5 The Empire - fleetwoodchampagne
... • Roman roads were primarily made by the legions. • The military used the roads mostly to move soldiers to the frontiers. • Also used for transportation and trade of goods across the country.. • The metals used for commercial transactions were gold, silver, bronze. • Olive oil and wine were Italy's ...
... • Roman roads were primarily made by the legions. • The military used the roads mostly to move soldiers to the frontiers. • Also used for transportation and trade of goods across the country.. • The metals used for commercial transactions were gold, silver, bronze. • Olive oil and wine were Italy's ...
The Late Roman Army - Nipissing University Word
... interior; Rhine and Danube – rivers formed boundaries – legions stationed at strategic points close to river banks Auxiliary troops stationed in forts on frontier lines; most frontiers had small fortlets, with watchtowers in between ...
... interior; Rhine and Danube – rivers formed boundaries – legions stationed at strategic points close to river banks Auxiliary troops stationed in forts on frontier lines; most frontiers had small fortlets, with watchtowers in between ...
History Unit 3: Chapter 11
... founded the city of Rome and named it for Romulus. B. The story of the twin brothers is a myth, but the city became the center of a great empire. C. Ruled first by kings, Rome was later governed by the Senate. D. Republican Rome was ruled by representatives of the Roman elite. E. Early Rome was divi ...
... founded the city of Rome and named it for Romulus. B. The story of the twin brothers is a myth, but the city became the center of a great empire. C. Ruled first by kings, Rome was later governed by the Senate. D. Republican Rome was ruled by representatives of the Roman elite. E. Early Rome was divi ...
Rome – A Troubled Empire
... Persian armies invaded the eastern part of the empire. Rome started hiring mercenaries* to fight for them, but the mercenaries were not loyal to Rome. ...
... Persian armies invaded the eastern part of the empire. Rome started hiring mercenaries* to fight for them, but the mercenaries were not loyal to Rome. ...
The Roman Legions
... A legion usually consisted of approximately 5,000-6,000 soldiers. In 58 BC, Caesar had six legions, eight in 58-57 B. C., and ten in 53 B. C. By the Second Century A.D. the Roman Army consisted of about 28 Legions with approximately 160,000 legionaries, along with an additional force of some 220,000 ...
... A legion usually consisted of approximately 5,000-6,000 soldiers. In 58 BC, Caesar had six legions, eight in 58-57 B. C., and ten in 53 B. C. By the Second Century A.D. the Roman Army consisted of about 28 Legions with approximately 160,000 legionaries, along with an additional force of some 220,000 ...
ch_ 6 overview - Flushing Community Schools
... – Plebian-commoners who gained power via tribunes ...
... – Plebian-commoners who gained power via tribunes ...
Rise of the Roman Republic
... absolute power to make laws and command the army. Dictators were chosen by the consuls and then elected by the senate. ...
... absolute power to make laws and command the army. Dictators were chosen by the consuls and then elected by the senate. ...
4_-_beginnings_of_government
... and set up in the Forum for all to see. The laws covered everything from wills, property rights, court cases and even public behavior of citizens. The Law of the Twelve Tablets remained the foundation of Roman civil and criminal law for a thousand years. ...
... and set up in the Forum for all to see. The laws covered everything from wills, property rights, court cases and even public behavior of citizens. The Law of the Twelve Tablets remained the foundation of Roman civil and criminal law for a thousand years. ...
The Roman Army
... Among the four main types that had evolved by the early Empire was the heavily armed Samnite, later called a hoplomachus or secutor. (The Romans may have recognized these three as separate and distinct types, but any such distinctions are now unclear; all employed basically the same weapons and tact ...
... Among the four main types that had evolved by the early Empire was the heavily armed Samnite, later called a hoplomachus or secutor. (The Romans may have recognized these three as separate and distinct types, but any such distinctions are now unclear; all employed basically the same weapons and tact ...
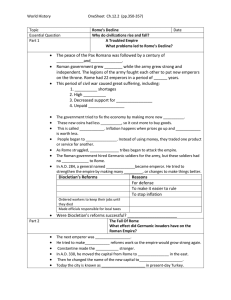
Topic
... The government tried to fix the economy by making more new __________. These new coins had less __________, so it cost more to buy goods. This is called ____________. Inflation happens when prices go up and ____________ is worth less. People began to _______________. Instead of using money, they tra ...
... The government tried to fix the economy by making more new __________. These new coins had less __________, so it cost more to buy goods. This is called ____________. Inflation happens when prices go up and ____________ is worth less. People began to _______________. Instead of using money, they tra ...
The Roman Army Who was in the Roman army?
... The lower classes were foot soldiers (the infantry) The soldiers on horse back were the rich classes (the cavalry) The cavalry were those who could afford to have a horse Officers bought their own armor and weapons If an officer wanted a horse, he had to provide and care for the horse hims ...
... The lower classes were foot soldiers (the infantry) The soldiers on horse back were the rich classes (the cavalry) The cavalry were those who could afford to have a horse Officers bought their own armor and weapons If an officer wanted a horse, he had to provide and care for the horse hims ...
