Digestive Enzymes - Village Health Clinic
... seriously ill people with pancreatic insufficiency caused by pancreatitis are given very high levels of enzymes to improve fat digestion. In one successful trial, enough pancreatin was used with each meal to supply slightly over 1,000,000 USP units of lipase.12 Supplemental enzymes that state only p ...
... seriously ill people with pancreatic insufficiency caused by pancreatitis are given very high levels of enzymes to improve fat digestion. In one successful trial, enough pancreatin was used with each meal to supply slightly over 1,000,000 USP units of lipase.12 Supplemental enzymes that state only p ...
biochem 31 [3-20
... 12. What enzyme converts fructose 1,6 bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate? How about glucose 6-phosphate to glucose? Both release Pi a. Fructose 1,6-bisphophatase; glucose 6-phosphatase 13. How do glucocorticoids stimulate gluconeogenisis via PEPCK? a. The increase the levels of it synthesized 14. ...
... 12. What enzyme converts fructose 1,6 bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate? How about glucose 6-phosphate to glucose? Both release Pi a. Fructose 1,6-bisphophatase; glucose 6-phosphatase 13. How do glucocorticoids stimulate gluconeogenisis via PEPCK? a. The increase the levels of it synthesized 14. ...
BCHEM 253 – METABOLISM IN HEALTH AND DISEASES
... = -31.4 kJ/mol; In erythrocytes ΔG = -23.0 kJ/mol; Far from equilibrium.) Since 2 PEP are formed for every glucose molecule that enters the Glycolytic pathway, 2 ATP molecules are formed in this step. The ATP debt generated during phase 1 of glycolysis was paid by the formation of ATP by the substra ...
... = -31.4 kJ/mol; In erythrocytes ΔG = -23.0 kJ/mol; Far from equilibrium.) Since 2 PEP are formed for every glucose molecule that enters the Glycolytic pathway, 2 ATP molecules are formed in this step. The ATP debt generated during phase 1 of glycolysis was paid by the formation of ATP by the substra ...
Chapter 9 Notes
... • About 40% of the energy in a glucose molecule – Is transferred to ATP during cellular respiration, making approximately 38 ATP Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... • About 40% of the energy in a glucose molecule – Is transferred to ATP during cellular respiration, making approximately 38 ATP Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Peroxisomal oxidation of fatty acids
... Most of the steps are same as b-oxidation in mitochondria except that the first dehydrogenase is not linked to ETC in proxisomes. Electrons from the first reaction are transferred directly to O2 producing p hydrogen peroxide. Peroxisomal enzymes are up-regulated when fat rich diets are consumed. Gen ...
... Most of the steps are same as b-oxidation in mitochondria except that the first dehydrogenase is not linked to ETC in proxisomes. Electrons from the first reaction are transferred directly to O2 producing p hydrogen peroxide. Peroxisomal enzymes are up-regulated when fat rich diets are consumed. Gen ...
Enzymes 1 and 2
... • Enzymes have a variety of ionizable side chains that determine its secondary and tertiary structure and also affect events in the active site • Substrate may also have ionizable groups • Enzymes are usually active only over a limited range of pH • The effects of pH may be due to effects on Km or V ...
... • Enzymes have a variety of ionizable side chains that determine its secondary and tertiary structure and also affect events in the active site • Substrate may also have ionizable groups • Enzymes are usually active only over a limited range of pH • The effects of pH may be due to effects on Km or V ...
Enzymes - Philadelphia University Jordan
... chemical reaction, and are not consumed during the reaction. A. Active sites The active site contains amino acid side chains that participate in substrate binding and catalysis (Figure 5.2). E+S ES→EP→E+P complex ...
... chemical reaction, and are not consumed during the reaction. A. Active sites The active site contains amino acid side chains that participate in substrate binding and catalysis (Figure 5.2). E+S ES→EP→E+P complex ...
video slide
... electron transport chain to ATP synthesis 5. The H+ gradient is referred to as a protonmotive force a. emphasizing its capacity to do work b. the force drives H+ back across the ...
... electron transport chain to ATP synthesis 5. The H+ gradient is referred to as a protonmotive force a. emphasizing its capacity to do work b. the force drives H+ back across the ...
Citric acid cycle ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN AND
... 6.5 Hydrogen carriers such as NAD+ shuttle electrons in redox reactions • However, ATP will not be produced directly most of the time during cellular respiration. • Instead, enzymes remove electrons from glucose molecules and transfer them to a coenzyme (for example, NAD+) OXIDATION Dehydrogenase a ...
... 6.5 Hydrogen carriers such as NAD+ shuttle electrons in redox reactions • However, ATP will not be produced directly most of the time during cellular respiration. • Instead, enzymes remove electrons from glucose molecules and transfer them to a coenzyme (for example, NAD+) OXIDATION Dehydrogenase a ...
BC 367 Biochemistry of the Cell I
... Production of acetyl-CoA (e.g., during glycolysis and the bridging reaction) Oxidation of acetyl-CoA via the citric acid cycle Electon transport and oxidative phosphorylation to produce lots of ATP Fig 16-1 ...
... Production of acetyl-CoA (e.g., during glycolysis and the bridging reaction) Oxidation of acetyl-CoA via the citric acid cycle Electon transport and oxidative phosphorylation to produce lots of ATP Fig 16-1 ...
Pathways of Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism Glycolysis • Is the
... The coenzyme A is released during this conversion • 4/8 reactions are oxidations (those which form NADH and FADH 2) • The net result of the cycle is generation of 3 NADHs, 1 FADH2, and 1 GTP (GTP is sometimes interchangeably referred to as ATP because it is essentially converted to ATP very rapidl ...
... The coenzyme A is released during this conversion • 4/8 reactions are oxidations (those which form NADH and FADH 2) • The net result of the cycle is generation of 3 NADHs, 1 FADH2, and 1 GTP (GTP is sometimes interchangeably referred to as ATP because it is essentially converted to ATP very rapidl ...
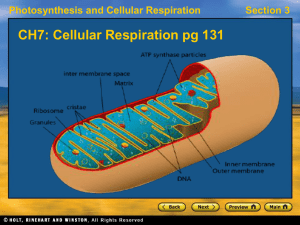
CH7Cellular-Respiration
... Efficiency of Cellular Respiration • In the first stage of cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to pyruvate during glycolysis, an anaerobic process. • Glycolysis results in 2 ATP molecules for each glucose molecule that is broken down. • In the 2nd stage, pyruvate EITHER passes through the ...
... Efficiency of Cellular Respiration • In the first stage of cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to pyruvate during glycolysis, an anaerobic process. • Glycolysis results in 2 ATP molecules for each glucose molecule that is broken down. • In the 2nd stage, pyruvate EITHER passes through the ...
Ch.21Pt.4_000
... Amino acid R group interactions bind a substrate to enzyme’s active site until reaction is complete ...
... Amino acid R group interactions bind a substrate to enzyme’s active site until reaction is complete ...
Lecture Fermentation
... Acetate Major pathway for five carbon sugars Source of five carbon sugars for biosynthesis 2 ATP, 2 NADPH, 1 NADH/Glucose ...
... Acetate Major pathway for five carbon sugars Source of five carbon sugars for biosynthesis 2 ATP, 2 NADPH, 1 NADH/Glucose ...
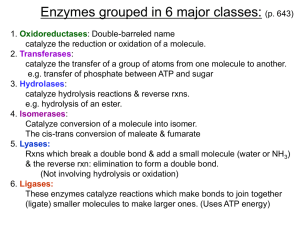
Lecture Notes Ch21
... – A product of a reaction acts as a negative regulator – An end product binds with the first enzyme in a sequence when sufficient product is present ...
... – A product of a reaction acts as a negative regulator – An end product binds with the first enzyme in a sequence when sufficient product is present ...
Enzymes - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... amt of enzyme needed for 1 micromol of substrate into products in one minute (std conditions) mole of substrate consumed or product formed per second Enzyme activity / protein concentration (for enzyme purity) measure of maximal catalytic activity Number of substrate molecules converted into produce ...
... amt of enzyme needed for 1 micromol of substrate into products in one minute (std conditions) mole of substrate consumed or product formed per second Enzyme activity / protein concentration (for enzyme purity) measure of maximal catalytic activity Number of substrate molecules converted into produce ...
Lecture 5 - Fermentation and CHO feeder
... lactate dehydrogenase (ie. muscle cells) -Pyruvate is converted to ethanol via ethanol dehydrogenase (ie. yeast) Anaerobic pyruvate utilization = Fermentation Both pathways use the NADH (produced in glycolysis): Overall: Glucose → 2 lactate + 2 ATP Biochemistry 3300 ...
... lactate dehydrogenase (ie. muscle cells) -Pyruvate is converted to ethanol via ethanol dehydrogenase (ie. yeast) Anaerobic pyruvate utilization = Fermentation Both pathways use the NADH (produced in glycolysis): Overall: Glucose → 2 lactate + 2 ATP Biochemistry 3300 ...
