enzyme
... Enzymes are proteins (made up of amino acids) Enzymes function by lowering the activation energy of reactions. Enzymes can act rapidly and can cause chemicals to act 107 times faster than without the enzyme present. There are over 2000 known enzymes, each of which is involved with one specific chemi ...
... Enzymes are proteins (made up of amino acids) Enzymes function by lowering the activation energy of reactions. Enzymes can act rapidly and can cause chemicals to act 107 times faster than without the enzyme present. There are over 2000 known enzymes, each of which is involved with one specific chemi ...
Factoids about Bacteria and Fungi rev
... They inhabit virtually all the earth’s surface environments and thrive in temperatures ranging from below zero to well over 100 C. under intense pressure beneath the sea. If Bacteria excel in replication, fungi excel in growth. A fungal hypha 10-40 micrometers in diameter can grow as much as 40 mic ...
... They inhabit virtually all the earth’s surface environments and thrive in temperatures ranging from below zero to well over 100 C. under intense pressure beneath the sea. If Bacteria excel in replication, fungi excel in growth. A fungal hypha 10-40 micrometers in diameter can grow as much as 40 mic ...
Section 2.5 Enzymes
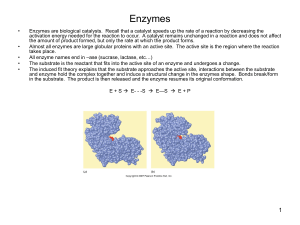
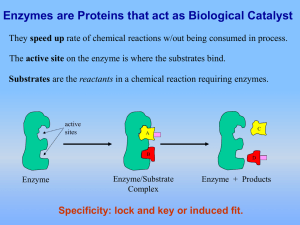
... • Each enzyme has a unique 3-D shape, including a surface groove called an ACTIVE SITE. • One or more molecules called SUBSTRATES chemically bond to the enzyme’s active site. • When joined they are called an ENZYME-SUBSTRATE COMPLEX • Changes in how the atoms are bonded occur resulting in new molecu ...
... • Each enzyme has a unique 3-D shape, including a surface groove called an ACTIVE SITE. • One or more molecules called SUBSTRATES chemically bond to the enzyme’s active site. • When joined they are called an ENZYME-SUBSTRATE COMPLEX • Changes in how the atoms are bonded occur resulting in new molecu ...
Lesson 5: Enzymes
... vitamins (respectively) are sometimes need for proper enzymatic activity. • Example: Iron must be present in the quaternary structure - hemoglobin in order for it to pick up oxygen. ...
... vitamins (respectively) are sometimes need for proper enzymatic activity. • Example: Iron must be present in the quaternary structure - hemoglobin in order for it to pick up oxygen. ...
Chapter 6: An introduction to metabolism
... i. Competitive inhibitor mimics the substrate and blocks the active site ii. Noncompetitive inhibitor binds to a location (allosteric site) away from the active site but changes the conformation so that the active site does not function iii. Allosteric enzymes are usually made of multiple polypeptid ...
... i. Competitive inhibitor mimics the substrate and blocks the active site ii. Noncompetitive inhibitor binds to a location (allosteric site) away from the active site but changes the conformation so that the active site does not function iii. Allosteric enzymes are usually made of multiple polypeptid ...
3)Synthetic Analogues of Nucleotides
... Antiviral drugs Anticancer drugs Drugs used for hyperuricemia Organ transplant drugs Drugs used for Asthma ...
... Antiviral drugs Anticancer drugs Drugs used for hyperuricemia Organ transplant drugs Drugs used for Asthma ...
Reading GuideMetabolismchapter6
... make ATP within a metabolic pathway such as glycolysis by the transfer of a phosphate group from an organic compound to ADP? Which process is the generation of ATP through oxidation/reduction reactions in the electron transport chain? Another concept key to the topic of bacterial metabolism is enzym ...
