How Do Enzymes Work?
... orient reactive groups and bring them into proximity with one another favoring their participation in catalysis – Such arrangements have been termed near-attack conformations (NACs) – NACs are precursors to reaction transition states ...
... orient reactive groups and bring them into proximity with one another favoring their participation in catalysis – Such arrangements have been termed near-attack conformations (NACs) – NACs are precursors to reaction transition states ...
Enzymes Biotechnology Handbook
... processes, without them biotechnology as a subject would not exist. The main advantage of enzymes compared to most other catalysts is their stereo, region and chemo selectivity and specificity. Enzymes are responsible for many essential biochemical reactions in micro organisms, plants, animals, and ...
... processes, without them biotechnology as a subject would not exist. The main advantage of enzymes compared to most other catalysts is their stereo, region and chemo selectivity and specificity. Enzymes are responsible for many essential biochemical reactions in micro organisms, plants, animals, and ...
Homeostasis Invertase
... level of the protein (e.g. enzyme). In fact, there is coordination across these levels to maintain homeostasis of critical factors such as body temperature, ionic concentrations (like protons and calcium), and "building blocks" like amino acids and nucleic acids. From an evolutionary perspective, th ...
... level of the protein (e.g. enzyme). In fact, there is coordination across these levels to maintain homeostasis of critical factors such as body temperature, ionic concentrations (like protons and calcium), and "building blocks" like amino acids and nucleic acids. From an evolutionary perspective, th ...
Chapter 2-ROLE OF ENZYMES
... 21. Is this inhibitor able to do this because it is similar or different to the molecular structure of the substrate? 22. At low concentrations of competitive inhibitor the reaction rate is still high as few active sites are blocked by the inhibitor leaving the substrates no difficulty in finding fr ...
... 21. Is this inhibitor able to do this because it is similar or different to the molecular structure of the substrate? 22. At low concentrations of competitive inhibitor the reaction rate is still high as few active sites are blocked by the inhibitor leaving the substrates no difficulty in finding fr ...
Enzyme Activity - Model High School
... and enzymes work together like puzzles. A substrate is a chemical that can bond onto a specific enzyme. Only one type of enzyme with lock onto the active site of the substrate chemical (like a puzzle piece). Thus, they are very specific.When the reaction occurs, products are made from the substrate. ...
... and enzymes work together like puzzles. A substrate is a chemical that can bond onto a specific enzyme. Only one type of enzyme with lock onto the active site of the substrate chemical (like a puzzle piece). Thus, they are very specific.When the reaction occurs, products are made from the substrate. ...
Enzymes - OpenStax CNX
... the reaction of their substrates is by creating an optimal environment within the active site for the reaction to occur. Certain chemical reactions might proceed best in a slightly acidic or non-polar environment. The chemical properties that emerge from the particular arrangement of amino acid resi ...
... the reaction of their substrates is by creating an optimal environment within the active site for the reaction to occur. Certain chemical reactions might proceed best in a slightly acidic or non-polar environment. The chemical properties that emerge from the particular arrangement of amino acid resi ...
Enzymes - OpenStax CNX
... the reaction of their substrates is by creating an optimal environment within the active site for the reaction to occur. Certain chemical reactions might proceed best in a slightly acidic or non-polar environment. The chemical properties that emerge from the particular arrangement of amino acid resi ...
... the reaction of their substrates is by creating an optimal environment within the active site for the reaction to occur. Certain chemical reactions might proceed best in a slightly acidic or non-polar environment. The chemical properties that emerge from the particular arrangement of amino acid resi ...
Ecotek Students Improve Protocol for the Enzyme Hydrolysis of Starch
... An enzyme is made up of a group of proteins that perform different biochemical functions. They serve as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions. An enzyme is formed by stringing together between 100 and 1,000 amino acids. The shape of an enzyme allows it to carry out specific chemical reactions. En ...
... An enzyme is made up of a group of proteins that perform different biochemical functions. They serve as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions. An enzyme is formed by stringing together between 100 and 1,000 amino acids. The shape of an enzyme allows it to carry out specific chemical reactions. En ...
Unit-III Enzymes
... • Adding the suffix –ase to the name of the substrates (urease) • Adding the suffix –ase to a descriptive term for the reactions they catalyze (glutemate dehydrogenase) • For historic names (trypsin, amylase) • Being named after their genes (Rec A –recA, HSP70) ...
... • Adding the suffix –ase to the name of the substrates (urease) • Adding the suffix –ase to a descriptive term for the reactions they catalyze (glutemate dehydrogenase) • For historic names (trypsin, amylase) • Being named after their genes (Rec A –recA, HSP70) ...
Slide 1
... • Is it wise to mask inflammation/pain? • The mode of action of Tylenol is not yet understood …. ...
... • Is it wise to mask inflammation/pain? • The mode of action of Tylenol is not yet understood …. ...
UNIT 2: The Chemistry of Life
... Example: Solution A has a pH of 8. Solution B has a pH of 3. Because Solution B has a lower pH, it has a greater concentration of hydrogen ions present. The more acidic a solution is, the greater the concentration of hydrogen ions. 1. An unknown solution has a very high concentration of hydrogen ion ...
... Example: Solution A has a pH of 8. Solution B has a pH of 3. Because Solution B has a lower pH, it has a greater concentration of hydrogen ions present. The more acidic a solution is, the greater the concentration of hydrogen ions. 1. An unknown solution has a very high concentration of hydrogen ion ...
Enzyme_Activity_and_Regulation_Internet_Activity updated 1
... Describe the effects of the following on enzyme activity: a. pH b. temperature c. salt concentration d. concentration of enzyme or substrate e. cofactors ...
... Describe the effects of the following on enzyme activity: a. pH b. temperature c. salt concentration d. concentration of enzyme or substrate e. cofactors ...
Enzymes
... To explain this, Fischer proposed the lock and key hypothesis. This theory suggests that the active site of the enzyme (lock) has a particular shape, due to its specific tertiary structure and it will therefore only accept a particular substrate (key). It now seems probably that the match between en ...
... To explain this, Fischer proposed the lock and key hypothesis. This theory suggests that the active site of the enzyme (lock) has a particular shape, due to its specific tertiary structure and it will therefore only accept a particular substrate (key). It now seems probably that the match between en ...
Characterization of α-galactosidase belonging to family-4 glycoside hidrolases Bacillus halodurans
... The α-galactosidase MelA (BH2228) gene of Bacillus halodurans was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. The melA gene consists of 1305 nucleotides encoding a protein of 434 amino acids with a predicted molecular weight of 49,761. It was assigned to family 4 of glycoside hidrolases. Almost all of ...
... The α-galactosidase MelA (BH2228) gene of Bacillus halodurans was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. The melA gene consists of 1305 nucleotides encoding a protein of 434 amino acids with a predicted molecular weight of 49,761. It was assigned to family 4 of glycoside hidrolases. Almost all of ...
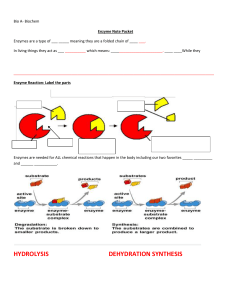
Bio A- Biochem Enzyme Note Packet Enzymes are a type of ___
... Coenzyme: organic molecules (like vitamins) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme o Organic means??? _CONTAINS C and H (and since it is found in living things..Oxygen! _____ Cofactors: inorganic molecules (like Zn, Cu) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme Both coenzymes and cofactors bind to ...
... Coenzyme: organic molecules (like vitamins) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme o Organic means??? _CONTAINS C and H (and since it is found in living things..Oxygen! _____ Cofactors: inorganic molecules (like Zn, Cu) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme Both coenzymes and cofactors bind to ...
Catalase Lab How do enzymes work in living tissues? Introduction
... die. In fact, your cells are always making poisonous chemical. They do not die because your cells use enzymes to break down these poisonous chemicals into harmless substances. Enzymes are proteins that speed up the rate of reactions that would otherwise happen more slowly. The enzyme is not altered ...
... die. In fact, your cells are always making poisonous chemical. They do not die because your cells use enzymes to break down these poisonous chemicals into harmless substances. Enzymes are proteins that speed up the rate of reactions that would otherwise happen more slowly. The enzyme is not altered ...
Biochemistry and Enzymes - St. John the Baptist Diocesan High
... reaction rate will initially increase. However, as all of the substrate is broken down, the excess enzymes have nothing to combine with, so reaction rate levels off. If the concentration of the substrate increases, reaction rate will initially increase. However, as all of the enzyme is used up, th ...
... reaction rate will initially increase. However, as all of the substrate is broken down, the excess enzymes have nothing to combine with, so reaction rate levels off. If the concentration of the substrate increases, reaction rate will initially increase. However, as all of the enzyme is used up, th ...
Enzymes
... Poisons • Many enzyme inhibitors are poisonous because of their effect on enzyme activity. • Mercury and lead compounds are poisonous because they react with the sulfhydryl group (SH) of an enzyme and so change its conformation. • The subsequent loss of enzyme activity leads to the various symptoms ...
... Poisons • Many enzyme inhibitors are poisonous because of their effect on enzyme activity. • Mercury and lead compounds are poisonous because they react with the sulfhydryl group (SH) of an enzyme and so change its conformation. • The subsequent loss of enzyme activity leads to the various symptoms ...
The Digestive System
... The enzyme sucrase catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose (a disaccharide) into glucose and fructose (both monosaccharides) with the addition of water ...
... The enzyme sucrase catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose (a disaccharide) into glucose and fructose (both monosaccharides) with the addition of water ...
ENZYMES AND PROTEINS
... Uses: Malt extract and purified diastase, both are used as amylolytic enzymes and as an aid in digesting starch. They are used as bulk producing laxatives. 4. Streptokinase Synonym: Estreptokinase, Plasminokinase Biological Source: Estreptokinase, Plasminokinase is a purified bacterial protein produ ...
... Uses: Malt extract and purified diastase, both are used as amylolytic enzymes and as an aid in digesting starch. They are used as bulk producing laxatives. 4. Streptokinase Synonym: Estreptokinase, Plasminokinase Biological Source: Estreptokinase, Plasminokinase is a purified bacterial protein produ ...
Bio 210 Cell Chemistry Lecture 7 “Enzymes”
... The activation energy represents the uphill portion of the graph. As the reactants absorb energy, they become unstable. This is the “transition state”. As new bonds are formed, energy is released into the surroundings. This is the downhill portion of the curve which indicates a loss of free energy ...
... The activation energy represents the uphill portion of the graph. As the reactants absorb energy, they become unstable. This is the “transition state”. As new bonds are formed, energy is released into the surroundings. This is the downhill portion of the curve which indicates a loss of free energy ...
CHAPTER-VI PROTEIN METABOLISM
... Transaminases catalyze the transfer of -NH2 groups from the amino acids, onto alphaketoglutarate. Many different transaminases are known, and they are generally of broad specificity for amino acids (that is, one enzyme can accept as substrates two or more different amino acids). All have the same co ...
... Transaminases catalyze the transfer of -NH2 groups from the amino acids, onto alphaketoglutarate. Many different transaminases are known, and they are generally of broad specificity for amino acids (that is, one enzyme can accept as substrates two or more different amino acids). All have the same co ...
enzyme - iGEM 2014
... • Sometimes common names are used, particularly for the digestion enzymes such as pepsin and trypsin • Some names describe both the substrate and the function – For example, alcohol dehydrogenase oxides ethanol ...
... • Sometimes common names are used, particularly for the digestion enzymes such as pepsin and trypsin • Some names describe both the substrate and the function – For example, alcohol dehydrogenase oxides ethanol ...
Enzymes
... • The product separates from the enzyme, leaving the enzyme molecule unchanged and free to combine again with more substrate molecules ...
... • The product separates from the enzyme, leaving the enzyme molecule unchanged and free to combine again with more substrate molecules ...
enzymes 2016
... • Products: the molecules that the enzyme is broken down into, the result of the reaction • Induced Fit: the way in which the enzyme and substrate bond to one another • Each enzyme is only capable of metabolizing (breaking down) one type of substrate. • The enzyme and the substrate must fit together ...
... • Products: the molecules that the enzyme is broken down into, the result of the reaction • Induced Fit: the way in which the enzyme and substrate bond to one another • Each enzyme is only capable of metabolizing (breaking down) one type of substrate. • The enzyme and the substrate must fit together ...
Beta-lactamase

Beta-lactamases are enzymes (EC 3.5.2.6) produced by some bacteria that provide resistance to β-lactam antibiotics like penicillins, cephamycins, and carbapenems (ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a β-lactam. Through hydrolysis, the lactamase enzyme breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties.Beta-lactam antibiotics are typically used to treat a broad spectrum of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.Beta-lactamases produced by Gram-negative organisms are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment.