Enzymes - CynthiaJankowski
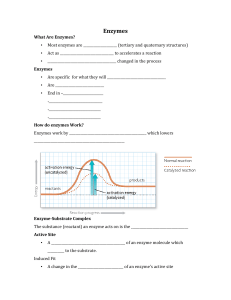
... an enzyme of a specific shape can fit the reactants of the reaction that it is catalyzing. • The reactant an enzyme works on is called a substrate. • The substrate binds to the active site to make the enzyme active. • Factors such as temperature, and pH affect enzyme activity. ...
... an enzyme of a specific shape can fit the reactants of the reaction that it is catalyzing. • The reactant an enzyme works on is called a substrate. • The substrate binds to the active site to make the enzyme active. • Factors such as temperature, and pH affect enzyme activity. ...
a study on cell culture model
... accumulation of glycosaminoglycans (GAG) in lysosomes. These usually fatal disorders are caused by mutations in genes coding for enzymes involved in degradation of GAGs. The deficiencies in activity of appropriate lysosomal enzymes result in various clinical phenotypes which include organomegaly, dy ...
... accumulation of glycosaminoglycans (GAG) in lysosomes. These usually fatal disorders are caused by mutations in genes coding for enzymes involved in degradation of GAGs. The deficiencies in activity of appropriate lysosomal enzymes result in various clinical phenotypes which include organomegaly, dy ...
How Antibiotics Work PPT
... • Where do they come from? • How does our antibiotic, streptomycin, kill bacteria? ...
... • Where do they come from? • How does our antibiotic, streptomycin, kill bacteria? ...
ENZYMES Worksheet 1. What is an enzyme?
... ______ 2. Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes. ______ 3. Sucrose and sucrase are both enzymes. ______ 4. Coenzymes are usually large globular proteins. ______ 5. Enzymes are not able to withstand temperatures higher than 50°C. ______ 6. Enzymes are able to reduce the activation energy of chemical re ...
... ______ 2. Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes. ______ 3. Sucrose and sucrase are both enzymes. ______ 4. Coenzymes are usually large globular proteins. ______ 5. Enzymes are not able to withstand temperatures higher than 50°C. ______ 6. Enzymes are able to reduce the activation energy of chemical re ...
Enzymes - Net Start Class
... the enzyme-substrate reaction; found on the right side of a chemical equation Optimum – the best conditions for a reaction to occur. In your body, optimum conditions are a pH of 7 and a temperature of 37oC ...
... the enzyme-substrate reaction; found on the right side of a chemical equation Optimum – the best conditions for a reaction to occur. In your body, optimum conditions are a pH of 7 and a temperature of 37oC ...
Name: Date: ______ Per: ______ Chemical Reactions and
... B Most enzymes can catalyze many different reactions. C An enzyme binds to a specific substrate (reactant) for the reaction catalyzed. D Enzymes are transported to specific substrates (reactants) by ribosomes. 14. Some snake venoms are harmful because they contain enzymes that destroy blood cells or ...
... B Most enzymes can catalyze many different reactions. C An enzyme binds to a specific substrate (reactant) for the reaction catalyzed. D Enzymes are transported to specific substrates (reactants) by ribosomes. 14. Some snake venoms are harmful because they contain enzymes that destroy blood cells or ...
Enzyme Foldable
... a. Draw and label the enzyme and the substrate. Explain the role of an enzyme in the body. 3. Enzyme Vocabulary a. These are the key words in the reading packet. 4. Graphs a. Draw and label the 4 graphs associated with enzymes. i. Temperature ii. PH iii. Concentrations iv. Activation Energy b. Write ...
... a. Draw and label the enzyme and the substrate. Explain the role of an enzyme in the body. 3. Enzyme Vocabulary a. These are the key words in the reading packet. 4. Graphs a. Draw and label the 4 graphs associated with enzymes. i. Temperature ii. PH iii. Concentrations iv. Activation Energy b. Write ...
Industrial enzyme production
... expensive and not always suitable for small-scale operations. It is economically prudent to feed the product locally and soon after it is produced. ...