... make ATP within a metabolic pathway such as glycolysis by the transfer of a phosphate group from an organic compound to ADP? Which process is the generation of ATP through oxidation/reduction reactions in the electron transport chain? Another concept key to the topic of bacterial metabolism is enzym ...
Enzymes - Healing Energies at London West
... substrates and the catalytic relationship cannot take place. Although the body produces its own enzymes, as a generalisation it is considered that these are not sufficient to meet the needs of the body and that additional enzymes need to be ingested with the food. Enzymes can be damaged by high temp ...
... substrates and the catalytic relationship cannot take place. Although the body produces its own enzymes, as a generalisation it is considered that these are not sufficient to meet the needs of the body and that additional enzymes need to be ingested with the food. Enzymes can be damaged by high temp ...
Enzyme
... Enzymes speed up reactions by reducing the amount of energy substrates need to react. In other words, they reduce the activation energy of the reaction. The activation energy of a reaction is the minimum amount of energy needed to start a reaction. ...
... Enzymes speed up reactions by reducing the amount of energy substrates need to react. In other words, they reduce the activation energy of the reaction. The activation energy of a reaction is the minimum amount of energy needed to start a reaction. ...
Restriction Enzymes
... recognition nucleotide sequences known as restriction sites. Such enzymes, found in bacteria and archaea, are thought to have evolved to provide a defense mechanism against invading viruses ...
... recognition nucleotide sequences known as restriction sites. Such enzymes, found in bacteria and archaea, are thought to have evolved to provide a defense mechanism against invading viruses ...
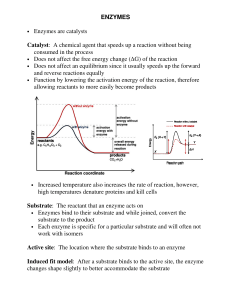
ENZYMES • Enzymes are catalysts Catalyst: A chemical agent that
... • Usually temporary but could be permanent (e.g. hydrogen cyanide – humans, penicillin – bacteria) Competitive inhibitors • Fit into the active site and block the substrate ...
... • Usually temporary but could be permanent (e.g. hydrogen cyanide – humans, penicillin – bacteria) Competitive inhibitors • Fit into the active site and block the substrate ...
Example4
... CHALLENGE ACTIVITY Group 1 Challenge! Which organelles involved in the synthesis of pepsin; a digestive enzyme formed by stomach cells. ...
... CHALLENGE ACTIVITY Group 1 Challenge! Which organelles involved in the synthesis of pepsin; a digestive enzyme formed by stomach cells. ...
Enzymes
... describe one way that enzymes operate-enzymes can operate in several different ways to speed reactions. In this process, the reactant that binds loosely to the active site at the start of the reaction is called the substrate (f). In reaction 1, we see the enzyme and substrate combine at the active s ...
... describe one way that enzymes operate-enzymes can operate in several different ways to speed reactions. In this process, the reactant that binds loosely to the active site at the start of the reaction is called the substrate (f). In reaction 1, we see the enzyme and substrate combine at the active s ...
Enzymes
... – Reversible inhibition: A reversible inhibitor is a compound that inactivates an enzyme by forming noncovalent interactions with the enzyme. Many enzymes use this for natural regulation of enzyme activity, and many drugs are reversible inhibitors • Competitive inhibitors: compete with the substrate ...
... – Reversible inhibition: A reversible inhibitor is a compound that inactivates an enzyme by forming noncovalent interactions with the enzyme. Many enzymes use this for natural regulation of enzyme activity, and many drugs are reversible inhibitors • Competitive inhibitors: compete with the substrate ...
5 Slides About: Dioxygen Activation in Non-Heme
... peroxo bond (P Q) forms a Fe(IV)Fe(IV)-oxo species, termed Q. sMMOOx can directly convert to P by the addition of peroxide. *Rates reported at 4ºC ...
... peroxo bond (P Q) forms a Fe(IV)Fe(IV)-oxo species, termed Q. sMMOOx can directly convert to P by the addition of peroxide. *Rates reported at 4ºC ...
University of Groningen Characterization of 4,6
... enzyme may thus find industrial application in synthesis of IMMP modified starch. However, the expression level of soluble enzymes, which is preferable for industrial production, has remained unsatisfactorily low. The LAB GS are homologous to 4,6-α-GTase enzymes, and deletion of (parts of) their N-t ...
... enzyme may thus find industrial application in synthesis of IMMP modified starch. However, the expression level of soluble enzymes, which is preferable for industrial production, has remained unsatisfactorily low. The LAB GS are homologous to 4,6-α-GTase enzymes, and deletion of (parts of) their N-t ...
Selection Qs - Mrs Bradford`s Science Revision Page
... able to recognise that they were expected to draw on their knowledge of enzymes. They experienced considerable difficulties, however, in identifying the enzyme and its substrate in the context of this question. Thus the enzyme was often incorrectly given as the penicillin molecule or equated with th ...
... able to recognise that they were expected to draw on their knowledge of enzymes. They experienced considerable difficulties, however, in identifying the enzyme and its substrate in the context of this question. Thus the enzyme was often incorrectly given as the penicillin molecule or equated with th ...
2. Enzymes
... A) Competitive Inhibitors bind to the active site without being acted on, thus reducing reaction rate of true substrate(s). In other cases, the competing molecule is acted on by the enzyme, but again, inhibits reaction with natural substrate. ...
... A) Competitive Inhibitors bind to the active site without being acted on, thus reducing reaction rate of true substrate(s). In other cases, the competing molecule is acted on by the enzyme, but again, inhibits reaction with natural substrate. ...
Adding Enzymes To Dairy Diets
... Enzymes are routinely included in poultry diets to remove antinutritional factors from feeds, to increase feed digestibility and to supplement the enzymes secreted by the bird’s own digestive system. Similar enzyme preparations have been promoted for swine diets, but economic responses are less pred ...
... Enzymes are routinely included in poultry diets to remove antinutritional factors from feeds, to increase feed digestibility and to supplement the enzymes secreted by the bird’s own digestive system. Similar enzyme preparations have been promoted for swine diets, but economic responses are less pred ...
The link between Darwin and antioxidants from olives
... process. Eschericia coli cells manipulated to express TMOs are capable of oxidizing a wide range of substituted aromatic and phenolic compounds with high regiospecificity. Despite the resemblance of PEA to the natural substrate, toluene, it was found to be a very poor substrate for the wild-type enz ...
... process. Eschericia coli cells manipulated to express TMOs are capable of oxidizing a wide range of substituted aromatic and phenolic compounds with high regiospecificity. Despite the resemblance of PEA to the natural substrate, toluene, it was found to be a very poor substrate for the wild-type enz ...
Slide 1
... concentration on the activity of enzymes. • Skill: Experimental investigation of a factor affecting enzyme activity. (Practical 3) ...
... concentration on the activity of enzymes. • Skill: Experimental investigation of a factor affecting enzyme activity. (Practical 3) ...
Active Transport - stephen fleenor
... Describe how the allosteric inhibitor below will inhibit (deactivate) the enzyme. Describe in detail. Like, molecular detail. Like, maybe, using the word “R group.” using Do not just say “…and then the active site won’t work.” That would be lazy, and you’re in the ...
... Describe how the allosteric inhibitor below will inhibit (deactivate) the enzyme. Describe in detail. Like, molecular detail. Like, maybe, using the word “R group.” using Do not just say “…and then the active site won’t work.” That would be lazy, and you’re in the ...
Beta-lactamase

Beta-lactamases are enzymes (EC 3.5.2.6) produced by some bacteria that provide resistance to β-lactam antibiotics like penicillins, cephamycins, and carbapenems (ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a β-lactam. Through hydrolysis, the lactamase enzyme breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties.Beta-lactam antibiotics are typically used to treat a broad spectrum of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.Beta-lactamases produced by Gram-negative organisms are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment.