* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 5: Enzymes
Inositol-trisphosphate 3-kinase wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Transferase wikipedia , lookup
Lactoylglutathione lyase wikipedia , lookup
Beta-lactamase wikipedia , lookup
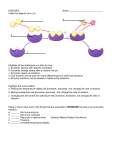
Lesson 5: Enzymes 1 Competencies 1. describe the components of an enzyme – (STEM_BIO11/12-Ii-j-17) 2. determine how factors such as pH, temperature, and substrate affect enzyme activity- (STEM_BIO11/12 -Ii-j19) 2 Youtube Clip: Fun Facts About Enzyme Guide Questions: 1. What are enzymes? 2. What functions of enzymes in our body? 3. What are the types of enzymes? 4. How does enzyme work? 3 What Are Enzymes? • Most enzymes are Proteins (tertiary and quaternary structures) • Act as Catalyst to accelerates a reaction • Not permanently changed in the process 4 Enzymes • Are specific for what they will catalyze • Are Reusable • End in –ase -Sucrase -Lactase -Maltase 5 How do enzymes Work? Enzymes work by weakening bonds which lowers activation energy 6 Enzymes Without Enzyme With Enzyme Free Energy Free energy of activation Reactants Products Progress of the reaction 7 8 Enzyme-Substrate Complex The substance (reactant) an enzyme acts on is the substrate Substrate Joins Enzyme 9 Active Site • A restricted region of an enzyme molecule which binds to the substrate. Active Site Substrate Enzyme 10 Induced Fit • A change in the shape of an enzyme’s active site • Induced by the substrate 11 Induced Fit • A change in the configuration of an enzyme’s active site (H+ and ionic bonds are involved). • Induced by the substrate. Active Site substrate Enzyme induced fit 12 What Affects Enzyme Activity? • Three factors: 1. Environmental Conditions 2. Cofactors and Coenzymes 3. Enzyme Inhibitors 13 1. Environmental Conditions 1. Extreme Temperature are the most dangerous - high temps may denature (unfold) the enzyme. 2. pH (most like 6 - 8 pH near neutral) 3. Ionic concentration (salt ions) 14 2. Cofactors and Coenzymes • Inorganic substances (zinc, iron) and vitamins (respectively) are sometimes need for proper enzymatic activity. • Example: Iron must be present in the quaternary structure - hemoglobin in order for it to pick up oxygen. 15 Two examples of Enzyme Inhibitors a. Competitive inhibitors: are chemicals that resemble an enzyme’s normal substrate and compete with it for the active site. Substrate Competitive inhibitor Enzyme 16 Inhibitors b. Noncompetitive inhibitors: Inhibitors that do not enter the active site, but bind to another part of the enzyme causing the enzyme to change its shape, which in turn alters the active site. Substrate active site altered Enzyme Noncompetitive Inhibitor 17 Enzymes are used all over your body! http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Digestive_system_diagram_en.svg Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2009 President and Fellows of Harvard College http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6f/Major_digestive_enzymes.png/750px-Major_digestive_enzymes.png Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2009 President and Fellows of Harvard College Application: Sketch an enzyme 20