enzymology
... This type of control in cells is exercised at the gene level. If the gene for that enzyme is activated then enzyme synthesis takes place and the process is called enzyme induction. On the contrary, if enzyme synthesis is inhibited it is called repression. This type of control mechanism is operative ...
... This type of control in cells is exercised at the gene level. If the gene for that enzyme is activated then enzyme synthesis takes place and the process is called enzyme induction. On the contrary, if enzyme synthesis is inhibited it is called repression. This type of control mechanism is operative ...
WEEK 11
... catalysts for many reactions. The specificity of biological catalysts accounts for the large number of different enzymes in every living cell. Studies show that the active site on the enzyme assumes the shape of the substrate only after binding occurs. Interactions between enzyme and substrate befor ...
... catalysts for many reactions. The specificity of biological catalysts accounts for the large number of different enzymes in every living cell. Studies show that the active site on the enzyme assumes the shape of the substrate only after binding occurs. Interactions between enzyme and substrate befor ...
Glycolysis
... provides the electrons and enough reduction potential to do the job. In fact, consuming NADH is the main goal of this reaction. Cellular levels of NAD+/NADH are limited, and oxidation of NADH back to NAD+, provides an ongoing supply of this reactant for continued oxidation of GAP and continued produ ...
... provides the electrons and enough reduction potential to do the job. In fact, consuming NADH is the main goal of this reaction. Cellular levels of NAD+/NADH are limited, and oxidation of NADH back to NAD+, provides an ongoing supply of this reactant for continued oxidation of GAP and continued produ ...
(cobalamin)-dependent enzymes
... coenzyme and carbon. One form, methylcobalamin (MeCbl), is involved in methylation reactions in which the methyl group is transferred to and from cobalt. The other form, adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl), serves as a source of carbon-based free radicals that are ‘unmasked’ by homolysis of the bond between ...
... coenzyme and carbon. One form, methylcobalamin (MeCbl), is involved in methylation reactions in which the methyl group is transferred to and from cobalt. The other form, adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl), serves as a source of carbon-based free radicals that are ‘unmasked’ by homolysis of the bond between ...
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The role of yeast NAD+
... Too characterize the RNA-binding property of Idh, we wanted to analyze RNAbindingg mutants which were still enzymatically active. Since no obvious RNAbindingg domain was found in Idh, we screened two other yeast species (K. lactis and S.S. pombe) for the RNA-binding capacity of their NAD-Idh's (chap ...
... Too characterize the RNA-binding property of Idh, we wanted to analyze RNAbindingg mutants which were still enzymatically active. Since no obvious RNAbindingg domain was found in Idh, we screened two other yeast species (K. lactis and S.S. pombe) for the RNA-binding capacity of their NAD-Idh's (chap ...
ENZYMES AND PROTEINS
... Tertiary structures involves further folding of amino acid chains including the alpha helices and beta - pleated sheets that have been formed as a part of secondary structure and it establishes the conformation of each amino acid side chain. Enzymes generally have tertiary structures, which provide ...
... Tertiary structures involves further folding of amino acid chains including the alpha helices and beta - pleated sheets that have been formed as a part of secondary structure and it establishes the conformation of each amino acid side chain. Enzymes generally have tertiary structures, which provide ...
Enzyme immobilization
... The inefficiency of nonenzymatic detergents at removing proteins can result in permanent stains due to oxidation and denaturing caused by bleaching and drying. • Blood, for example, will leave a rustcoloured spot unless it is removed before bleaching. • Proteases hydrolyse proteins and break them do ...
... The inefficiency of nonenzymatic detergents at removing proteins can result in permanent stains due to oxidation and denaturing caused by bleaching and drying. • Blood, for example, will leave a rustcoloured spot unless it is removed before bleaching. • Proteases hydrolyse proteins and break them do ...
Document
... 1) General Aspects. Enzymes catalyze reactions by lowering the activation energy barrier for the reaction and often providing alternate pathways for a reaction to occur. We will discuss four general categories of catalytic mechanisms including a) transition state stabilization, b) general acid-base ...
