enzyme
... Enzymes are proteins (made up of amino acids) Enzymes function by lowering the activation energy of reactions. Enzymes can act rapidly and can cause chemicals to act 107 times faster than without the enzyme present. There are over 2000 known enzymes, each of which is involved with one specific chemi ...
... Enzymes are proteins (made up of amino acids) Enzymes function by lowering the activation energy of reactions. Enzymes can act rapidly and can cause chemicals to act 107 times faster than without the enzyme present. There are over 2000 known enzymes, each of which is involved with one specific chemi ...
enzymes powerpoint - Pasadena High School
... occur spontaneously, but at very slow rates. Catalysts are substances that speed up reactions without being permanently altered. No catalyst makes a reaction occur that cannot otherwise occur quick enough for life. Most biological catalysts are proteins (enzymes); a few are RNA molecules (ribozymes) ...
... occur spontaneously, but at very slow rates. Catalysts are substances that speed up reactions without being permanently altered. No catalyst makes a reaction occur that cannot otherwise occur quick enough for life. Most biological catalysts are proteins (enzymes); a few are RNA molecules (ribozymes) ...
Enzyme Notes
... our body happen at a faster rate • A chemical that speeds up a reaction is called a catalyst. • Enzymes are often called biological catalysts. • http://www.lpscience.fatcow.com/jwanama ker/animations/Enzyme%20activity.html ...
... our body happen at a faster rate • A chemical that speeds up a reaction is called a catalyst. • Enzymes are often called biological catalysts. • http://www.lpscience.fatcow.com/jwanama ker/animations/Enzyme%20activity.html ...
Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Notes
... • Catalyst – a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy. • Enzymes – are proteins that act as a biological catalyst. ...
... • Catalyst – a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy. • Enzymes – are proteins that act as a biological catalyst. ...
BIOLOGY REVIEW:
... 21. What does denatured mean? When enzymes are destroyed after they have changed shape so much that they are no longer effective. 22. Describe how an enzyme is specific. Only one enzyme is made for a particular chemical reaction. 23. Describe the lock and key hypothesis. Draw and label an example. A ...
... 21. What does denatured mean? When enzymes are destroyed after they have changed shape so much that they are no longer effective. 22. Describe how an enzyme is specific. Only one enzyme is made for a particular chemical reaction. 23. Describe the lock and key hypothesis. Draw and label an example. A ...
Avrama Blackwell George Mason University
... •Keep track of molecule quantities and concentrations ...
... •Keep track of molecule quantities and concentrations ...
Organic chem and enzyme review game
... True or False: 1. enzymes are not changed by the reaction they speed up 2. enzymes cannot be recycled and reused many times. 3. Enzymes are specific to the reactions that they catalyze. 4. One enzyme can catalyze reactions at a variety of pH and temperature levels. 5. The substrate of a reaction is ...
... True or False: 1. enzymes are not changed by the reaction they speed up 2. enzymes cannot be recycled and reused many times. 3. Enzymes are specific to the reactions that they catalyze. 4. One enzyme can catalyze reactions at a variety of pH and temperature levels. 5. The substrate of a reaction is ...
Enzymes
... 2. Cofactors and Coenzymes • Inorganic substances (zinc, iron) and vitamins (respectively) are sometimes need for proper enzymatic activity. • Example: Iron must be present in hemoglobin in order for it to pick up oxygen. ...
... 2. Cofactors and Coenzymes • Inorganic substances (zinc, iron) and vitamins (respectively) are sometimes need for proper enzymatic activity. • Example: Iron must be present in hemoglobin in order for it to pick up oxygen. ...
What is an Enzyme? How Do Enzymes Work? Chemistry of Life
... An enzyme is a “matchmaker” – it brings chemicals together so the reaction will happen more quickly. Different enzymes have different shapes and affect different chemical reactions. The specific 3-D shape of each enzyme is ideally suited to bring together two specific molecules, line them up, and in ...
... An enzyme is a “matchmaker” – it brings chemicals together so the reaction will happen more quickly. Different enzymes have different shapes and affect different chemical reactions. The specific 3-D shape of each enzyme is ideally suited to bring together two specific molecules, line them up, and in ...
logcsscibap_2_4_2_c_..
... Are the shapes of the reactant and active site similar or different? Explain your answer. (2 marks) ...
... Are the shapes of the reactant and active site similar or different? Explain your answer. (2 marks) ...
Document
... What is the chemical formula for a carbohydrate? _____________is broken down in cellular respiration and turned into ______ that gives cells the energy they need. Name this process.______________ ____________________ Carbohydrates aren’t always sugary. What is the name of the carbohydrate that plant ...
