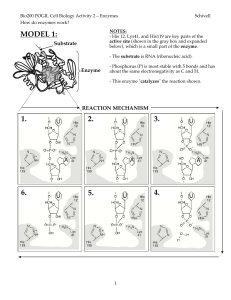
Class3 POGIL Enzyme Mechanics Worksheet
... b. Which mutant helps to answer this question? ________ 14. When the transfer of a proton between the enzyme and substrate is prevented, is the reaction rate changed slightly or dramatically? __________ 15. Even if an R-group (that is part of the active site) does not normally accept or donate proto ...
... b. Which mutant helps to answer this question? ________ 14. When the transfer of a proton between the enzyme and substrate is prevented, is the reaction rate changed slightly or dramatically? __________ 15. Even if an R-group (that is part of the active site) does not normally accept or donate proto ...
Enzymes - Guided Notes - Flip-Flop
... things that speed up chemical reactions. *2*Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy (hillspeed bump), so that less energy is needed to start the reaction. *3*Enzymes are NOT “used up” or altered by the reaction – they are reused/recycled over and over. ...
... things that speed up chemical reactions. *2*Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy (hillspeed bump), so that less energy is needed to start the reaction. *3*Enzymes are NOT “used up” or altered by the reaction – they are reused/recycled over and over. ...
Characterization of α-galactosidase belonging to family-4 glycoside hidrolases Bacillus halodurans
... expressed in Escherichia coli. The melA gene consists of 1305 nucleotides encoding a protein of 434 amino acids with a predicted molecular weight of 49,761. It was assigned to family 4 of glycoside hidrolases. Almost all of the enzyme was produced as inclusion bodies at 37oC. In order to reduce the ...
... expressed in Escherichia coli. The melA gene consists of 1305 nucleotides encoding a protein of 434 amino acids with a predicted molecular weight of 49,761. It was assigned to family 4 of glycoside hidrolases. Almost all of the enzyme was produced as inclusion bodies at 37oC. In order to reduce the ...
lab 3 enzymes F09
... a difference of 1 unit represents a 10-fold change in concentration of hydrogen ions Solution of pH 3 is 10 times more acidic than a solution of pH 4 and 100 times more acidic than a solution of pH 5 ...
... a difference of 1 unit represents a 10-fold change in concentration of hydrogen ions Solution of pH 3 is 10 times more acidic than a solution of pH 4 and 100 times more acidic than a solution of pH 5 ...
PBHS AP Biology Lab 2
... illustrate the themes of this class. These labs are very important as the AP Test will have least one essay question and several multiple choice questions based on these labs. ...
... illustrate the themes of this class. These labs are very important as the AP Test will have least one essay question and several multiple choice questions based on these labs. ...
How Enzymes Work - Liberty Union High School District
... 2) Chemical bonds are formed or broken in the substrate 3) Products of substrate are released 4) Enzyme goes back and grabs another substrate, and continues this process until the substrate is all broken down ...
... 2) Chemical bonds are formed or broken in the substrate 3) Products of substrate are released 4) Enzyme goes back and grabs another substrate, and continues this process until the substrate is all broken down ...
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Enzymes
... Different enzymes have different ideal pH and temperature conditions. If the pH or temperature is extreme for a particular enzyme, it can even denature an enzyme, which can prevent it from binding and acting on its substrate. For the following two scenarios, name the variable (temperature or pH) tha ...
... Different enzymes have different ideal pH and temperature conditions. If the pH or temperature is extreme for a particular enzyme, it can even denature an enzyme, which can prevent it from binding and acting on its substrate. For the following two scenarios, name the variable (temperature or pH) tha ...
E = enzyme, S= substrate • The key does not fit the lock quite
... with a hinge. Some of the amino acids required for catalysis are in one domain and some in the other. When the hinge closes these amino acids come in contact with each other and the substrates, phosphoglycerate and ADP . ...
... with a hinge. Some of the amino acids required for catalysis are in one domain and some in the other. When the hinge closes these amino acids come in contact with each other and the substrates, phosphoglycerate and ADP . ...
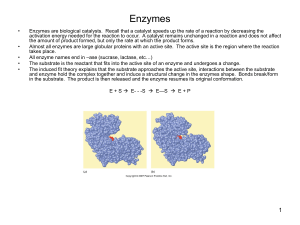
Enzymes
... The induced fit theory explains that the substrate approaches the active site, interactions between the substrate and enzyme hold the complex together and induce a structural change in the enzymes shape. Bonds break/form in the substrate. The product is then released and the enzyme resumes its origi ...
... The induced fit theory explains that the substrate approaches the active site, interactions between the substrate and enzyme hold the complex together and induce a structural change in the enzymes shape. Bonds break/form in the substrate. The product is then released and the enzyme resumes its origi ...
Basic Enzyme Kinetics
... Figure 3: Relationship between the rate of reaction for a cooperative enzyme. The reasons for this behavior is often related to the multimeric (multiple subunits) nature of regulated enzymes. Thus when a substrate binds to one of the subunits, a conformational change occurs which increases the bindi ...
... Figure 3: Relationship between the rate of reaction for a cooperative enzyme. The reasons for this behavior is often related to the multimeric (multiple subunits) nature of regulated enzymes. Thus when a substrate binds to one of the subunits, a conformational change occurs which increases the bindi ...
DO NOW Monday 2/12
... • Enzymes lower the activation energy of a chemical reaction. • Activation energy is the amount of energy it takes for a reaction to “go” ...
... • Enzymes lower the activation energy of a chemical reaction. • Activation energy is the amount of energy it takes for a reaction to “go” ...
Chapter 16.6 & 16.7 Enzymes & Enzyme Actions
... Increases chance of substrate molecules fitting into the active sites of enzyme molecules More rapid formation of enzyme-substrate complexes Increase in formation of products ...
... Increases chance of substrate molecules fitting into the active sites of enzyme molecules More rapid formation of enzyme-substrate complexes Increase in formation of products ...
ENZYMES MAKE THE WORLD GO `ROUND
... everywhere in life. Catalysts are also used in the human body in order to make very difficult reactions happen. They help very large molecules combine. There is another interesting fact about catalysts. Catalysts lower the activation energy required for a reaction to occur. With the activation energ ...
... everywhere in life. Catalysts are also used in the human body in order to make very difficult reactions happen. They help very large molecules combine. There is another interesting fact about catalysts. Catalysts lower the activation energy required for a reaction to occur. With the activation energ ...
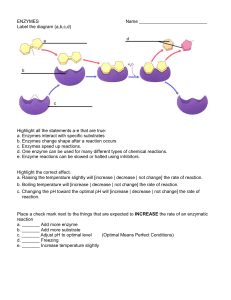
ENZYMES
... a. _______ Add more enzyme b. _______ Add more substrate c. _______ Adjust pH to optimal level (Optimal Means Perfect Conditions) d. _______ Freezing e. _______ Increase temperature slightly ...
... a. _______ Add more enzyme b. _______ Add more substrate c. _______ Adjust pH to optimal level (Optimal Means Perfect Conditions) d. _______ Freezing e. _______ Increase temperature slightly ...
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... • are most active at an optimum temperature (usually 37°C in humans). • show little activity at low temperatures. • lose activity at high temperatures as denaturation occurs. ...
... • are most active at an optimum temperature (usually 37°C in humans). • show little activity at low temperatures. • lose activity at high temperatures as denaturation occurs. ...
3.2.1 enzymes - Haiku Learning : Login
... – found in vitamin B, milk, meat – Function: reactions in ...
... – found in vitamin B, milk, meat – Function: reactions in ...
Ecotek Students Improve Protocol for the Enzyme Hydrolysis of Starch
... An enzyme is made up of a group of proteins that perform different biochemical functions. They serve as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions. An enzyme is formed by stringing together between 100 and 1,000 amino acids. The shape of an enzyme allows it to carry out specific chemical reactions. En ...
... An enzyme is made up of a group of proteins that perform different biochemical functions. They serve as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions. An enzyme is formed by stringing together between 100 and 1,000 amino acids. The shape of an enzyme allows it to carry out specific chemical reactions. En ...
Establishing Structure-Activity Relationship of an Enzyme with
... One of the most important challenges in biology is to identify the function of a protein that a gene encodes. As a result of structural genomics project a large number of protein structures are deposited in protein data bank (PDB) with no functional information. Deciphering the exact function of the ...
... One of the most important challenges in biology is to identify the function of a protein that a gene encodes. As a result of structural genomics project a large number of protein structures are deposited in protein data bank (PDB) with no functional information. Deciphering the exact function of the ...
Cardiff International School Dhaka (CISD) Lost Class Make Up
... Q2. (a) At temperatures between 0o C and about 40 o C the rate of enzyme activity increases with temperature. Enzyme activity decreases markedly above 40 o C. (b) As temperature increases the molecules move faster, a greater proportion of the molecules collide etc. (c) Extremes of pH denature enzyme ...
... Q2. (a) At temperatures between 0o C and about 40 o C the rate of enzyme activity increases with temperature. Enzyme activity decreases markedly above 40 o C. (b) As temperature increases the molecules move faster, a greater proportion of the molecules collide etc. (c) Extremes of pH denature enzyme ...
Enzymes
... 5. Molecules diffuse from an area of [high] [low] OR [low] [high]? (note [ ] = concentration) 6. What is an enzyme? 7. What do enzymes work on? And where? 8. A solution has 85% water & 15% sugar while a cell has 97% water and 3% sugar. Which is hypertonic (the solution or the cell)? What directi ...
... 5. Molecules diffuse from an area of [high] [low] OR [low] [high]? (note [ ] = concentration) 6. What is an enzyme? 7. What do enzymes work on? And where? 8. A solution has 85% water & 15% sugar while a cell has 97% water and 3% sugar. Which is hypertonic (the solution or the cell)? What directi ...
Name: Date: Block: ______ Objective: IWBAT summarize how
... Enzymes are proteins. All proteins have a specific shape based on their sequence of amino acids. Part of the enzyme’s shape is an active site. The substrates bind to this active site, reducing the activation energy, and allowing the chemical reaction to occur. The lock-and-key model illustrates this ...
... Enzymes are proteins. All proteins have a specific shape based on their sequence of amino acids. Part of the enzyme’s shape is an active site. The substrates bind to this active site, reducing the activation energy, and allowing the chemical reaction to occur. The lock-and-key model illustrates this ...
1. Vmax, the maximum velocity, of an enzyme-catalyzed
... a. the rate observed when all enzyme active sites are saturated with substrate. b. independent of the amount of enzyme present. c. the rate observed at the highest substrate concentration that can be experimentally obtained. d. the initial rate observed at very low substrate concentrations. 2. When ...
... a. the rate observed when all enzyme active sites are saturated with substrate. b. independent of the amount of enzyme present. c. the rate observed at the highest substrate concentration that can be experimentally obtained. d. the initial rate observed at very low substrate concentrations. 2. When ...
(most also have sulfur) The monomers of proteins are amino acids.
... carboxyl group, and a variable R-group. ...
... carboxyl group, and a variable R-group. ...
Enzyme kinetics

Enzyme kinetics is the study of the chemical reactions that are catalysed by enzymes. In enzyme kinetics, the reaction rate is measured and the effects of varying the conditions of the reaction are investigated. Studying an enzyme's kinetics in this way can reveal the catalytic mechanism of this enzyme, its role in metabolism, how its activity is controlled, and how a drug or an agonist might inhibit the enzyme.Enzymes are usually protein molecules that manipulate other molecules — the enzymes' substrates. These target molecules bind to an enzyme's active site and are transformed into products through a series of steps known as the enzymatic mechanismE + S <——> ES <——> ES*< ——> EP <——> E + P. These mechanisms can be divided into single-substrate and multiple-substrate mechanisms. Kinetic studies on enzymes that only bind one substrate, such as triosephosphate isomerase, aim to measure the affinity with which the enzyme binds this substrate and the turnover rate. Some other examples of enzymes are phosphofructokinase and hexokinase, both of which are important for cellular respiration (glycolysis).When enzymes bind multiple substrates, such as dihydrofolate reductase (shown right), enzyme kinetics can also show the sequence in which these substrates bind and the sequence in which products are released. An example of enzymes that bind a single substrate and release multiple products are proteases, which cleave one protein substrate into two polypeptide products. Others join two substrates together, such as DNA polymerase linking a nucleotide to DNA. Although these mechanisms are often a complex series of steps, there is typically one rate-determining step that determines the overall kinetics. This rate-determining step may be a chemical reaction or a conformational change of the enzyme or substrates, such as those involved in the release of product(s) from the enzyme.Knowledge of the enzyme's structure is helpful in interpreting kinetic data. For example, the structure can suggest how substrates and products bind during catalysis; what changes occur during the reaction; and even the role of particular amino acid residues in the mechanism. Some enzymes change shape significantly during the mechanism; in such cases, it is helpful to determine the enzyme structure with and without bound substrate analogues that do not undergo the enzymatic reaction.Not all biological catalysts are protein enzymes; RNA-based catalysts such as ribozymes and ribosomes are essential to many cellular functions, such as RNA splicing and translation. The main difference between ribozymes and enzymes is that RNA catalysts are composed of nucleotides, whereas enzymes are composed of amino acids. Ribozymes also perform a more limited set of reactions, although their reaction mechanisms and kinetics can be analysed and classified by the same methods.