Guide to Chapter 17. Thermodynamics
... (endothermic and exothermic reactions) and introduce entropy. We will define spontaneity and spontaneous reactions. We will learn about absolute molar entropies and how to calculate changes in entropy (S), from So tables. We will learn how entropy-favored reactions are associated with a + sign for ...
... (endothermic and exothermic reactions) and introduce entropy. We will define spontaneity and spontaneous reactions. We will learn about absolute molar entropies and how to calculate changes in entropy (S), from So tables. We will learn how entropy-favored reactions are associated with a + sign for ...
electrical energy and capacitance
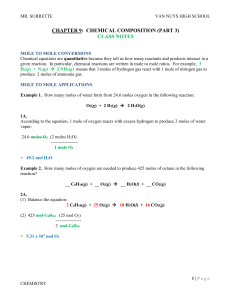
... CHAPTER 9: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION (PART 3) CLASS NOTES MOLE TO MOLE CONVERSIONS Chemical equations are quantitative because they tell us how many reactants and products interact in a given reaction. In particular, chemical reactions are written in mole to mole ratios. For example, 3 H2(g) + N2(g) 2 ...
... CHAPTER 9: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION (PART 3) CLASS NOTES MOLE TO MOLE CONVERSIONS Chemical equations are quantitative because they tell us how many reactants and products interact in a given reaction. In particular, chemical reactions are written in mole to mole ratios. For example, 3 H2(g) + N2(g) 2 ...
Document
... (a) It is possible to identify the sulfite ion without memorizing all the ions in Table 2.4. If you remember the name and formula of one of the sulfur–oxygen polyatomic anions, you should be able to deduce the names of others. Suppose you remember that sulfate is SO42–. The -ite anion has one fewer ...
... (a) It is possible to identify the sulfite ion without memorizing all the ions in Table 2.4. If you remember the name and formula of one of the sulfur–oxygen polyatomic anions, you should be able to deduce the names of others. Suppose you remember that sulfate is SO42–. The -ite anion has one fewer ...
CHAPTER-7 EQUILIBRIUM Equilibrium state- When
... The acid-base pair thatdiffers only by one proton is called a conjugateacidbase pair. IfBrönsted acid is a strong acid then itsconjugate base is a weak base and viceversa. Ionic product of water.Kw = [H+][OH–] pH = -log [H+] ; here[H+] is molar concentration of hydrogen ion. pH + pOH =14 p ...
... The acid-base pair thatdiffers only by one proton is called a conjugateacidbase pair. IfBrönsted acid is a strong acid then itsconjugate base is a weak base and viceversa. Ionic product of water.Kw = [H+][OH–] pH = -log [H+] ; here[H+] is molar concentration of hydrogen ion. pH + pOH =14 p ...
Chapters 13 and 14
... c. Complete combustion of a 1.05-gram sample of the compound with the stoichiometric amount of oxygen gas produces a mixture of H2O(g) and CO2(g). What is the pressure of this gas when it is contained in a 3.00-liter flask at 127 °C? ...
... c. Complete combustion of a 1.05-gram sample of the compound with the stoichiometric amount of oxygen gas produces a mixture of H2O(g) and CO2(g). What is the pressure of this gas when it is contained in a 3.00-liter flask at 127 °C? ...
unit 8 – compound stoichiometry
... NOTE: formulas are typically written from least electronegative to most electronegative. METALS FIRST! STEPS to solve empirical formula problems: 1. % to mass – the easiest way to convert % to mass is to assume 100 grams. (42% of 100 g = 42 g!) 2. mass to mole – USE MOLAR MASS! Be sure to leave your ...
... NOTE: formulas are typically written from least electronegative to most electronegative. METALS FIRST! STEPS to solve empirical formula problems: 1. % to mass – the easiest way to convert % to mass is to assume 100 grams. (42% of 100 g = 42 g!) 2. mass to mole – USE MOLAR MASS! Be sure to leave your ...
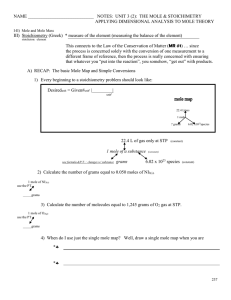
Unit 3 2 Basic Mole Conversions and Mole Maps
... We've introduced the issues of balancing in light of the Law of the Conservation of Matter. Now, very briefly, I would like to introduce the role of the balanced equation in terms of stoichiometry. I am quite aware that you may not yet know how to balance an equation ... but I wish to discuss what a ...