Roman Army
... whole Mediterranean Sea. Without this massive Roman army, many modern armies probably would never have become professional fighters. The brave soldiers of Ancient Rome changed the ancient world as well as ours. This report is about how the Roman army did all these things and how they lived. The Roma ...
... whole Mediterranean Sea. Without this massive Roman army, many modern armies probably would never have become professional fighters. The brave soldiers of Ancient Rome changed the ancient world as well as ours. This report is about how the Roman army did all these things and how they lived. The Roma ...
BYZANTINE MILITARY SYSTEM developed after Constantine
... Constantinople in 330, when the Roman Empire was divided into two parts in 376, and with the fall of the western division of that empire a century later. As a direct descendant of the Roman Empire, the early Byzantine Empire largely followed the military precedents set by the late imperial emperors, ...
... Constantinople in 330, when the Roman Empire was divided into two parts in 376, and with the fall of the western division of that empire a century later. As a direct descendant of the Roman Empire, the early Byzantine Empire largely followed the military precedents set by the late imperial emperors, ...
Chap. 14 Section 1 and 2 Notes
... To protect their new boundaries, Romans either conquered their neighbors or made alliances with them By 146 B.C., Rome ruled most of the Mediterranean world Able to gain territory because of their strong army, which was organized into legions, divisions of Roman soldiers Each legion containe ...
... To protect their new boundaries, Romans either conquered their neighbors or made alliances with them By 146 B.C., Rome ruled most of the Mediterranean world Able to gain territory because of their strong army, which was organized into legions, divisions of Roman soldiers Each legion containe ...
Blank Jeopardy
... the Roman Republic’s army (name withheld b/c it is the answer to a question). ...
... the Roman Republic’s army (name withheld b/c it is the answer to a question). ...
File - Coach Fleenor
... "Remember, Roman, that it is for thee to rule the nations. This shall be thy task, to impose the ways of peace, to spare the vanquished, and to tame the proud by war." The history of Rome is in many ways, the history of its highly successful armies. Between the 2nd century BC and the 1st century AD ...
... "Remember, Roman, that it is for thee to rule the nations. This shall be thy task, to impose the ways of peace, to spare the vanquished, and to tame the proud by war." The history of Rome is in many ways, the history of its highly successful armies. Between the 2nd century BC and the 1st century AD ...
File
... In 338 B.C. they finally defeated the other Latins living nearby. Next they attack the Etruscans and defeat them in 284 B.C. By 267 B.C. the Romans had conquered the Greeks in Southern Italy. With this the Romans became the masters of almost all of Italy. ...
... In 338 B.C. they finally defeated the other Latins living nearby. Next they attack the Etruscans and defeat them in 284 B.C. By 267 B.C. the Romans had conquered the Greeks in Southern Italy. With this the Romans became the masters of almost all of Italy. ...
The Roman Republic
... In 494 B.C. many of them went on strike by: 1. refusing to serve in army 2. leaving to start republic of their own ...
... In 494 B.C. many of them went on strike by: 1. refusing to serve in army 2. leaving to start republic of their own ...
DOC
... The Roman Army had 4 different parts to it. Each part was called a ‘legion’, and each legion had 5,000 soldiers in it. Soldiers in the Roman Army wore metal armour and a helmet for protection. The helmets sometimes looked like this: ...
... The Roman Army had 4 different parts to it. Each part was called a ‘legion’, and each legion had 5,000 soldiers in it. Soldiers in the Roman Army wore metal armour and a helmet for protection. The helmets sometimes looked like this: ...
Fall of the Roman Republic
... to be not from old senatorial families. The Senate was jealous of the power of these generals, and didn’t want to share land Soldiers who didn’t own any land with their landless soldiers. It were taken into the army, and after refused to give Pompey’s fighting for several years, they came veterans a ...
... to be not from old senatorial families. The Senate was jealous of the power of these generals, and didn’t want to share land Soldiers who didn’t own any land with their landless soldiers. It were taken into the army, and after refused to give Pompey’s fighting for several years, they came veterans a ...
The Roman Army or a
... • The first thing the soldiers were taught to do, was to march. The historian Vegetius tells us that it was seen as of greatest importance to the Roman army that its soldiers could march at speed. Any army which would be split up by stragglers at the back or soldiers trundling along at differing spe ...
... • The first thing the soldiers were taught to do, was to march. The historian Vegetius tells us that it was seen as of greatest importance to the Roman army that its soldiers could march at speed. Any army which would be split up by stragglers at the back or soldiers trundling along at differing spe ...
Roman army

The Roman army (Latin: exercitus Romanus, literally: Roman Army; Ancient Greek: στρατός/φοσσᾶτον Ῥωμαίων, transcription: stratos/fossaton Romaion) is a term encompassing the terrestrial armed forces deployed by the Roman Kingdom (to c. 500 BC), the Roman Republic (500–31 BC), the Roman Empire (31 BC – 395/476 AD) and its successor the East Roman or Byzantine Empire. It is thus a term that spans approximately 2,000 years, during which the Roman armed forces underwent numerous permutations in composition, organization, equipment and tactics, while conserving a core of lasting traditions.