Cardiff International School Dhaka (CISD) Lost Class Make Up
... Q2. (a) At temperatures between 0o C and about 40 o C the rate of enzyme activity increases with temperature. Enzyme activity decreases markedly above 40 o C. (b) As temperature increases the molecules move faster, a greater proportion of the molecules collide etc. (c) Extremes of pH denature enzyme ...
... Q2. (a) At temperatures between 0o C and about 40 o C the rate of enzyme activity increases with temperature. Enzyme activity decreases markedly above 40 o C. (b) As temperature increases the molecules move faster, a greater proportion of the molecules collide etc. (c) Extremes of pH denature enzyme ...
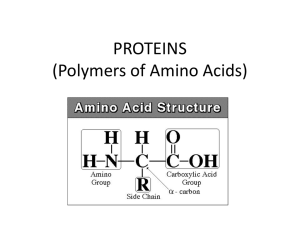
PROTEINS (Polymers of Amino Acids)
... – Hydrophobic interaction – nonpolar sections of molecule clump to middle of protein away from any possible sources of water ...
... – Hydrophobic interaction – nonpolar sections of molecule clump to middle of protein away from any possible sources of water ...
UNIT 1 PART 1: THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD
... Multicellular, cells do not have cell walls Eukaryotic Must get food from the environment ...
... Multicellular, cells do not have cell walls Eukaryotic Must get food from the environment ...
Bio- Chapter 2 section 4 kearns 2014
... Catalysts work by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction ...
... Catalysts work by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction ...
logcsscibap_2_4_2_c_..
... Are the shapes of the reactant and active site similar or different? Explain your answer. (2 marks) ...
... Are the shapes of the reactant and active site similar or different? Explain your answer. (2 marks) ...
Slideshow
... Sucrose + water glucose + fructose • For the reaction to take place a number of things must happen. • 1st the sucrose & water must collide with sufficient energy to form glucose & fructose. • The energy of the products must be less than that of the substrates. • An initial boost of energy is neede ...
... Sucrose + water glucose + fructose • For the reaction to take place a number of things must happen. • 1st the sucrose & water must collide with sufficient energy to form glucose & fructose. • The energy of the products must be less than that of the substrates. • An initial boost of energy is neede ...
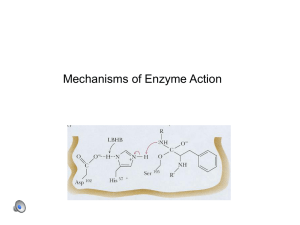
How do Enzymes work?
... considered and known to be proteins. All chemical reactions in all living organisms require enzymes to function; actually, no existing reaction can take place without an enzyme. They have the principal function of being biological catalysts (speed up reactions), but they also work as being synthesis ...
... considered and known to be proteins. All chemical reactions in all living organisms require enzymes to function; actually, no existing reaction can take place without an enzyme. They have the principal function of being biological catalysts (speed up reactions), but they also work as being synthesis ...
Enzymes! - Mrs. Ahrens` Science Site
... Enzymes: Catch & Release • After the enzyme has complexed with the substrate, the change molecule is released (called a product) to be used by the body. • Each protein has a specific shape, therefore enzymes bind to substrates based on shape. – the substrates are based on the complementary shape of ...
... Enzymes: Catch & Release • After the enzyme has complexed with the substrate, the change molecule is released (called a product) to be used by the body. • Each protein has a specific shape, therefore enzymes bind to substrates based on shape. – the substrates are based on the complementary shape of ...
National 4- Production of cheese
... As the pH is decreased below this value the enzyme becomes less and less effective until it is almost inactive. As the pH is increased above this value the enzyme becomes less and less effective until it is almost inactive. pH’s which are very different from an enzymes optimum will denature th ...
... As the pH is decreased below this value the enzyme becomes less and less effective until it is almost inactive. As the pH is increased above this value the enzyme becomes less and less effective until it is almost inactive. pH’s which are very different from an enzymes optimum will denature th ...
Purification and Reengineering of Plastic
... Changes in percent elongation extension of material under load ...
... Changes in percent elongation extension of material under load ...
Proteins
... or substrate, which has a complementary shape. Enzymes following the Lock and Key Hypothesis. o For every substrate there is one and only one enzyme that causes the substrate to occur just like there is a specific key, which fits a specific lock. o A substrate is the substance which needs to be di ...
... or substrate, which has a complementary shape. Enzymes following the Lock and Key Hypothesis. o For every substrate there is one and only one enzyme that causes the substrate to occur just like there is a specific key, which fits a specific lock. o A substrate is the substance which needs to be di ...
Enzymes
... (1) An enzyme and a SUBSTRATE are in the same area. The substrate is the biological molecule that the enzyme will work on. (2) The enzyme grabs onto the substrate with a special area called the ACTIVE SITE. The active site is a specially shaped area of the enzyme that fits around the substrate. The ...
... (1) An enzyme and a SUBSTRATE are in the same area. The substrate is the biological molecule that the enzyme will work on. (2) The enzyme grabs onto the substrate with a special area called the ACTIVE SITE. The active site is a specially shaped area of the enzyme that fits around the substrate. The ...
Enzymes worksheet
... (1) An enzyme and a SUBSTRATE are in the same area. The substrate is the biological molecule that the enzyme will work on. (2) The enzyme grabs onto the substrate with a special area called the ACTIVE SITE. The active site is a specially shaped area of the enzyme that fits around the substrate. The ...
... (1) An enzyme and a SUBSTRATE are in the same area. The substrate is the biological molecule that the enzyme will work on. (2) The enzyme grabs onto the substrate with a special area called the ACTIVE SITE. The active site is a specially shaped area of the enzyme that fits around the substrate. The ...
Enzymes
... (1) An enzyme and a SUBSTRATE are in the same area. The substrate is the biological molecule that the enzyme will work on. (2) The enzyme grabs onto the substrate with a special area called the ACTIVE SITE. The active site is a specially shaped area of the enzyme that fits around the substrate. The ...
... (1) An enzyme and a SUBSTRATE are in the same area. The substrate is the biological molecule that the enzyme will work on. (2) The enzyme grabs onto the substrate with a special area called the ACTIVE SITE. The active site is a specially shaped area of the enzyme that fits around the substrate. The ...
Enzymology - Lectures For UG-5
... terms of volume and value. The major component is proteases, but other and very different hydrolases are introduced to provide various benefits, such as the efficient removal of specific stains . To save energy, the temperature used in household laundering and automated dishwashers has been redu ...
... terms of volume and value. The major component is proteases, but other and very different hydrolases are introduced to provide various benefits, such as the efficient removal of specific stains . To save energy, the temperature used in household laundering and automated dishwashers has been redu ...
Document
... The purine ring structure is first built up to one or few atoms and then attached to ribose sugar to form nucleotides. ...
... The purine ring structure is first built up to one or few atoms and then attached to ribose sugar to form nucleotides. ...
Text 5- Pre and Post Reading Activities Enzymes
... called biotechnology. There are great benefits in using enzymes as catalysts to make products. They can be some 10,000 times more efficient than ordinary inorganic catalysts used in industry. One enzyme molecule can catalyse 10 million reactions in a single second! They also work at relatively low t ...
... called biotechnology. There are great benefits in using enzymes as catalysts to make products. They can be some 10,000 times more efficient than ordinary inorganic catalysts used in industry. One enzyme molecule can catalyse 10 million reactions in a single second! They also work at relatively low t ...
Enzymes
... (4) The enzyme lets go. Big idea - When the enzyme lets go, it returns to normal, ready to do another reaction. The substrate is no longer the same. The substrate is now called the PRODUCT. ...
... (4) The enzyme lets go. Big idea - When the enzyme lets go, it returns to normal, ready to do another reaction. The substrate is no longer the same. The substrate is now called the PRODUCT. ...
Chapter 3-5 Organic Chemistry
... concentration of a substrate • More substrate = more frequently access active sites of enzyme • There is a limit to this… • Sometimes all enzymes are “busy” • Enzyme is said to be “saturated” ...
... concentration of a substrate • More substrate = more frequently access active sites of enzyme • There is a limit to this… • Sometimes all enzymes are “busy” • Enzyme is said to be “saturated” ...
lab 3 enzymes F09
... The pH scale is logarithmic a difference of 1 unit represents a 10-fold change in concentration of hydrogen ions Solution of pH 3 is 10 times more acidic than a solution of pH 4 and 100 times more acidic than a solution of pH 5 ...
... The pH scale is logarithmic a difference of 1 unit represents a 10-fold change in concentration of hydrogen ions Solution of pH 3 is 10 times more acidic than a solution of pH 4 and 100 times more acidic than a solution of pH 5 ...
Enzymes and Protein Structure
... Why the Lock and Key Model is Useless - So the Enzyme and Substrate structures are complimentary… So I can predict the structure of a substrate or an inhibitor by wedging small molecules into the enzyme structure: Rational Drug Design ...
... Why the Lock and Key Model is Useless - So the Enzyme and Substrate structures are complimentary… So I can predict the structure of a substrate or an inhibitor by wedging small molecules into the enzyme structure: Rational Drug Design ...
Beta-lactamase

Beta-lactamases are enzymes (EC 3.5.2.6) produced by some bacteria that provide resistance to β-lactam antibiotics like penicillins, cephamycins, and carbapenems (ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a β-lactam. Through hydrolysis, the lactamase enzyme breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties.Beta-lactam antibiotics are typically used to treat a broad spectrum of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.Beta-lactamases produced by Gram-negative organisms are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment.