File - Ingolstadt Academy
... Density (definition and equation) Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
... Density (definition and equation) Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
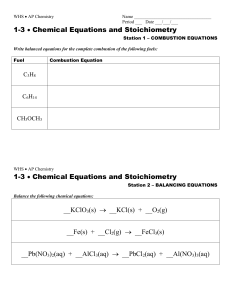
___Mg + ___O ___MgO • Mole : Mole ratio
... reacts with nitrogen gas to form 20.4 grams of ammonia (nitrogen trihydride)? 2) What is the percent yield when 2.37 grams of silver nitrate reacts with sodium hydroxide to produce water, sodium nitrate and 1.55 grams of silver oxide? ...
... reacts with nitrogen gas to form 20.4 grams of ammonia (nitrogen trihydride)? 2) What is the percent yield when 2.37 grams of silver nitrate reacts with sodium hydroxide to produce water, sodium nitrate and 1.55 grams of silver oxide? ...
Document
... In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical changes are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are usually reversible. You can tell that a react ...
... In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical changes are not easily reversed; they are irreversible. In a physical change no new substance is formed. Melting and evaporation are examples of physical changes. Physical changes are usually reversible. You can tell that a react ...
ppt
... The enthalpy of reaction is indicated by a separate expression beside the chemical equation »Remember: exothermic reactions have -ΔH endothermic reactions have +ΔH Examples: H2 (g) + ½O2 (g) H2O(l) ...
... The enthalpy of reaction is indicated by a separate expression beside the chemical equation »Remember: exothermic reactions have -ΔH endothermic reactions have +ΔH Examples: H2 (g) + ½O2 (g) H2O(l) ...
Chapter 5 – Chemical Reactions
... Particle size – the smaller the particles the faster the reaction (example – dust explosion) Higher temperature – the higher the temperature the faster the reaction Increase concentration of solution (a more concentrated acid will react faster than a dilute ...
... Particle size – the smaller the particles the faster the reaction (example – dust explosion) Higher temperature – the higher the temperature the faster the reaction Increase concentration of solution (a more concentrated acid will react faster than a dilute ...
Ch. 3 9-Station Review
... A student is assigned the task of determining the number of moles of water in one mole of MgCl2 · n H2O. The student collects the data shown in the following table. Mass of empty container Initial mass of sample and container Mass of sample and container after first heating Mass of sample and contai ...
... A student is assigned the task of determining the number of moles of water in one mole of MgCl2 · n H2O. The student collects the data shown in the following table. Mass of empty container Initial mass of sample and container Mass of sample and container after first heating Mass of sample and contai ...
Chapter 7
... 1. Hydrogen chloride, or HCl, is an important industrial chemical. Write a balanced equation for the production of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine. 2. Balance the following chemical equations. ...
... 1. Hydrogen chloride, or HCl, is an important industrial chemical. Write a balanced equation for the production of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine. 2. Balance the following chemical equations. ...
File
... produced through a combination reaction involving nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas. If 10 moles of hydrogen gas reacts with an excess of nitrogen gas, how many moles of ammonia are produced? 2pts N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) ...
... produced through a combination reaction involving nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas. If 10 moles of hydrogen gas reacts with an excess of nitrogen gas, how many moles of ammonia are produced? 2pts N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) ...
Extra Unit 3 Problems for the Web Site (Honors
... 14. A compound is analyzed and found to contain 12.1% carbon, 16.2% oxygen, and 71.7% chlorine. What is the empirical formula of this compound? a) COCl b) COCl2 c) CO2Cl d) CO2Cl2 e) COCl4 15. A certain compound has an empirical formula of NH2O. Its molar mass was experimentally determined to be bet ...
... 14. A compound is analyzed and found to contain 12.1% carbon, 16.2% oxygen, and 71.7% chlorine. What is the empirical formula of this compound? a) COCl b) COCl2 c) CO2Cl d) CO2Cl2 e) COCl4 15. A certain compound has an empirical formula of NH2O. Its molar mass was experimentally determined to be bet ...
Mole Equation Homework Hint: Start equations with the numbers
... Hint: Start equations with the numbers given, and pay close attention to what the question is asking you to find. Usually, the first step in most stoichiometry problems (calculation of quantities in chemical equations) is to convert the given numbers to moles. SHOW YOUR WORK!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ...
... Hint: Start equations with the numbers given, and pay close attention to what the question is asking you to find. Usually, the first step in most stoichiometry problems (calculation of quantities in chemical equations) is to convert the given numbers to moles. SHOW YOUR WORK!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ...
File
... It’s time to practice what you have already learned about moles, chemical reactions and dimensional analysis. We will learn one new conversion factor and then combine it with other concepts. Molar Volume is the volume of one mole of gas. Since the space between molecules in a gas is very great compa ...
... It’s time to practice what you have already learned about moles, chemical reactions and dimensional analysis. We will learn one new conversion factor and then combine it with other concepts. Molar Volume is the volume of one mole of gas. Since the space between molecules in a gas is very great compa ...
Unit 8 Powerpoint
... 4. Balance the elements one at a time by using coefficients. Begin by balancing elements that appear only once on each side of the equation. Unwritten coefficients are assumed to be 1 Once you are certain you have the correct chemical ...
... 4. Balance the elements one at a time by using coefficients. Begin by balancing elements that appear only once on each side of the equation. Unwritten coefficients are assumed to be 1 Once you are certain you have the correct chemical ...
Document
... changed to new substances (a chemical change occurs) 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(l) reactants products -substances -new substance about to react formed ...
... changed to new substances (a chemical change occurs) 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(l) reactants products -substances -new substance about to react formed ...
Stoichiometry intro
... 2) Every time 4 moles of Al atoms react with 3 moles of O2 molecules, 2 moles of Al2O3 molecules form. ...
... 2) Every time 4 moles of Al atoms react with 3 moles of O2 molecules, 2 moles of Al2O3 molecules form. ...
Chapter 3 Lecture Notes
... • convert moles of one reactant to moles of other reactants and products (use the stoichiometric ratio from the balanced chemical equation), and then • convert moles back into grams for desired product (use molar mass). ...
... • convert moles of one reactant to moles of other reactants and products (use the stoichiometric ratio from the balanced chemical equation), and then • convert moles back into grams for desired product (use molar mass). ...
Notes for Types of Reactions:
... chemical reaction = the _________ by which one or more substances are __________ into one or more _________ substances. in any chemical reaction, the _________ substances are known as the reactants and the __________ substances are known as the products. total mass of reactants = according to ...
... chemical reaction = the _________ by which one or more substances are __________ into one or more _________ substances. in any chemical reaction, the _________ substances are known as the reactants and the __________ substances are known as the products. total mass of reactants = according to ...
NM Strand
... 52. A characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the sample’s composition is 53. An experiment that determines the maximum number of grams of a substance that will dissolve in 100 grams of water measures: 54. Counting the number of cookies on a plate is what type of observation ...
... 52. A characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the sample’s composition is 53. An experiment that determines the maximum number of grams of a substance that will dissolve in 100 grams of water measures: 54. Counting the number of cookies on a plate is what type of observation ...
Chapter 3
... Zn. It reacts with HCl by the following reaction Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2 (aq) + H2(g) Cu does not react. When 0.5065 g of brass is reacted with excess HCl, 0.0985 g of ZnCl2 are eventually isolated. What is the composition of the brass? ...
... Zn. It reacts with HCl by the following reaction Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2 (aq) + H2(g) Cu does not react. When 0.5065 g of brass is reacted with excess HCl, 0.0985 g of ZnCl2 are eventually isolated. What is the composition of the brass? ...
Review for SNC 2P Chemistry Unit(SPRING 2014)
... example: Elements and solutions are pure substances. (a) An atom with more electrons than protons will be a positive ion. (b) A molecular compound is held together with ionic bonds. (c) The chloride ion is an example of a polyatomic ion. (d) The chemical test for hydrogen gas of to use a glowing spl ...
... example: Elements and solutions are pure substances. (a) An atom with more electrons than protons will be a positive ion. (b) A molecular compound is held together with ionic bonds. (c) The chloride ion is an example of a polyatomic ion. (d) The chemical test for hydrogen gas of to use a glowing spl ...
Chemical Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry
... reacting with hydrogen gas to form ammonia. How many moles of ammonia can be produced from 3 moles of nitrogen and 6 moles of hydrogen? ...
... reacting with hydrogen gas to form ammonia. How many moles of ammonia can be produced from 3 moles of nitrogen and 6 moles of hydrogen? ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.