* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
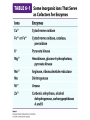
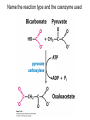
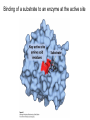
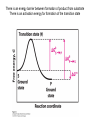
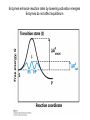
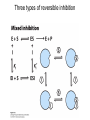
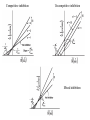
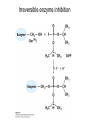
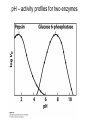
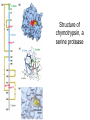
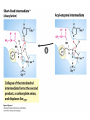
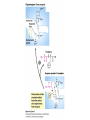
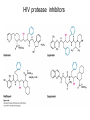
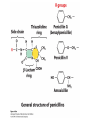
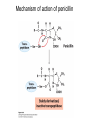
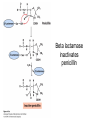
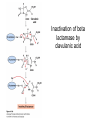
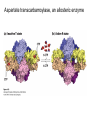
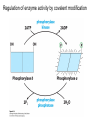
David L. Nelson and Michael M. Cox LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY Sixth Edition CHAPTER 6 Enzymes © 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Name the reaction type and the coenzyme used Binding of a substrate to an enzyme at the active site There is an energy barrier between formation of product from substrate There is an activation energy for formation of the transition state Enzymes enhance reaction rates by lowering activation energies Enzymes do not affect equilibrium How a catalyst circumvents unfavorable charge development during cleavage of an amide Amino acids in general acid-base catalysis Effect of substrate concentration on the initial velocity of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction Michaelis-Menten plot Double-reciprocal or Lineweaver-Burk plot kcat = Vmax / [E]total kcat has units of reciprocal time kcat / Km is a measure of catalytic efficiency Many enzymes catalyze reactions with two or more substrates Three types of reversible inhibition Three types of reversible inhibition Three types of reversible inhibition Competitive inhibition Uncompetitive inhibition Mixed inhibition Molecules that are transition state analogs are effective reversible competitive inhibitors Irreversible enzyme inhibition pH – activity profiles for two enzymes Structure of chymotrypsin, a serine protease Mechanism of action of HIV protease HIV protease inhibitors The transpeptidase reaction Mechanism of action of penicillin Beta lactamase inactivates penicillin Inactivation of beta lactamase by clavulanic acid Subunit interactions in an allosteric enzyme, and interactions with inhibitors and activators Aspartate transcarbamoylase, an allosteric enzyme Regulation of enzyme activity by covalent modification Regulation of enzyme activity by covalent modification Regulation of enzyme activity by proteolytic cleavage Example: Activation of zymogens, inactive precursors of proteases