... expensive and not always suitable for small-scale operations. It is economically prudent to feed the product locally and soon after it is produced. ...
Multi Drug Resistant Gram Negative Organisms (MDRO)
... As these bacteria are resistant to some, but not all, antibiotics, your Doctor will prescribe an antibiotic which will be active against your infection. You, or your relative, may be moved to a single room within the hospital for your treatment. This is to prevent the infection being spread to other ...
... As these bacteria are resistant to some, but not all, antibiotics, your Doctor will prescribe an antibiotic which will be active against your infection. You, or your relative, may be moved to a single room within the hospital for your treatment. This is to prevent the infection being spread to other ...
BioNews
... Simon Lee, a postgraduate researcher who is presenting his work at the Society for General Microbiology's autumn meeting in Nottingham, describes how the group identified up to nine different molecules in the insect tissues that were toxic to bacteria. These substances could lead to novel treatments ...
... Simon Lee, a postgraduate researcher who is presenting his work at the Society for General Microbiology's autumn meeting in Nottingham, describes how the group identified up to nine different molecules in the insect tissues that were toxic to bacteria. These substances could lead to novel treatments ...
Enzyme Fundamental Concepts Enzymes are biological catalysts
... 7. An increase in the concentration of enzyme will result in an increase in the rate of reaction. 8. An increase in the amount of substrate will most significantly result in an increase of the amount of product produced. 9. An increase in temperature will result in an increase in the rate of reactio ...
... 7. An increase in the concentration of enzyme will result in an increase in the rate of reaction. 8. An increase in the amount of substrate will most significantly result in an increase of the amount of product produced. 9. An increase in temperature will result in an increase in the rate of reactio ...
Document
... enzymes to control the functions of the cell. Enzymes must physically fit a specific substrate(s) to work properly. The place where a substrate fits an enzyme to be catalyzed is called the active site. Excess heat, a change in pH from neutral, etc. change the shape of enzymes and their active sites ...
... enzymes to control the functions of the cell. Enzymes must physically fit a specific substrate(s) to work properly. The place where a substrate fits an enzyme to be catalyzed is called the active site. Excess heat, a change in pH from neutral, etc. change the shape of enzymes and their active sites ...
Enzymes09
... ▫ b) Students know enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions without altering the reaction equilibrium and the activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic conditions, and the pH of the surroundings. ...
... ▫ b) Students know enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions without altering the reaction equilibrium and the activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic conditions, and the pH of the surroundings. ...
Enzymes - Science Geek
... CA Standard Students know enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions without altering the reaction equilibrium and the activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic conditions, and the pH of the surroundings. ...
... CA Standard Students know enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions without altering the reaction equilibrium and the activities of enzymes depend on the temperature, ionic conditions, and the pH of the surroundings. ...
Digestive Enzymes - World of Teaching
... them into a form that can be absorbed into the blood and used by cells. Enzymes make this possible. ...
... them into a form that can be absorbed into the blood and used by cells. Enzymes make this possible. ...
Enzymes - Cedar City
... thus lower the pH within the interceptor body to a point where the pH is at or below 4.0. Additionally, the importance of retention time within the interceptor cells can not be overstated. At a minimum and depending on site specific bacteria application rate, gallons per day (GPD), and flow to inter ...
... thus lower the pH within the interceptor body to a point where the pH is at or below 4.0. Additionally, the importance of retention time within the interceptor cells can not be overstated. At a minimum and depending on site specific bacteria application rate, gallons per day (GPD), and flow to inter ...
Beta-lactamase

Beta-lactamases are enzymes (EC 3.5.2.6) produced by some bacteria that provide resistance to β-lactam antibiotics like penicillins, cephamycins, and carbapenems (ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a β-lactam. Through hydrolysis, the lactamase enzyme breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties.Beta-lactam antibiotics are typically used to treat a broad spectrum of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.Beta-lactamases produced by Gram-negative organisms are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment.