Apple Molecular Biology: Animation 1
... Cloning can mean several things. Most people associate cloning with 'copying'. In molecular biology, cloning can be a process of recreating individuals from their own DNA but a more common use of cloning refers to the insertion of a short piece of DNA into a bacterial plasmid for replication purpose ...
... Cloning can mean several things. Most people associate cloning with 'copying'. In molecular biology, cloning can be a process of recreating individuals from their own DNA but a more common use of cloning refers to the insertion of a short piece of DNA into a bacterial plasmid for replication purpose ...
Ch. 13 – Biotechnology
... § restriction endonucleases § discovered in 1960s § evolved in bacteria to cut up foreign DNA § “restrict” action of attacking organisms (viruses and other bacteria) § How do bacteria protect their own DNA? § Methylation ...
... § restriction endonucleases § discovered in 1960s § evolved in bacteria to cut up foreign DNA § “restrict” action of attacking organisms (viruses and other bacteria) § How do bacteria protect their own DNA? § Methylation ...
35. Modeling Recominant DNA
... enzymes are used, which can be thought of as DNA scissors. Enzymes occur naturally in organisms, particularly valuable to scientists are restriction enzymes found in bacteria. Each particular enzyme recognizes a specific, short, nucleotide sequence in DNA molecules. The restriction enzyme will cut t ...
... enzymes are used, which can be thought of as DNA scissors. Enzymes occur naturally in organisms, particularly valuable to scientists are restriction enzymes found in bacteria. Each particular enzyme recognizes a specific, short, nucleotide sequence in DNA molecules. The restriction enzyme will cut t ...
Genetics Laboratory (BIOL 311L)
... http://www.carolina.com/pdf/activities-articles/plasmidmapping-exercises-2008.pdf MOVIE: Cracking Your Genetic Code Restriction mapping exercise, pp. 10-12 Week 3 ...
... http://www.carolina.com/pdf/activities-articles/plasmidmapping-exercises-2008.pdf MOVIE: Cracking Your Genetic Code Restriction mapping exercise, pp. 10-12 Week 3 ...
Genetic Engineering
... It is also possible to transform multicellular organisms such as plants and animals To do so, microorganisms, such as bacteria and viruses, must be used For example, a bacteria that causes tumors in plants can be altered so the tumor gene is replaced by a useful gene However, these methods can only ...
... It is also possible to transform multicellular organisms such as plants and animals To do so, microorganisms, such as bacteria and viruses, must be used For example, a bacteria that causes tumors in plants can be altered so the tumor gene is replaced by a useful gene However, these methods can only ...
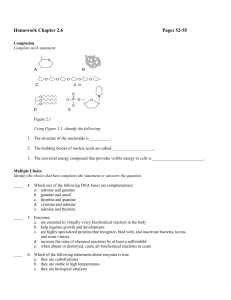
Homework Chapter 2.6 Pages 52-55 Completion Complete each
... b. help regulate growth and development c. are highly specialized proteins that recognize, bind with, and inactivate bacteria, toxins, and some viruses d. increase the rates of chemical reactions by at least a millionfold e. when absent or destroyed, cause all biochemical reactions to cease ...
... b. help regulate growth and development c. are highly specialized proteins that recognize, bind with, and inactivate bacteria, toxins, and some viruses d. increase the rates of chemical reactions by at least a millionfold e. when absent or destroyed, cause all biochemical reactions to cease ...
Worksheet Lesson 5: The discovery of DNA`s
... Worksheet Lesson 5: The discovery of DNA's structure We can't credit just one scientist with the discovery of the structure of DNA. It was the work of many different scientists who built on the work of others before them. In this activity you will be finding out about some of these scientists and th ...
... Worksheet Lesson 5: The discovery of DNA's structure We can't credit just one scientist with the discovery of the structure of DNA. It was the work of many different scientists who built on the work of others before them. In this activity you will be finding out about some of these scientists and th ...
markscheme File
... GU-R and SU-R individually give highest resistance, (but when combined, give the same resistance); in graph 1, GP-R and BR-R give least resistance, but in graph 2 give highest resistance / GP-R and BR-R are additive; data shows interference between BR-R and GU-R; ...
... GU-R and SU-R individually give highest resistance, (but when combined, give the same resistance); in graph 1, GP-R and BR-R give least resistance, but in graph 2 give highest resistance / GP-R and BR-R are additive; data shows interference between BR-R and GU-R; ...
Discussion Guide Chapter 15
... 6. Differentiate between the three main replication enzymes. (see Science Focus p. 218) Helicase DNA Polymerase DNA Ligase ...
... 6. Differentiate between the three main replication enzymes. (see Science Focus p. 218) Helicase DNA Polymerase DNA Ligase ...