2-Phospho
... with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
... with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
Glycolysis - Fairfield Public Schools
... Energy is stockpiled in the form of an H+ electrochemical gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane, via a series of oxidation-reduction reactions. The electron transport system accepts hydrogens from NADH and FADH2. The system passes the hydrogens’ electrons through a series of redox r ...
... Energy is stockpiled in the form of an H+ electrochemical gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane, via a series of oxidation-reduction reactions. The electron transport system accepts hydrogens from NADH and FADH2. The system passes the hydrogens’ electrons through a series of redox r ...
Cellular Respiration & Fermentation
... • Electrons from NADH and FADH2 – Travel down the electron transport chain to oxygen, which picks up H+ to form water • Energy released by the redox reactions ...
... • Electrons from NADH and FADH2 – Travel down the electron transport chain to oxygen, which picks up H+ to form water • Energy released by the redox reactions ...
No Slide Title
... Nitrogen Excretion & Urea Cycle Ammonia is toxic, if not used for synthesis of new AAs or other nitrogenous products - excreted! Ammonium deposited in mitochondria of hepatocytes is converted to urea in the urea cycle ...
... Nitrogen Excretion & Urea Cycle Ammonia is toxic, if not used for synthesis of new AAs or other nitrogenous products - excreted! Ammonium deposited in mitochondria of hepatocytes is converted to urea in the urea cycle ...
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
... Conjugation Reactions: UDP‐glucuronic acid is used for conjugation with many compounds to make them more soluble before excretion eg. steroid hormones and bilirubin ...
... Conjugation Reactions: UDP‐glucuronic acid is used for conjugation with many compounds to make them more soluble before excretion eg. steroid hormones and bilirubin ...
RESPIRATION PPT...Campbell Powerpoint presentation
... with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
... with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
... consumption and fewer unwanted by-products. However, a natural enzyme that can catalyze the desired reaction does not exist for most industrial chemical processes. While there have been successes in the protein design field, including de novo enzyme design for a few different reactions that have ...
Chapter 9—Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... As molecular oxygen is reduced it also picks up two protons from the medium to form water. For every two NADHs, one O2 is reduced to two H2O molecules FADH2 also donates electrons to the electron transport chain, but those electrons are added at a lower energy level than NADH The electron transp ...
... As molecular oxygen is reduced it also picks up two protons from the medium to form water. For every two NADHs, one O2 is reduced to two H2O molecules FADH2 also donates electrons to the electron transport chain, but those electrons are added at a lower energy level than NADH The electron transp ...
How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy
... 6.9 The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic fuel, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules • In the citric acid cycle ...
... 6.9 The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic fuel, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules • In the citric acid cycle ...
Applied and Environmental Microbiology
... a Each value is the mean ± standard deviation of three or four independent experiments. b Data were obtained from a single experiment. ...
... a Each value is the mean ± standard deviation of three or four independent experiments. b Data were obtained from a single experiment. ...
Enzymes & pH - SchoolWorld an Edline Solution
... The rate at which enzymes catalyze their reactions changes as the conditions inside the cell change! Conditions that effect enzyme reaction rate are: 1. Temperature 2. Relative concentrations of enzyme and substrate 3. pH (acidic, basic, neutral) ...
... The rate at which enzymes catalyze their reactions changes as the conditions inside the cell change! Conditions that effect enzyme reaction rate are: 1. Temperature 2. Relative concentrations of enzyme and substrate 3. pH (acidic, basic, neutral) ...
Chapter 7 - HCC Southeast Commons
... All organisms produce ATP by degradative pathways that extract chemical energy from glucose and other organic compounds Aerobic respiration yields the most ATP from each glucose molecule In eukaryotes, aerobic respiration is completed inside mitochondria ...
... All organisms produce ATP by degradative pathways that extract chemical energy from glucose and other organic compounds Aerobic respiration yields the most ATP from each glucose molecule In eukaryotes, aerobic respiration is completed inside mitochondria ...
Help is just a phone call away!
... An herbal product was mixed with a solution and the child washed down with this. The child was then wrapped in a blanket and placed in bed to sleep. Three hours later the mother tried to awaken the child and could not. Mother stated child had a 5 second seizure. The child was taken to the ED ...
... An herbal product was mixed with a solution and the child washed down with this. The child was then wrapped in a blanket and placed in bed to sleep. Three hours later the mother tried to awaken the child and could not. Mother stated child had a 5 second seizure. The child was taken to the ED ...
21. Which of the electron carriers in the electron transport
... d) prepares glucose for fermentation e) provides signals to neighboring cells 30. Which of the following statements about mitochondria is false? a) They contain an inner and an outer ...
... d) prepares glucose for fermentation e) provides signals to neighboring cells 30. Which of the following statements about mitochondria is false? a) They contain an inner and an outer ...
Chapter 7
... • One glucose (6C) is broken into two molecules of pyruvic acid (3C) • If oxygen is available, the pyruvic acid will move into the mitochondria and aerobic respiration will begin. • 4 ATP molecules are produced. Two are used to break apart the next glucose molecule and keep glycolysis going. • This ...
... • One glucose (6C) is broken into two molecules of pyruvic acid (3C) • If oxygen is available, the pyruvic acid will move into the mitochondria and aerobic respiration will begin. • 4 ATP molecules are produced. Two are used to break apart the next glucose molecule and keep glycolysis going. • This ...
Metabolizma - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... • The sum of the chemical changes that convert nutrients into energy and the chemically complex products of cells • Hundreds of enzyme reactions organized into discrete pathways • Substrates are transformed to products via many specific intermediates • Metabolic maps portray the reactions • Intermed ...
... • The sum of the chemical changes that convert nutrients into energy and the chemically complex products of cells • Hundreds of enzyme reactions organized into discrete pathways • Substrates are transformed to products via many specific intermediates • Metabolic maps portray the reactions • Intermed ...
question sheet - Sackville School
... Commercial uses of enzymes Enzymes are used in industrial processes and the development of enzyme technology has resulted in the large-scale production of enzymes from microorganisms. These microbial enzymes are used in the production of paper, textiles, food and biological detergents. Pectinases ar ...
... Commercial uses of enzymes Enzymes are used in industrial processes and the development of enzyme technology has resulted in the large-scale production of enzymes from microorganisms. These microbial enzymes are used in the production of paper, textiles, food and biological detergents. Pectinases ar ...
ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration Powerpoint
... The Krebs Cycle (mitochondria matrix) The Electron Transport Chain (inner mitochondrial membrane) ...
... The Krebs Cycle (mitochondria matrix) The Electron Transport Chain (inner mitochondrial membrane) ...
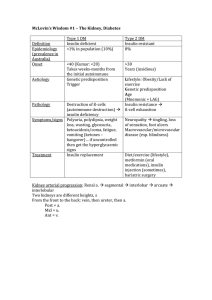
McLovin`s Wisdom #1 – The Kidney, Diabetes Type 1 DM Type 2
... At complex 4, 1/2O2 + 2H+ H2O (the H+s are reacted with oxygen to reduce it to water. Hence oxygen is needed). ATP synthase. 4H+ going through ATP synthase produce 1 ATP (3H+ go through there, and 1H+ used to transport the ATP back out into the intermembrane space – the outer mitochondrial membra ...
... At complex 4, 1/2O2 + 2H+ H2O (the H+s are reacted with oxygen to reduce it to water. Hence oxygen is needed). ATP synthase. 4H+ going through ATP synthase produce 1 ATP (3H+ go through there, and 1H+ used to transport the ATP back out into the intermembrane space – the outer mitochondrial membra ...
Chapter 8 Learning Targets(141- 150)
... c. I can describe the role of NAD+ in cellular respiration. d. I can name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. 2. I can explain how glycolysis harvests chemical energy by oxidizing glucose to pyruvate. a. I can list the reactan ...
... c. I can describe the role of NAD+ in cellular respiration. d. I can name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. 2. I can explain how glycolysis harvests chemical energy by oxidizing glucose to pyruvate. a. I can list the reactan ...
GI Digest - Douglas Labs
... by pepsin and hydrochloric acid, which denature and break large proteins down to smaller polypeptides. In the small intestine, proteases break down these polypeptides into free amino acids, and di- and tripeptides, which are directly absorbed by the intestinal mucosa. Some individuals require enzyme ...
... by pepsin and hydrochloric acid, which denature and break large proteins down to smaller polypeptides. In the small intestine, proteases break down these polypeptides into free amino acids, and di- and tripeptides, which are directly absorbed by the intestinal mucosa. Some individuals require enzyme ...
Cellular Respiration
... compounds and break them down to release their stored energy (ATP) • When the bond to the last phosphate group is broken, leaving ADP and a free phosphate group, the energy released is available to do cellular work. • In P/S the CO2 and H2O are involved in two separate sets of reactions: • H2O is sp ...
... compounds and break them down to release their stored energy (ATP) • When the bond to the last phosphate group is broken, leaving ADP and a free phosphate group, the energy released is available to do cellular work. • In P/S the CO2 and H2O are involved in two separate sets of reactions: • H2O is sp ...
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms, an oxidized and reduced form abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH respectively.In metabolism, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The coenzyme is, therefore, found in two forms in cells: NAD+ is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced. This reaction forms NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, the most notable one being a substrate of enzymes that add or remove chemical groups from proteins, in posttranslational modifications. Because of the importance of these functions, the enzymes involved in NAD metabolism are targets for drug discovery.In organisms, NAD can be synthesized from simple building-blocks (de novo) from the amino acids tryptophan or aspartic acid. In an alternative fashion, more complex components of the coenzymes are taken up from food as the vitamin called niacin. Similar compounds are released by reactions that break down the structure of NAD. These preformed components then pass through a salvage pathway that recycles them back into the active form. Some NAD is also converted into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP); the chemistry of this related coenzyme is similar to that of NAD, but it has different roles in metabolism.Although NAD+ is written with a superscript plus sign because of the formal charge on a particular nitrogen atom, at physiological pH for the most part it is actually a singly charged anion (charge of minus 1), while NADH is a doubly charged anion.