... 1) General Aspects. Enzymes catalyze reactions by lowering the activation energy barrier for the reaction and often providing alternate pathways for a reaction to occur. We will discuss four general categories of catalytic mechanisms including a) transition state stabilization, b) general acid-base ...
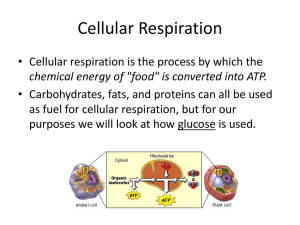
Cellular Respiration
... process that uses energy extracted from macromolecules (glucose) to produce energy (ATP) and water (H2O). ...
... process that uses energy extracted from macromolecules (glucose) to produce energy (ATP) and water (H2O). ...
Cellular Respiration
... process that uses energy extracted from macromolecules (glucose) to produce energy (ATP) and water (H2O). ...
... process that uses energy extracted from macromolecules (glucose) to produce energy (ATP) and water (H2O). ...
Chapter 5 (part 4) Enzyme Regulation
... • End products are often inhibitors • Allosteric modulators bind to site other than the active site ...
... • End products are often inhibitors • Allosteric modulators bind to site other than the active site ...
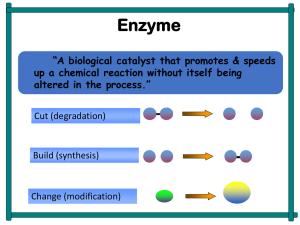
Enzymes
... reactions that keep a cell alive, for if the temperature is too cold, then the chemicals move too slowly, and the chemical reactions don’t occur fast enough to support life. If the temperature is too high, the enzymes, which are needed to speed up the reactions, become denatured (destroyed). The sec ...
... reactions that keep a cell alive, for if the temperature is too cold, then the chemicals move too slowly, and the chemical reactions don’t occur fast enough to support life. If the temperature is too high, the enzymes, which are needed to speed up the reactions, become denatured (destroyed). The sec ...
Amino Acid Metabolism
... regardless of whether they are released from dietary or intracellular proteins • The metabolism of the resulting amino group and nitrogen excretion are a central part of nitrogen metabolism ...
... regardless of whether they are released from dietary or intracellular proteins • The metabolism of the resulting amino group and nitrogen excretion are a central part of nitrogen metabolism ...
N x C (N-2)
... former depends upon the rate at which various organelles reach the bottom of the centrifuge tube to form a pellet. Organelles that do not reach the bottom so rapidly remain in the supernatant. On the next page a schematic of how differential centrifugation can be use to separate various organelles i ...
... former depends upon the rate at which various organelles reach the bottom of the centrifuge tube to form a pellet. Organelles that do not reach the bottom so rapidly remain in the supernatant. On the next page a schematic of how differential centrifugation can be use to separate various organelles i ...
Dr. V. Main Powerpoint
... which exist in multiprotein complexes • The carriers alternate reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons • Electrons drop in free energy as they go down the chain and are finally passed to O2, forming H2O Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin ...
... which exist in multiprotein complexes • The carriers alternate reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons • Electrons drop in free energy as they go down the chain and are finally passed to O2, forming H2O Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin ...
Lesson Overview - Midland Park School
... from the food we eat, but what if oxygen is not around? Is there a pathway that allows cells to extract energy from food in the absence of oxygen? ...
... from the food we eat, but what if oxygen is not around? Is there a pathway that allows cells to extract energy from food in the absence of oxygen? ...
Cellular Respiration
... water. – The H+ that has built up in the intermembrane space wants out! It flows through a molecule called ATP synthase. As it does ATP is formed. • Each NADH that donates electrons to the chain will fuel the creation of 3 ATP. • Each FADH2 that donates elections to the chain will fuel the creation ...
... water. – The H+ that has built up in the intermembrane space wants out! It flows through a molecule called ATP synthase. As it does ATP is formed. • Each NADH that donates electrons to the chain will fuel the creation of 3 ATP. • Each FADH2 that donates elections to the chain will fuel the creation ...
Metabolism and Glycolysis
... 6) Relationship with other pathways. (Shared metabolites, enzymes and regulations). 7) Later, you will have to visualize each pathway interacting with other pathways in normal and in pathological conditions. Anabolic reactions consume energy and nutrients to synthesize cell components like proteins. ...
... 6) Relationship with other pathways. (Shared metabolites, enzymes and regulations). 7) Later, you will have to visualize each pathway interacting with other pathways in normal and in pathological conditions. Anabolic reactions consume energy and nutrients to synthesize cell components like proteins. ...
ภาพนิ่ง 1
... enzyme will utilize (an example will be discussed). • It is also useful for comparing similar enzymes from different tissues or different organisms. • Also, it is the Km of the rate-limiting enzyme in many of the biochemical metabolic pathways that determines the amount of product and overall regula ...
... enzyme will utilize (an example will be discussed). • It is also useful for comparing similar enzymes from different tissues or different organisms. • Also, it is the Km of the rate-limiting enzyme in many of the biochemical metabolic pathways that determines the amount of product and overall regula ...
Metabolism: Energy, Enzymes, and Regulation
... principles of thermodynamics is required. The science of thermodynamics analyzes energy changes in a collection of matter (e.g., a cell or a plant) called a system. All other matter in the universe is called the surroundings. Thermodynamics focuses on the energy differences between the initial state ...
... principles of thermodynamics is required. The science of thermodynamics analyzes energy changes in a collection of matter (e.g., a cell or a plant) called a system. All other matter in the universe is called the surroundings. Thermodynamics focuses on the energy differences between the initial state ...
Chapter 26 - Palm Beach State College
... – Safe estimate of daily intake that would meet the nutritional needs of most healthy people ...
... – Safe estimate of daily intake that would meet the nutritional needs of most healthy people ...
Lecture 13: Krebs` Cycle / Citric Acid
... and ubiquinone (UQ) which are hydrogen carriers, the other components of electron transport chain (cytochromes) are only electron carriers i.e. they cannot give or take protons (H+) During the electron transport, FAD and the iron atom of different cytochromes get successively reduced (Fe++) and oxi ...
... and ubiquinone (UQ) which are hydrogen carriers, the other components of electron transport chain (cytochromes) are only electron carriers i.e. they cannot give or take protons (H+) During the electron transport, FAD and the iron atom of different cytochromes get successively reduced (Fe++) and oxi ...
Cellular Respiration - Napa Valley College
... § Requires oxygen: Oxygen is the final electron acceptor on the electron transport chain. § One glucose can produce a total of 36 ATP ...
... § Requires oxygen: Oxygen is the final electron acceptor on the electron transport chain. § One glucose can produce a total of 36 ATP ...
Triacylglycerol Metabolism Gone Bad: A major cause of disease
... – For each two carbons removed, 1 FADH2 and 1 NADH + H+ are produced – For palmitoyl-CoA, the reaction is: ...
... – For each two carbons removed, 1 FADH2 and 1 NADH + H+ are produced – For palmitoyl-CoA, the reaction is: ...
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms, an oxidized and reduced form abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH respectively.In metabolism, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The coenzyme is, therefore, found in two forms in cells: NAD+ is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced. This reaction forms NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, the most notable one being a substrate of enzymes that add or remove chemical groups from proteins, in posttranslational modifications. Because of the importance of these functions, the enzymes involved in NAD metabolism are targets for drug discovery.In organisms, NAD can be synthesized from simple building-blocks (de novo) from the amino acids tryptophan or aspartic acid. In an alternative fashion, more complex components of the coenzymes are taken up from food as the vitamin called niacin. Similar compounds are released by reactions that break down the structure of NAD. These preformed components then pass through a salvage pathway that recycles them back into the active form. Some NAD is also converted into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP); the chemistry of this related coenzyme is similar to that of NAD, but it has different roles in metabolism.Although NAD+ is written with a superscript plus sign because of the formal charge on a particular nitrogen atom, at physiological pH for the most part it is actually a singly charged anion (charge of minus 1), while NADH is a doubly charged anion.