Full_ppt_ch21
... – Only certain substrates can fit the active site – Amino acid R groups in the active site help substrate bind and align correctly ...
... – Only certain substrates can fit the active site – Amino acid R groups in the active site help substrate bind and align correctly ...
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS)
... Mitochondrial aging is characterized by destruction of structural integrity of the membrane, leading to a decline in mitochondrial membrane fluidity and activities of enzymes associated with membrane lipids [1]. As the activities of most enzymes are regulated by the physicochemical state of the lipi ...
... Mitochondrial aging is characterized by destruction of structural integrity of the membrane, leading to a decline in mitochondrial membrane fluidity and activities of enzymes associated with membrane lipids [1]. As the activities of most enzymes are regulated by the physicochemical state of the lipi ...
An Introduction to Metabolism and Energetics
... • Can diffuse easily across plasma membranes • In blood, are generally bound to albumin (most abundant plasma ...
... • Can diffuse easily across plasma membranes • In blood, are generally bound to albumin (most abundant plasma ...
0495116572_102921
... • Hydrolysis of thioester bond of acetyl CoA drives phosphorylation of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) • Succinate dehydrogenase reaction • Fumerase incorporates H2O across double bond of fumarate to form malate • Malate converted to oxaloacetate ...
... • Hydrolysis of thioester bond of acetyl CoA drives phosphorylation of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) • Succinate dehydrogenase reaction • Fumerase incorporates H2O across double bond of fumarate to form malate • Malate converted to oxaloacetate ...
Full text in pdf - International Microbiology
... plant enzymes of the GAPDHN family have a much closer affiliation among each other than with other enzymes of the ALDH superfamily. For example, S. mutans GAPDHN shows about 50% amino acid identity with the enzyme of photosynthetic eukaryotes [11]. By contrast, the archaeon Methanococcus jannaschii ...
... plant enzymes of the GAPDHN family have a much closer affiliation among each other than with other enzymes of the ALDH superfamily. For example, S. mutans GAPDHN shows about 50% amino acid identity with the enzyme of photosynthetic eukaryotes [11]. By contrast, the archaeon Methanococcus jannaschii ...
IB-Respiration-Notepacket
... molecules are produced per glucose a. Carbon dioxide = (How many total does that bring us to?_________) b. ATP= (How many total does that bring us to? _________) c. NADH = d. FADH = (How many total electron carrier molecules do we have all together so far? _________________________) e. Where does th ...
... molecules are produced per glucose a. Carbon dioxide = (How many total does that bring us to?_________) b. ATP= (How many total does that bring us to? _________) c. NADH = d. FADH = (How many total electron carrier molecules do we have all together so far? _________________________) e. Where does th ...
allosteric inhibition
... • Studies on Inhibitors are useful for: • Mechanistic studies to learn about how enzymes interact with their substrates. • Role of inhibitors in enzyme regulation. • Drugs if they inhibit abberrant biochemical reactions: – penicillin, ampicillin, et al.: interfere with the synthesis of bacterial cel ...
... • Studies on Inhibitors are useful for: • Mechanistic studies to learn about how enzymes interact with their substrates. • Role of inhibitors in enzyme regulation. • Drugs if they inhibit abberrant biochemical reactions: – penicillin, ampicillin, et al.: interfere with the synthesis of bacterial cel ...
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms, an oxidized and reduced form abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH respectively.In metabolism, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The coenzyme is, therefore, found in two forms in cells: NAD+ is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced. This reaction forms NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, the most notable one being a substrate of enzymes that add or remove chemical groups from proteins, in posttranslational modifications. Because of the importance of these functions, the enzymes involved in NAD metabolism are targets for drug discovery.In organisms, NAD can be synthesized from simple building-blocks (de novo) from the amino acids tryptophan or aspartic acid. In an alternative fashion, more complex components of the coenzymes are taken up from food as the vitamin called niacin. Similar compounds are released by reactions that break down the structure of NAD. These preformed components then pass through a salvage pathway that recycles them back into the active form. Some NAD is also converted into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP); the chemistry of this related coenzyme is similar to that of NAD, but it has different roles in metabolism.Although NAD+ is written with a superscript plus sign because of the formal charge on a particular nitrogen atom, at physiological pH for the most part it is actually a singly charged anion (charge of minus 1), while NADH is a doubly charged anion.