... What is the chemical formula for a carbohydrate? _____________is broken down in cellular respiration and turned into ______ that gives cells the energy they need. Name this process.______________ ____________________ Carbohydrates aren’t always sugary. What is the name of the carbohydrate that plant ...
2. Enzymes
... *Allosteric Modulators - these bind away from active site but in doing so alter the shape of the active site. This can increase or decrease enzyme affinity for substrates. Covalent Modulators - bind covalently to enzyme away from the active site, change the shape, thus function of the enzyme. e.g., ...
... *Allosteric Modulators - these bind away from active site but in doing so alter the shape of the active site. This can increase or decrease enzyme affinity for substrates. Covalent Modulators - bind covalently to enzyme away from the active site, change the shape, thus function of the enzyme. e.g., ...
Enzyme Activity - Model High School
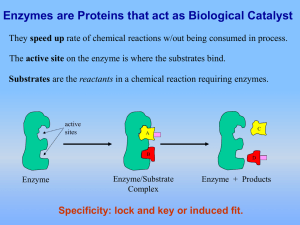
... and enzymes work together like puzzles. A substrate is a chemical that can bond onto a specific enzyme. Only one type of enzyme with lock onto the active site of the substrate chemical (like a puzzle piece). Thus, they are very specific.When the reaction occurs, products are made from the substrate. ...
... and enzymes work together like puzzles. A substrate is a chemical that can bond onto a specific enzyme. Only one type of enzyme with lock onto the active site of the substrate chemical (like a puzzle piece). Thus, they are very specific.When the reaction occurs, products are made from the substrate. ...
Enzymes
... We've been talking about the kind of reactions that happen in your body (DNA, Protein synthesis, Cellular respiration etc.) and how molecules can change. You should know that It doesn't happen on its own. If you leave a blob of protein in a petri dish will it just break down to the amino acids? No. ...
... We've been talking about the kind of reactions that happen in your body (DNA, Protein synthesis, Cellular respiration etc.) and how molecules can change. You should know that It doesn't happen on its own. If you leave a blob of protein in a petri dish will it just break down to the amino acids? No. ...
Enzymes worksheet
... We've been talking about the kind of reactions that happen in your body (DNA, Protein synthesis, Cellular respiration etc.) and how molecules can change. You should know that It doesn't happen on its own. If you leave a blob of protein in a petri dish will it just break down to the amino acids? No. ...
... We've been talking about the kind of reactions that happen in your body (DNA, Protein synthesis, Cellular respiration etc.) and how molecules can change. You should know that It doesn't happen on its own. If you leave a blob of protein in a petri dish will it just break down to the amino acids? No. ...
Enzymes
... We've been talking about the kind of reactions that happen in your body (DNA, Protein synthesis, Cellular respiration etc.) and how molecules can change. You should know that It doesn't happen on its own. If you leave a blob of protein in a petri dish will it just break down to the amino acids? No. ...
... We've been talking about the kind of reactions that happen in your body (DNA, Protein synthesis, Cellular respiration etc.) and how molecules can change. You should know that It doesn't happen on its own. If you leave a blob of protein in a petri dish will it just break down to the amino acids? No. ...
This syllabus was adapted from Introduction to Biochemistry I taught
... Read the following sentences and choose the right choice: 1. Type of regulation of enzyme activity occurs when the same enzyme appears in different forms in different tissues (a) Proenzyme (b) allosteric enzyme (c) Isoenzyme (d) Zymogens 2. Binding of 2,3-bisposphoglycerate to deoxyhemoglobin will ...
... Read the following sentences and choose the right choice: 1. Type of regulation of enzyme activity occurs when the same enzyme appears in different forms in different tissues (a) Proenzyme (b) allosteric enzyme (c) Isoenzyme (d) Zymogens 2. Binding of 2,3-bisposphoglycerate to deoxyhemoglobin will ...
Enzyme Puzzle Activity
... Enzyme Puzzle Activity Purpose: In this activity, you will make up your own enzyme-substrate complex. Substrates and enzymes work together like puzzles. A substrate is a chemical that can bond onto a specific enzyme. Only one type of enzyme with lock onto the active site of the substrate chemical (l ...
... Enzyme Puzzle Activity Purpose: In this activity, you will make up your own enzyme-substrate complex. Substrates and enzymes work together like puzzles. A substrate is a chemical that can bond onto a specific enzyme. Only one type of enzyme with lock onto the active site of the substrate chemical (l ...
KEY CONCEPT Enzymes are catalysts for chemical
... • Disruptions in homeostasis can prevent enzymes from functioning. – Enzymes function best in a small range of conditions. – Changes in temperature and pH can break hydrogen bonds. – An enzyme’s function depends on its structure. ...