... We've introduced the issues of balancing in light of the Law of the Conservation of Matter. Now, very briefly, I would like to introduce the role of the balanced equation in terms of stoichiometry. I am quite aware that you may not yet know how to balance an equation ... but I wish to discuss what a ...
Multiple Choice Math Practice File
... answer. The exponent will always give you the characteristic of the number…unless the number in front of the “x” sign is 1, then your answer (when you take the log) will be (exponent – 1) – in this case B - 1. Look at the following chart and look at the pattern of the numbers: ...
... answer. The exponent will always give you the characteristic of the number…unless the number in front of the “x” sign is 1, then your answer (when you take the log) will be (exponent – 1) – in this case B - 1. Look at the following chart and look at the pattern of the numbers: ...
Chapter 1 Matter and Change
... 1) Solid- matter that can not flow (definite shape) and has definite volume. 2) Liquid- definite volume but takes the shape of its container (flows). 3) Gas- a substance without definite volume or shape and can flow. – Vapor- a substance that is currently a gas, but normally is a liquid or solid at ...
... 1) Solid- matter that can not flow (definite shape) and has definite volume. 2) Liquid- definite volume but takes the shape of its container (flows). 3) Gas- a substance without definite volume or shape and can flow. – Vapor- a substance that is currently a gas, but normally is a liquid or solid at ...
Oxygen Reduction Reaction with the Rotating Ring Disk Electrode
... the onset of ORR gives rise to a negative (cathodic) signal that is observable at approximately 0.65 V. The current increases with decreasing potential then reaches a plateau region at approximately E = 0.20 to –0.10V. This plateau is also known as the mass transfer limited region of the voltammetry ...
... the onset of ORR gives rise to a negative (cathodic) signal that is observable at approximately 0.65 V. The current increases with decreasing potential then reaches a plateau region at approximately E = 0.20 to –0.10V. This plateau is also known as the mass transfer limited region of the voltammetry ...
Document
... reaction was practically complete ( 95 per cent yield) in four days. In the winter there action may take as long as two weeks [11] ...
... reaction was practically complete ( 95 per cent yield) in four days. In the winter there action may take as long as two weeks [11] ...
Chapter 2. The Chemical Context of Life
... Life requires ~25 chemical elements Atomic structure determines behavior of an element Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form molecules Weak chemical bonds play important roles in chemistry of ...
... Life requires ~25 chemical elements Atomic structure determines behavior of an element Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form molecules Weak chemical bonds play important roles in chemistry of ...
No Slide Title
... Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 6NaOH(aq) → 2Al(OH)3(s) + 3Na2SO4(aq) *Do not carry the subscripts over (except for polyatomic ions) 2. Write the ionic equation showing the soluble product dissociated into ions, but the insoluble product left together. 2Al+3 + 3SO4-2 + 6Na+ + 6OH- → 2Al(OH)3(s) + 6Na+ + 3SO4-2 3. C ...
... Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 6NaOH(aq) → 2Al(OH)3(s) + 3Na2SO4(aq) *Do not carry the subscripts over (except for polyatomic ions) 2. Write the ionic equation showing the soluble product dissociated into ions, but the insoluble product left together. 2Al+3 + 3SO4-2 + 6Na+ + 6OH- → 2Al(OH)3(s) + 6Na+ + 3SO4-2 3. C ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
+2 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... HgCl. What is the molecular formula, knowing that molar mass is 472.08 g/mol? Empirical formula HgCl Molar mass of unknown = 472.08 g/mol 1 mol Hg = 200.59 g/mol 1 mol Cl = 35.45 g/mol Molar mass of HgCl = 236.04 g/mol ...
... HgCl. What is the molecular formula, knowing that molar mass is 472.08 g/mol? Empirical formula HgCl Molar mass of unknown = 472.08 g/mol 1 mol Hg = 200.59 g/mol 1 mol Cl = 35.45 g/mol Molar mass of HgCl = 236.04 g/mol ...
spontaneous processes
... -- For elements in their standard states… DGfo = 0 -- For a reaction, the standard free-energy change is found by… ...
... -- For elements in their standard states… DGfo = 0 -- For a reaction, the standard free-energy change is found by… ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.