* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enzyme Activity - Model High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
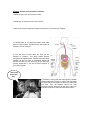
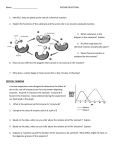
Enzyme Puzzle Activity Purpose: In this activity, you will make up your own enzyme-substrate complex. Substrates and enzymes work together like puzzles. A substrate is a chemical that can bond onto a specific enzyme. Only one type of enzyme with lock onto the active site of the substrate chemical (like a puzzle piece). Thus, they are very specific.When the reaction occurs, products are made from the substrate. The enzyme is not used in the reaction, and will then continue to work on another substrate molecule. Keep in mind that every enzyme has its optimum conditions. 1) 3) 2) *Key Definitions: Label the diagram above using the key terms *may be used more than once -Enzyme: A protein that speeds up reaction rates by lowering the activation energy of the reaction (less energy needed to make the reaction go!) They are not used up in the reaction. Enzymes are made up of a chain of amino acids. -Substrate: The molecule that the enzyme latches onto. AKA Reactants -Active Site: bonding area of the enzyme to the substrate “lock and key” -Products: The end result of the reaction: could be synthesis or decomposition Materials: -Different colors of construction paper -scissors -markers -glue sticks Procedure: 1) Using the paper provided, you will make an enzyme puzzle. You need to create a substrate, an enzyme with a matching active site, and reactants that are formed after the enzyme speeds up the reaction. If you have problems, refer to page 76 in your biology book. 2) You will have to name your enzyme. Usually, enzymes end in ‘ase.” For example, catalase is an enzyme used frequently in the lab. Write the enzymes name on the paper. 3) Then, make sure to label each piece of your puzzle. If for example you have the substrate piece, label it SUBSTRATE. All pieces need to be labeled in order to get full credit. 5) Lastly, answer the analysis questions below using complete sentences. Analysis: Answer using complete sentences. 1) What did you name your enzyme? Why? 2) What type of macromolecule is an enzyme? 3) Why is the enzyme-substrate complex compared to a “lock and key?” Explain. 5) Thinking back to our chemistry section, what other types of environmental conditions may slow down an enzyme? Give an example. 6) You are able to break down the food you eat because of enzymes. Your body makes enzyme throughout the digestive tract. Doctors say that it takes between 24 and 72 hours to completely digest and excrete food that you eat. How long do you think this process would take if you did not have enzymes in your body? Explain. “This could be you one day” 7) Penicillin is a drug that was discovered by Scottish scientist Alexander Fleming in 1928. This drug stops enzymes that are necessary for bacteria to make their cell walls. Thus, the bacteria cannot live. How important was the discovery of this drug? Have you ever taken penicillin? Was it effective (did it work)?