enzyme kinetics
... Enzymes are the most selective and powerful catalysts known. An understanding of their detailed mechanisms provides a critical tool for the discovery of new drugs, for the large-scale industrial synthesis of useful chemicals, and for appreciating the chemistry of cells and organisms. A detailed stud ...
... Enzymes are the most selective and powerful catalysts known. An understanding of their detailed mechanisms provides a critical tool for the discovery of new drugs, for the large-scale industrial synthesis of useful chemicals, and for appreciating the chemistry of cells and organisms. A detailed stud ...
Phosphorylation - Biology Junction
... 3 more C to strip off (to oxidize) if O2 is available, pyruvate enters mitochondria enzymes of Krebs cycle complete the full oxidation of sugar to CO2 ...
... 3 more C to strip off (to oxidize) if O2 is available, pyruvate enters mitochondria enzymes of Krebs cycle complete the full oxidation of sugar to CO2 ...
SELECTIVE INHIBITORS OF DIHYDROFOLATE REDUCTASE
... homology. Hitchings and Roth found 16 identities between the enzymes from Escherichia coli and those from the mouse tumor L1210 (12). They predicted correctly that study of a wider range of enzymes would reduce the number of identities. If one takes into account enzymes not in the mainstream, e.g. t ...
... homology. Hitchings and Roth found 16 identities between the enzymes from Escherichia coli and those from the mouse tumor L1210 (12). They predicted correctly that study of a wider range of enzymes would reduce the number of identities. If one takes into account enzymes not in the mainstream, e.g. t ...
The active site
... The Lock and Key Hypothesis (cont.,) Temporary structure called the enzymesubstrate complex formed PRODUCTS have a different shape from the SUBSTRATE Once formed, PRODUCTS are released from the active site Leaving it free to become attached to another substrate ...
... The Lock and Key Hypothesis (cont.,) Temporary structure called the enzymesubstrate complex formed PRODUCTS have a different shape from the SUBSTRATE Once formed, PRODUCTS are released from the active site Leaving it free to become attached to another substrate ...
When muscular work starts, the adrenal medulla secretes a
... This ends the preparatory phase of glycolysis. Two molecules of ATP must be invested to activate or prime the glucose molecule for its cleavage into two three carbon pieces; later there will be a good return on this investment. The energy gain comes in the payoff phase of glycolysis. Each molecule o ...
... This ends the preparatory phase of glycolysis. Two molecules of ATP must be invested to activate or prime the glucose molecule for its cleavage into two three carbon pieces; later there will be a good return on this investment. The energy gain comes in the payoff phase of glycolysis. Each molecule o ...
enzymes - La Salle High School
... Catalysts for biological reactions Most are proteins Lower the activation energy Increase the rate of reaction Activity lost if denatured May be simple proteins May contain cofactors such as metal ions or organic (vitamins) ...
... Catalysts for biological reactions Most are proteins Lower the activation energy Increase the rate of reaction Activity lost if denatured May be simple proteins May contain cofactors such as metal ions or organic (vitamins) ...
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... Catalysts for biological reactions Most are proteins Lower the activation energy Increase the rate of reaction Activity lost if denatured May be simple proteins May contain cofactors such as metal ions or organic (vitamins) ...
... Catalysts for biological reactions Most are proteins Lower the activation energy Increase the rate of reaction Activity lost if denatured May be simple proteins May contain cofactors such as metal ions or organic (vitamins) ...
BI0 120 cell and tissues
... B. The proton gradient established during electron transport is a form of potential energy. C. The electron transport chain can be found in the mitochondria of aerobic bacteria and other cells. D. The movement of protons down a concentration gradient is an endergonic process. E. ATP synthesis associ ...
... B. The proton gradient established during electron transport is a form of potential energy. C. The electron transport chain can be found in the mitochondria of aerobic bacteria and other cells. D. The movement of protons down a concentration gradient is an endergonic process. E. ATP synthesis associ ...
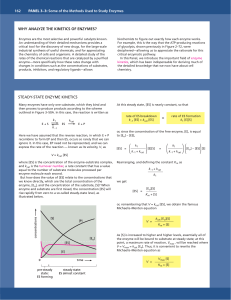
K m + [S]
... complex, and transforms it into product. The active site is a three-dimensional entity, often a cleft or crevice on the surface of the protein, in which the substrate is bound by multiple weak interactions. Two models have been proposed to explain how an enzyme binds its substrate: the lock-and –key ...
... complex, and transforms it into product. The active site is a three-dimensional entity, often a cleft or crevice on the surface of the protein, in which the substrate is bound by multiple weak interactions. Two models have been proposed to explain how an enzyme binds its substrate: the lock-and –key ...
Chapter 8 Enzymes: Basic Concepts and Kinetics
... -DIPF modifies only 1 of the 28 serine residues in the chymotrypsin and also modifies reactive serine residue in ...
... -DIPF modifies only 1 of the 28 serine residues in the chymotrypsin and also modifies reactive serine residue in ...
Lecture 26
... Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the process whereby precursors such as lactate, pyruvate, glycerol, and amino acids are converted to glucose. Fasting requires all the glucose to be synthesized from these non-carbohydrate precursors. Most precursors must enter the Krebs cycle at some point to be ...
... Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the process whereby precursors such as lactate, pyruvate, glycerol, and amino acids are converted to glucose. Fasting requires all the glucose to be synthesized from these non-carbohydrate precursors. Most precursors must enter the Krebs cycle at some point to be ...
Metabolism & Enzymes
... More accurate model of enzyme action 3-D structure of enzyme fits substrate substrate binding cause enzyme to change shape leading to a tighter fit ...
... More accurate model of enzyme action 3-D structure of enzyme fits substrate substrate binding cause enzyme to change shape leading to a tighter fit ...
Video Clip: Supersize Me in 7 Minutes
... Enzymes 4.1.3 Living organisms are dependent on certain ___________reactions that normally would occur too slowly or require too much ________ to be practical. To make these reactions possible, special ______ called ________ are used. What does an enzyme do? Enzymes 1. act as _______________ that _ ...
... Enzymes 4.1.3 Living organisms are dependent on certain ___________reactions that normally would occur too slowly or require too much ________ to be practical. To make these reactions possible, special ______ called ________ are used. What does an enzyme do? Enzymes 1. act as _______________ that _ ...
3+7 – HL Enzymes Page 1 1. Structure of Enzymes Like all proteins
... of the enzyme are fully occupied, so raising the substrate concentration has no effect. Define denaturing ...
... of the enzyme are fully occupied, so raising the substrate concentration has no effect. Define denaturing ...
The Effect of Temperature on the Metabolism of
... produce carbon dioxide but greater ability to take up oxygen. Enzymes associated with glycolysis, alcohol production, tricarboxylic acid cycle and respiratory chain in organisms cultured continuously at 25 and 38" showed few important differences. The most obvious ones were those involving a-ketoglu ...
... produce carbon dioxide but greater ability to take up oxygen. Enzymes associated with glycolysis, alcohol production, tricarboxylic acid cycle and respiratory chain in organisms cultured continuously at 25 and 38" showed few important differences. The most obvious ones were those involving a-ketoglu ...
Amino Acids and Simple Proteins
... The ability to understand modern problems in biochemistry and use the fundamental biological performance in the sphere of professional activities (PC-1); An independent analysis of available information, the identification of the fundamental problems, setting goals and objectives of the study; the ...
... The ability to understand modern problems in biochemistry and use the fundamental biological performance in the sphere of professional activities (PC-1); An independent analysis of available information, the identification of the fundamental problems, setting goals and objectives of the study; the ...
biological chemistry. the bank of mcq test questions 2016-2017
... 27. Optimal conditions for the determination of the enzyme activity in the blood are: A. 5oC; pH 7.3; high concentration of substrates B. 20oC; pH 6.5; low concentration of substrates C. 40oC; pH 7.3; high concentration of substrates D. 50oC; pH 5.8; low concentration of substrates E. 70oC; pH 7.8; ...
... 27. Optimal conditions for the determination of the enzyme activity in the blood are: A. 5oC; pH 7.3; high concentration of substrates B. 20oC; pH 6.5; low concentration of substrates C. 40oC; pH 7.3; high concentration of substrates D. 50oC; pH 5.8; low concentration of substrates E. 70oC; pH 7.8; ...
Biological monomers and polymers (1)
... and they are present in all organisms in roughly the same proportions; they make up what we visually recognize as life Macromolecules are giant polymers (poly means many; mer means units) constructed of many organic molecules called monomers. Some polymers are made of the same monomers, e.g. cellulo ...
... and they are present in all organisms in roughly the same proportions; they make up what we visually recognize as life Macromolecules are giant polymers (poly means many; mer means units) constructed of many organic molecules called monomers. Some polymers are made of the same monomers, e.g. cellulo ...
Digestive Enzymes Plus
... matter; they are essential to maintain all the body functions working properly. Each enzyme has a specific function in the body that no other enzyme can carry out. Digestive enzymes are specifically involved in the process of digestion. They are considered proteolytic enzymes since they only work on ...
... matter; they are essential to maintain all the body functions working properly. Each enzyme has a specific function in the body that no other enzyme can carry out. Digestive enzymes are specifically involved in the process of digestion. They are considered proteolytic enzymes since they only work on ...
Malate Dehydrogenases – Structure and Function
... with mitochondrial MDHs have shown that this enzyme is allosterically regulated. High concentrations of malate stimulate the production of oxaloacetate, while high concentrations of oxaloacetate inhibit the reaction (Mullinax et al. 1982; Fahien et al. 1988). Citrate also affects MDH activity by ver ...
... with mitochondrial MDHs have shown that this enzyme is allosterically regulated. High concentrations of malate stimulate the production of oxaloacetate, while high concentrations of oxaloacetate inhibit the reaction (Mullinax et al. 1982; Fahien et al. 1988). Citrate also affects MDH activity by ver ...
RACC BIO Cellular respiration
... For each molecule of glucose that Entered glycolysis, two molecules of acetyl CoA are produced and enter the citric acid cycle Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... For each molecule of glucose that Entered glycolysis, two molecules of acetyl CoA are produced and enter the citric acid cycle Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Homework # 9 Citric Acid Cycle, electron transport Chain, and
... unusual daily intake for an alcoholic) represents about half of the daily energy requirement. However, ethanol does not have any minerals, vitamins, carbohydrates, fats or protein associated with it. Alcohol causes inflammation of the stomach, pancreas, and intestines which impairs the digestion of ...
... unusual daily intake for an alcoholic) represents about half of the daily energy requirement. However, ethanol does not have any minerals, vitamins, carbohydrates, fats or protein associated with it. Alcohol causes inflammation of the stomach, pancreas, and intestines which impairs the digestion of ...
Essentials of Glycobiology Lecture 42 June 9, 1998 Jeff Esko
... ManNH2-Man-GlcN-PI is a poor substrate for the a2mannosyltransferase Trypanosomes selectively take up and exchange fatty acid analogs (10-(propoxy)decanoic acid) for acyl chains on glycosylphosphatidylinositol O O HO ...
... ManNH2-Man-GlcN-PI is a poor substrate for the a2mannosyltransferase Trypanosomes selectively take up and exchange fatty acid analogs (10-(propoxy)decanoic acid) for acyl chains on glycosylphosphatidylinositol O O HO ...
NO 2
... Asparagine and glutamine link carbon and nitrogen metabolism Asparagine serves not only as a protein precursor, but as a key compound for nitrogen transport and storage because of its stability and high nitrogen-tocarbon ratio (1:2). The major pathway for asparagine synthesis involves the trans ...
... Asparagine and glutamine link carbon and nitrogen metabolism Asparagine serves not only as a protein precursor, but as a key compound for nitrogen transport and storage because of its stability and high nitrogen-tocarbon ratio (1:2). The major pathway for asparagine synthesis involves the trans ...
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms, an oxidized and reduced form abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH respectively.In metabolism, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The coenzyme is, therefore, found in two forms in cells: NAD+ is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced. This reaction forms NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, the most notable one being a substrate of enzymes that add or remove chemical groups from proteins, in posttranslational modifications. Because of the importance of these functions, the enzymes involved in NAD metabolism are targets for drug discovery.In organisms, NAD can be synthesized from simple building-blocks (de novo) from the amino acids tryptophan or aspartic acid. In an alternative fashion, more complex components of the coenzymes are taken up from food as the vitamin called niacin. Similar compounds are released by reactions that break down the structure of NAD. These preformed components then pass through a salvage pathway that recycles them back into the active form. Some NAD is also converted into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP); the chemistry of this related coenzyme is similar to that of NAD, but it has different roles in metabolism.Although NAD+ is written with a superscript plus sign because of the formal charge on a particular nitrogen atom, at physiological pH for the most part it is actually a singly charged anion (charge of minus 1), while NADH is a doubly charged anion.








![K m + [S]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008289247_1-97eed219b6e242b1a447e591c5c01f05-300x300.png)














