restriction enzymes
... •Restriction Enzymes (endonucleases): molecular scissors that cut DNA •Properties of widely used Type II restriction enzymes: •recognize a single sequence of bases in dsDNA, usually symetrical (palindromic) •cleave both strands, generally within the recognition sequences •leaving “blunt” or “sticky” ...
... •Restriction Enzymes (endonucleases): molecular scissors that cut DNA •Properties of widely used Type II restriction enzymes: •recognize a single sequence of bases in dsDNA, usually symetrical (palindromic) •cleave both strands, generally within the recognition sequences •leaving “blunt” or “sticky” ...
Gene Isolation and Manipulation
... DNA used, 60 kb, the gene appears to be roughly 45 times larger than necessary. This “extra” DNA mostly represents the introns that must be correctly spliced out of the primary transcript during RNA processing for correct translation. (There are also comparatively very small amounts of both 5´ and 3 ...
... DNA used, 60 kb, the gene appears to be roughly 45 times larger than necessary. This “extra” DNA mostly represents the introns that must be correctly spliced out of the primary transcript during RNA processing for correct translation. (There are also comparatively very small amounts of both 5´ and 3 ...
DNA Review Name: Period: ______ Date: The process of making
... structure of DNA with the help of other scientists. 6. During transcription, the genetic information for making a protein is rewritten as a molecule of a. Messenger RNA b. Ribosomal RNA c. Transfer RNA d. Translation RNA 7. Like DNA, RNA contains which of the following? a. Phosphate b. Uracil c. Thy ...
... structure of DNA with the help of other scientists. 6. During transcription, the genetic information for making a protein is rewritten as a molecule of a. Messenger RNA b. Ribosomal RNA c. Transfer RNA d. Translation RNA 7. Like DNA, RNA contains which of the following? a. Phosphate b. Uracil c. Thy ...
deoxyribonucleic acid contained in the chromosomes humans have
... DNA Replication DNA can make a copy of it itself BECAUSE of the way the bases pair up 1) the DNA strand will 'unzip' as the chemical bonds are broken between each of the nitrogen bases 2) 'loose' nitrogen bases of the correct type will adhere to the free one 3) the ends of the newly attache ...
... DNA Replication DNA can make a copy of it itself BECAUSE of the way the bases pair up 1) the DNA strand will 'unzip' as the chemical bonds are broken between each of the nitrogen bases 2) 'loose' nitrogen bases of the correct type will adhere to the free one 3) the ends of the newly attache ...
Recombinant DNA Activity
... HUMAN DNA, which contains the gene for insulin production. The gene area is shaded. 3. Cut out the Restriction Enzyme Sequence Cards. Each card shows a sequence where a particular restriction enzyme cuts DNA. 4. Compare the sequence of base pairs on an enzyme card with the sequences of the plasmid b ...
... HUMAN DNA, which contains the gene for insulin production. The gene area is shaded. 3. Cut out the Restriction Enzyme Sequence Cards. Each card shows a sequence where a particular restriction enzyme cuts DNA. 4. Compare the sequence of base pairs on an enzyme card with the sequences of the plasmid b ...
Recombinant DNA Activity
... HUMAN DNA, which contains the gene for insulin production. The gene area is shaded. 3. Cut out the Restriction Enzyme Sequence Cards. Each card shows a sequence where a particular restriction enzyme cuts DNA. 4. Compare the sequence of base pairs on an enzyme card with the sequences of the plasmid b ...
... HUMAN DNA, which contains the gene for insulin production. The gene area is shaded. 3. Cut out the Restriction Enzyme Sequence Cards. Each card shows a sequence where a particular restriction enzyme cuts DNA. 4. Compare the sequence of base pairs on an enzyme card with the sequences of the plasmid b ...
Enzyme Foldable
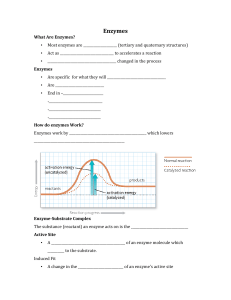
... a. Draw and label the enzyme and the substrate. Explain the role of an enzyme in the body. 3. Enzyme Vocabulary a. These are the key words in the reading packet. 4. Graphs a. Draw and label the 4 graphs associated with enzymes. i. Temperature ii. PH iii. Concentrations iv. Activation Energy b. Write ...
... a. Draw and label the enzyme and the substrate. Explain the role of an enzyme in the body. 3. Enzyme Vocabulary a. These are the key words in the reading packet. 4. Graphs a. Draw and label the 4 graphs associated with enzymes. i. Temperature ii. PH iii. Concentrations iv. Activation Energy b. Write ...
Polymerase Chain Reaction and PTC lab
... Gel Electrophoresis One indirect method of rapidly analyzing and comparing genomes is gel electrophoresis This technique uses a gel as a molecular sieve to separate nuclei acids or proteins by size Restriction fragment analysis detects DNA differences that affect restriction sites Restriction fra ...
... Gel Electrophoresis One indirect method of rapidly analyzing and comparing genomes is gel electrophoresis This technique uses a gel as a molecular sieve to separate nuclei acids or proteins by size Restriction fragment analysis detects DNA differences that affect restriction sites Restriction fra ...
Basics of Molecular Cloning
... and inserting it into a vector where it can be replicated by a host organism. (Sometimes called subcloning, because only part of the organism’s DNA is being cloned.) Using nuclear DNA from one organism to create a second organism with the same nuclear DNA ...
... and inserting it into a vector where it can be replicated by a host organism. (Sometimes called subcloning, because only part of the organism’s DNA is being cloned.) Using nuclear DNA from one organism to create a second organism with the same nuclear DNA ...
PCR – polymerace chain reaction
... No harm (for binding) of one or two mismatches Primers can be designed to contain errors Binding is not disturbed SILENT MUTATION: one base is placed by another base, witch won’t change amino acid sequence ...
... No harm (for binding) of one or two mismatches Primers can be designed to contain errors Binding is not disturbed SILENT MUTATION: one base is placed by another base, witch won’t change amino acid sequence ...
Nucleic Acid Enzymes - American Society of Cytopathology
... Type I Restriction Enzymes o Possess both nuclease and methylase activity in a single enzyme o Binds to host-specific DNA sites of 4-6 base pairs separated by 6-8 base pairs and containing methylated adenines o Site of cutting of DNA can be over 1000 base pairs from the binding site o EcoK from E. c ...
... Type I Restriction Enzymes o Possess both nuclease and methylase activity in a single enzyme o Binds to host-specific DNA sites of 4-6 base pairs separated by 6-8 base pairs and containing methylated adenines o Site of cutting of DNA can be over 1000 base pairs from the binding site o EcoK from E. c ...