... • Disruptions in homeostasis can prevent enzymes from functioning. – Enzymes function best in a small range of conditions. – Changes in temperature and pH can break hydrogen bonds. – An enzyme’s function depends on its structure. ...
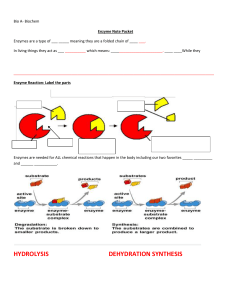
Bio A- Biochem Enzyme Note Packet Enzymes are a type of ___
... Coenzyme: organic molecules (like vitamins) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme o Organic means??? _CONTAINS C and H (and since it is found in living things..Oxygen! _____ Cofactors: inorganic molecules (like Zn, Cu) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme Both coenzymes and cofactors bind to ...
... Coenzyme: organic molecules (like vitamins) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme o Organic means??? _CONTAINS C and H (and since it is found in living things..Oxygen! _____ Cofactors: inorganic molecules (like Zn, Cu) that help a substrate bind to its enzyme Both coenzymes and cofactors bind to ...
Enzyme Activity
... are many active sites that are not occupied. This means that the reaction rate is low. When more substrate molecules are added, more enzymesubstrate complexes can be formed. As there are more active sites, and the rate of reaction increases. Eventually, increasing the substrate concentration yet fur ...
... are many active sites that are not occupied. This means that the reaction rate is low. When more substrate molecules are added, more enzymesubstrate complexes can be formed. As there are more active sites, and the rate of reaction increases. Eventually, increasing the substrate concentration yet fur ...
enzymes - kristashunkwiler
... • Non-protein molecules that help enzymes function. • Bind to active site to enhance enzymatic reactions or can bind to the substrate. • Cofactors may be inorganic metals such as zinc, iron, or copper. • Coenzymes are organic cofactors (e.g. vitamins) ...
... • Non-protein molecules that help enzymes function. • Bind to active site to enhance enzymatic reactions or can bind to the substrate. • Cofactors may be inorganic metals such as zinc, iron, or copper. • Coenzymes are organic cofactors (e.g. vitamins) ...
Enzyme kinetics

Enzyme kinetics is the study of the chemical reactions that are catalysed by enzymes. In enzyme kinetics, the reaction rate is measured and the effects of varying the conditions of the reaction are investigated. Studying an enzyme's kinetics in this way can reveal the catalytic mechanism of this enzyme, its role in metabolism, how its activity is controlled, and how a drug or an agonist might inhibit the enzyme.Enzymes are usually protein molecules that manipulate other molecules — the enzymes' substrates. These target molecules bind to an enzyme's active site and are transformed into products through a series of steps known as the enzymatic mechanismE + S <——> ES <——> ES*< ——> EP <——> E + P. These mechanisms can be divided into single-substrate and multiple-substrate mechanisms. Kinetic studies on enzymes that only bind one substrate, such as triosephosphate isomerase, aim to measure the affinity with which the enzyme binds this substrate and the turnover rate. Some other examples of enzymes are phosphofructokinase and hexokinase, both of which are important for cellular respiration (glycolysis).When enzymes bind multiple substrates, such as dihydrofolate reductase (shown right), enzyme kinetics can also show the sequence in which these substrates bind and the sequence in which products are released. An example of enzymes that bind a single substrate and release multiple products are proteases, which cleave one protein substrate into two polypeptide products. Others join two substrates together, such as DNA polymerase linking a nucleotide to DNA. Although these mechanisms are often a complex series of steps, there is typically one rate-determining step that determines the overall kinetics. This rate-determining step may be a chemical reaction or a conformational change of the enzyme or substrates, such as those involved in the release of product(s) from the enzyme.Knowledge of the enzyme's structure is helpful in interpreting kinetic data. For example, the structure can suggest how substrates and products bind during catalysis; what changes occur during the reaction; and even the role of particular amino acid residues in the mechanism. Some enzymes change shape significantly during the mechanism; in such cases, it is helpful to determine the enzyme structure with and without bound substrate analogues that do not undergo the enzymatic reaction.Not all biological catalysts are protein enzymes; RNA-based catalysts such as ribozymes and ribosomes are essential to many cellular functions, such as RNA splicing and translation. The main difference between ribozymes and enzymes is that RNA catalysts are composed of nucleotides, whereas enzymes are composed of amino acids. Ribozymes also perform a more limited set of reactions, although their reaction mechanisms and kinetics can be analysed and classified by the same methods.