ...
... Note: 1. Attempt all questions and return this part of the question paper to the invigilator after 20 Minutes. 2. Please tick (√) correct one only. Cutting, overwriting or any other marking are not allowed. 3. For answering please use Ball- pen only. Q.1 ...
Spring 03
... c) torn ACL results in “anterior drawer sign” d) posterior cruciate ligament attaches to the anterior aspect of the tibial plateau e) anterior cruciate ligament is pulled tight when the knee is extended 8) Which of the following bones touch the sphenoid bone? (MACA) a) lacrimal bone b) nasal bone c) ...
... c) torn ACL results in “anterior drawer sign” d) posterior cruciate ligament attaches to the anterior aspect of the tibial plateau e) anterior cruciate ligament is pulled tight when the knee is extended 8) Which of the following bones touch the sphenoid bone? (MACA) a) lacrimal bone b) nasal bone c) ...
Anatomy and Histology of the Canine and Feline Eye
... loose conjunctival stroma iv. intraconal- the area within the retrobulbar space enveloped by fascia and extraocular muscles that contains the optic nerve v. retrobulbar space- the space located behind the globe ...
... loose conjunctival stroma iv. intraconal- the area within the retrobulbar space enveloped by fascia and extraocular muscles that contains the optic nerve v. retrobulbar space- the space located behind the globe ...
Knee Summary
... • Scan with patient’s teeth clenched and temporal tap • With teeth clenched, TL for exact tooth • Challenge tooth in all directions • Phase positive challenge to respiration • Adjust with 6-8 oz pressure – In direction of positive challenge – On phase of respiration that chacelled weakening on chall ...
... • Scan with patient’s teeth clenched and temporal tap • With teeth clenched, TL for exact tooth • Challenge tooth in all directions • Phase positive challenge to respiration • Adjust with 6-8 oz pressure – In direction of positive challenge – On phase of respiration that chacelled weakening on chall ...
Annelid Webquest - Effingham County Schools
... 19. What is the function of the ovaries? Click out of the lab manual. Click on ‘External Anatomy’ and drag and drop the matching labels to the structures on the diagram. If you have trouble, click on the Lab manual and go to page 4 to review the labels. Check your answers and label the diagram belo ...
... 19. What is the function of the ovaries? Click out of the lab manual. Click on ‘External Anatomy’ and drag and drop the matching labels to the structures on the diagram. If you have trouble, click on the Lab manual and go to page 4 to review the labels. Check your answers and label the diagram belo ...
Descriptions and Pictures
... subject places the right foot on a bench so that a right angle is formed at the knee with the thigh horizontal and the leg vertical. The points on the distal end of the femur located most lateral to the median plane of the bone (i.e., condyles) are palpated. The ends of the bow caliper then are appl ...
... subject places the right foot on a bench so that a right angle is formed at the knee with the thigh horizontal and the leg vertical. The points on the distal end of the femur located most lateral to the median plane of the bone (i.e., condyles) are palpated. The ends of the bow caliper then are appl ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.