* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enzyme Substrate Reactions
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Beta-lactamase wikipedia , lookup
Lactoylglutathione lyase wikipedia , lookup
Transferase wikipedia , lookup
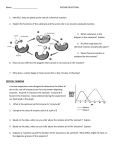
Biology Name _______________________ Enzyme Substrate Reactions Directions: Examine the shapes listed below. Try to match which substrate(s) fits into which enzyme. Draw 2 reactions showing the enzyme, its matching substrate, the enzyme-substrate complex, and the products. Recall how enzymes reactions proceed: E + S → ES complex → Products Enzymes Substrates A C Label all reactions. Reaction 1: Reaction 2: B D Questions: 1) Were there any substrates that fit more than one enzyme? _____________________ What can you conclude from this? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 2) What type of organic molecule is an enzyme? ______________________ 3) What two things can happen to substrates after they are acted on by an enzyme? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 4) What type of reaction is Reaction 1? ________________ Reaction 2: _________________ 5) What happens to an enzyme after a reaction takes place? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 6) Are enzymes usually bigger or smaller than the substrate? _________________________ 7) Assume that substrate C is a disaccharide, what are the products? ______________________ 8) Assume that substrate A and D are peptides, what is the product? ________________________ 9) How can you tell an enzyme by looking at its name? ________________________ 10) Enzymes are usually named for the substrates they act on. Give an example. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ Biology Name ___________________________ Homework: Enzymes 1. Which of the following enzymes would digest a fat? (1.) sucrase (2.) fatase (3.) protease (4.) lipase 2. At high temperatures, the rate of enzyme action decreases because the increased heat (1.) increases the concentration of the enzyme (3.) alters the active site of the enzyme (2.) changes the pH of the system (4.) neutralizes the acids and bases 3. Enzymes influence chemical reactions in living systems by (1.) providing the substrate required for the reaction to occur (2.) affecting the rate at which reactions occur (3.) absorbing water released when polymers are formed (4.) combining with excess hydrogen to form gaseous wastes 4. Which group of organic compounds includes the enzymes? (1.) proteins (3.) carbohydrates (2.) starches (4.) lipids 5. The "lock and key hypothesis" attempts to explain the mechanism of (1.) polarity of water (2.) reaction rate (3.) sharing of electrons (4.) enzyme specificity 6. Any substance that is acted upon by an enzyme is called a(n) (1.) coenzyme (2.) substrate (3.) vitamin 7. At about 00 C most enzymes are (1.) inactive (2.) active (3.) destroyed (4.) polypeptide (4.) replicated 8. Vitamins are essential to the survival of organisms because vitamins usually function as (1.) substrates (2.) nucleic acids (3.) coenzymes (4.) nucleotides 9. Which chemical is classified as an enzyme? (1.) galactose (2.) lipid (3.) protease (4.) manganese dioxide 10. Which element is present in maltase, but not in maltose? (1.) carbon (2.) hydrogen (3.) oxygen (4.) nitrogen 11. Salivary amylase is an enzyme in humans that breaks down starch. The optimum pH for this reaction is 6.7. The rate of this reaction would not be affected by (1.) maintaining the pH of the reaction at 6.7 (3.) substrate concentration (2.) decreasing the temperature of the reaction by 5oC (4.) enzyme concentration 12. A certain enzyme will hydrolyze egg white but not starch. Which statement best explains this observation? (1.) Starch molecules are too large to be hydrolyzed. (2.) Enzyme molecules are specific in their actions. (3.) Egg white acts as a coenzyme for hydrolysis. (4.) Starch is composed of amino acids. 13. Which environmental condition would most likely have the LEAST effect on the rate of enzyme controlled hydrolytic reactions in humans? (1.) the pH of the solution (2.) the temperature of the solution (3.) the amount of enzyme present (4.) the amount of light present 14. Which statement best expresses the information represented in the graph shown? (1.) The action of enzymes varies with pH. (2.) A pH of 7 provides the optimum environment for digestive enzymes (3.) Gastric juice is active at a pH extending from 0 to 12. (4.) Acids have a pH greater than 7. 15. The effect of temperature on the relative rate of action of an enzyme is represented in the graph below. The optimum temperature for the action of this enzyme is approximately (1.) 15 C (2.) 22 C (3.) 37 C (4.) 50 C 16. Lipase, maltase, and protease are members of a group of catalysts known as (1.) hormones (2.) carbohydrates (3.) lipids (4.) enzymes 17. Here are of some stages of an enzyme-controlled reaction . An enzyme-substrate complex is represented by diagram (1.) A (2.) B (3.) C (4.) D Use the information provided to answer questions 18 and 19 which follow. 18. The diagram below represents three steps in the hydrolysis of a molecule of sucrose. In this diagram, structure X is most likely (1.) a molecule of oxygen (2.) the end product (3.) an organic catalyst (4.) the substrate 19. List at least two reasons supporting your answer in question # 18. 1. _______________________________________________________________________________ 2. _______________________________________________________________________________ 1. Describe the effect of increasing pH on the rate of an enzymatic reaction. -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain the effect of increasing pH on the rate of an enzymatic reaction. -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Describe the effect of increasing temperature on the rate of an enzymatic reaction. -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Explain the effect of increasing temperature on the rate of an enzymatic reaction. -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ -__________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________