Final Exam - Dawson College
... on the linear form of the Arrhenius equation is obtained. Arrhenius plot for the determination of the activation energy for the reaction of iodide with peroxydisulfate ...
... on the linear form of the Arrhenius equation is obtained. Arrhenius plot for the determination of the activation energy for the reaction of iodide with peroxydisulfate ...
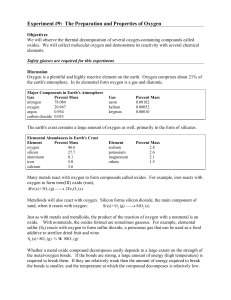
Chapter 3: Calculations with Chemical Formulas
... Li2O(s) + H2O(l) 2 LiOH(s) Li2OMM = 29.88 g/mol H2OMM = 18.02 g/mol ...
... Li2O(s) + H2O(l) 2 LiOH(s) Li2OMM = 29.88 g/mol H2OMM = 18.02 g/mol ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... • The equilibrium constant (K) is the ratio of the mathematical product of the concentrations of substances formed at equilibrium to the mathematical product of the concentrations of reacting substances. Each concentration is raised to a power equal to the coefficient of that substance in the chemic ...
... • The equilibrium constant (K) is the ratio of the mathematical product of the concentrations of substances formed at equilibrium to the mathematical product of the concentrations of reacting substances. Each concentration is raised to a power equal to the coefficient of that substance in the chemic ...
AP Chemistry: Chapter 13 Gaseous Equilibrium Section 1: Multiple
... pressure of the gases at equilibrium be greater than, less than, or equal to the final total pressure of the gases at equilibrium without the catalyst? Justify your answer. (Assume that the volume of the solid catalyst is negligible.) In another experiment involving the same reaction, a rigid 2.00 L ...
... pressure of the gases at equilibrium be greater than, less than, or equal to the final total pressure of the gases at equilibrium without the catalyst? Justify your answer. (Assume that the volume of the solid catalyst is negligible.) In another experiment involving the same reaction, a rigid 2.00 L ...
compound
... Salt (NaCl) is a common substance. Salt is which of these? atom element compound mixture ...
... Salt (NaCl) is a common substance. Salt is which of these? atom element compound mixture ...
- TestbankU
... C) The planetary theory of the atom. D) Both the planetary theory and the quantum theory of the atom. E) None of the above theories agree with all of the atomic experiments performed to date. 28) Suppose that a particular chemical substance A is "pure" [contains no "impurities"], and that it can be ...
... C) The planetary theory of the atom. D) Both the planetary theory and the quantum theory of the atom. E) None of the above theories agree with all of the atomic experiments performed to date. 28) Suppose that a particular chemical substance A is "pure" [contains no "impurities"], and that it can be ...
Page 1 MISE - Physical Basis of Chemistry First Set of Problems
... (2c) Through painstaking labor - and some luck - you determine that the atomic weight of Z (relative to unity for hydrogen) is about 32. Using this value for the atomic weight of Z, determine the atomic weight of X. Referring to a modern periodic table of the elements (which also lists hydrogen with ...
... (2c) Through painstaking labor - and some luck - you determine that the atomic weight of Z (relative to unity for hydrogen) is about 32. Using this value for the atomic weight of Z, determine the atomic weight of X. Referring to a modern periodic table of the elements (which also lists hydrogen with ...
5 SURFACE CHEMISTRY CATEGORY
... 7.Non-ideal solutions exhibit either positive or negative deviations from Raoult's law. What are these deviations and why are they caused? Explain with one example for each type. someglycerol in 500 g of water. This solution has a boiling point of 100.42°C. What mass of glycerol was dissolved to mak ...
... 7.Non-ideal solutions exhibit either positive or negative deviations from Raoult's law. What are these deviations and why are they caused? Explain with one example for each type. someglycerol in 500 g of water. This solution has a boiling point of 100.42°C. What mass of glycerol was dissolved to mak ...
CHEMISTRY 132
... 20) (3 points) Complete and balance the following acid-base neutralization reaction. What are the products with their respective coefficients when exact stoichiometric quantities of reactants are mixed? __ HBr (aq) + __ Ca(OH)2 a. 1 CaBr and 2 H2O b. 1 CaBr2 and 2 H2O c. 1 CaBr2 and 1 H3O+ d. 1 Ca ...
... 20) (3 points) Complete and balance the following acid-base neutralization reaction. What are the products with their respective coefficients when exact stoichiometric quantities of reactants are mixed? __ HBr (aq) + __ Ca(OH)2 a. 1 CaBr and 2 H2O b. 1 CaBr2 and 2 H2O c. 1 CaBr2 and 1 H3O+ d. 1 Ca ...
Moles Class Packet Unit 2
... The empirical formula of a compound is the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of the elements in a compound. It may be different from the molecular formula, which is the actual ratio of atoms in a molecule of that compound. (3.3d) In all chemical reactions there is a conservation of mass, energy, ...
... The empirical formula of a compound is the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of the elements in a compound. It may be different from the molecular formula, which is the actual ratio of atoms in a molecule of that compound. (3.3d) In all chemical reactions there is a conservation of mass, energy, ...
How many grams of NH4OH (ammonium hydroxide) are in 3.47
... If 2.33 L of propane (C3H8, 44.10 g/mol) reacts with excess oxygen (O2, 32.00 g/mol) at STP acording to the reaction below, how many moles of carbon dioxide (CO2, 44.01 g/mol) are produced? C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) →3 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(g) ...
... If 2.33 L of propane (C3H8, 44.10 g/mol) reacts with excess oxygen (O2, 32.00 g/mol) at STP acording to the reaction below, how many moles of carbon dioxide (CO2, 44.01 g/mol) are produced? C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) →3 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(g) ...
Lecture Resource ()
... The leaving group of a protonated amine cannot dissociate to form a carbocation or be replaced by a halide ion ...
... The leaving group of a protonated amine cannot dissociate to form a carbocation or be replaced by a halide ion ...
Topic 4 - Lloyd Crosby
... HNO3 H2SO4 HClO4 c. Group I A hydroxides and Group II A hydroxides (from Ca on) are strong electrolytes. d. Most other substances are nonelectrolytes. B. Nonelectrolytes 1. Definition A substance that does not ionize (does not produce any ions) when dissolved in water; a solution of a nonelectrolyte ...
... HNO3 H2SO4 HClO4 c. Group I A hydroxides and Group II A hydroxides (from Ca on) are strong electrolytes. d. Most other substances are nonelectrolytes. B. Nonelectrolytes 1. Definition A substance that does not ionize (does not produce any ions) when dissolved in water; a solution of a nonelectrolyte ...
aq - Moodle@FCT
... 4. The oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 except when it is bonded to metals in binary compounds. In these cases, its oxidation number is –1. 5. Group IA metals are +1, IIA metals are +2 and fluorine is always –1. 6. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms in a molecule or ion is equal to ...
... 4. The oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 except when it is bonded to metals in binary compounds. In these cases, its oxidation number is –1. 5. Group IA metals are +1, IIA metals are +2 and fluorine is always –1. 6. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms in a molecule or ion is equal to ...
Chapter_4_Reactions_in_Aqueous_Solution
... 4. The oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 except when it is bonded to metals in binary compounds. In these cases, its oxidation number is –1. 5. Group IA metals are +1, IIA metals are +2 and fluorine is always –1. 6. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms in a molecule or ion is equal to ...
... 4. The oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 except when it is bonded to metals in binary compounds. In these cases, its oxidation number is –1. 5. Group IA metals are +1, IIA metals are +2 and fluorine is always –1. 6. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms in a molecule or ion is equal to ...
File - Grade 12 Chemistry
... Other answers are possible for the alcohol and the ether. PTS: 1 9. ANS: Dispersion forces are very weak intermolecular forces that exist between molecules. When a carbon atom is bonded to another carbon atom, or to a hydrogen atom, the bond is not considered to be polar because the electronegativit ...
... Other answers are possible for the alcohol and the ether. PTS: 1 9. ANS: Dispersion forces are very weak intermolecular forces that exist between molecules. When a carbon atom is bonded to another carbon atom, or to a hydrogen atom, the bond is not considered to be polar because the electronegativit ...
AP® Chemistry
... 23. For the process of solid calcium chloride dissolving in water, represented above, the entropy change might be expected to be positive. However, ΔS for the process is actually negative. Which of the following best helps to account for the net loss of entropy? (A) Cl− ions are much larger in size ...
... 23. For the process of solid calcium chloride dissolving in water, represented above, the entropy change might be expected to be positive. However, ΔS for the process is actually negative. Which of the following best helps to account for the net loss of entropy? (A) Cl− ions are much larger in size ...
AP® Chemistry
... 23. For the process of solid calcium chloride dissolving in water, represented above, the entropy change might be expected to be positive. However, ΔS for the process is actually negative. Which of the following best helps to account for the net loss of entropy? (A) Cl− ions are much larger in size ...
... 23. For the process of solid calcium chloride dissolving in water, represented above, the entropy change might be expected to be positive. However, ΔS for the process is actually negative. Which of the following best helps to account for the net loss of entropy? (A) Cl− ions are much larger in size ...
AP CHEMISTRY – Source: 1999 AP Exam CHAPTER 8 PRACTICE
... Answer Question 4 below. The Section II score weighting for this question is 15 percent. 4. Write the formulas to show the reactants and the products for any FIVE of the laboratory situations described below. Answers to more than five choices will not be graded. In all cases a reaction occurs. Assum ...
... Answer Question 4 below. The Section II score weighting for this question is 15 percent. 4. Write the formulas to show the reactants and the products for any FIVE of the laboratory situations described below. Answers to more than five choices will not be graded. In all cases a reaction occurs. Assum ...
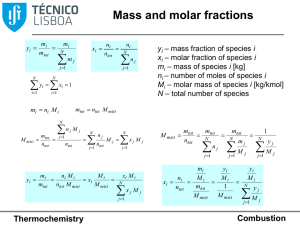
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.