Work Booklet - Brooks Composite High School
... Read all written instructions carefully before doing an activity. Listen to all instructions and follow them carefully. Wash your hands thoroughly after each activity and after handling chemicals. Wear safety goggles, gloves, or an apron as required. Think before you touch. Equipment may be hot and ...
... Read all written instructions carefully before doing an activity. Listen to all instructions and follow them carefully. Wash your hands thoroughly after each activity and after handling chemicals. Wear safety goggles, gloves, or an apron as required. Think before you touch. Equipment may be hot and ...
L-12 Spontaneity of chemical reactions
... the first law does not deny the possibility that a metal bar having a uniform temperature can spontaneously become warmer at one end and cooler at the other. But it is known from experience that such a change does not occur without expenditure of energy from an external source. The first law also st ...
... the first law does not deny the possibility that a metal bar having a uniform temperature can spontaneously become warmer at one end and cooler at the other. But it is known from experience that such a change does not occur without expenditure of energy from an external source. The first law also st ...
Pictures and Graphs
... Dena K. Leggett, PhD Advanced Chemistry Teacher Allen High School Copyright 2015 ...
... Dena K. Leggett, PhD Advanced Chemistry Teacher Allen High School Copyright 2015 ...
No Slide Title
... 2 atoms Mg + 1 molecule O2 makes 2 formula units MgO 2 moles Mg + 1 mole O2 makes 2 moles MgO 48.6 grams Mg + 32.0 grams O2 makes 80.6 g MgO ...
... 2 atoms Mg + 1 molecule O2 makes 2 formula units MgO 2 moles Mg + 1 mole O2 makes 2 moles MgO 48.6 grams Mg + 32.0 grams O2 makes 80.6 g MgO ...
CHEM 101 Final (Term 141)
... 31. A sample of (N2H5)2C3H4O4 contains 1.084 × 1024 carbon atoms. How many moles of hydrogen atoms are in the same sample? A) B) C) D) E) ...
... 31. A sample of (N2H5)2C3H4O4 contains 1.084 × 1024 carbon atoms. How many moles of hydrogen atoms are in the same sample? A) B) C) D) E) ...
Grade 11 Unit 6 - Amazon Web Services
... or the forming of new bonds or both. We know that every chemical bond contains energy or it would not exist. This result means that every chemical Do this investigation. ...
... or the forming of new bonds or both. We know that every chemical bond contains energy or it would not exist. This result means that every chemical Do this investigation. ...
SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY NOTES
... Law of conservation of Mass (Proposed by Antoine Lavoisier: It states that matter can neither be created nor destroyed. It can only be changed from one form to another during a chemical reaction. Law of Definite Proportions (Proposed by Joseph Proust): A given compound always contains exactly the sa ...
... Law of conservation of Mass (Proposed by Antoine Lavoisier: It states that matter can neither be created nor destroyed. It can only be changed from one form to another during a chemical reaction. Law of Definite Proportions (Proposed by Joseph Proust): A given compound always contains exactly the sa ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... Elements with atomic numbers 112 and 114 have been produced and their IUPAC names are pending approval. However, an element that would be put between these two elements on the Periodic Table has not yet been produced. If produced, this element will be identified by the symbol Uut until an IUPAC name ...
... Elements with atomic numbers 112 and 114 have been produced and their IUPAC names are pending approval. However, an element that would be put between these two elements on the Periodic Table has not yet been produced. If produced, this element will be identified by the symbol Uut until an IUPAC name ...
The Mole
... Molar Mass of an Element: an amount equal to the atomic mass of the element expressed in grams. ...
... Molar Mass of an Element: an amount equal to the atomic mass of the element expressed in grams. ...
Unit 1
... highest activation energy is the rate-determining step. In this example, step 2 is the rate-determining step since it has the highest “single reaction” activation energy out of the three elementary steps. 2. This reaction profile is consistent with the overall reaction being exothermic (as indicated ...
... highest activation energy is the rate-determining step. In this example, step 2 is the rate-determining step since it has the highest “single reaction” activation energy out of the three elementary steps. 2. This reaction profile is consistent with the overall reaction being exothermic (as indicated ...
Sample Chem 111 Final
... 40. A given mass of gas in a rigid container is heated from 100 ºC to 500 ºC. Which of the following responses best describes what will happen to the pressure of the gas? a) The pressure will decrease by a factor of five. b) The pressure will increase by a factor of five. c) The pressure will incre ...
... 40. A given mass of gas in a rigid container is heated from 100 ºC to 500 ºC. Which of the following responses best describes what will happen to the pressure of the gas? a) The pressure will decrease by a factor of five. b) The pressure will increase by a factor of five. c) The pressure will incre ...
Equilibrium - Clayton State University
... - Many reactions do not go to completion - Amount of products formed or reactants consumed cannot be predicted from stoichiometry alone - These reactions achieve a condition of equilibrium ...
... - Many reactions do not go to completion - Amount of products formed or reactants consumed cannot be predicted from stoichiometry alone - These reactions achieve a condition of equilibrium ...
THERMOCHEMISTRY
... 0.562 g of graphite is placed in a calorimeter with excess oxygen at 25.00 °C and 1 atm pressure. The graphite is ignited and burns completely to form CO2 as shown below: C (graphite) + O2 ® CO2 (g) After the completion of the reaction, the calorimeter temperature rises to 25.90 °C. The he ...
... 0.562 g of graphite is placed in a calorimeter with excess oxygen at 25.00 °C and 1 atm pressure. The graphite is ignited and burns completely to form CO2 as shown below: C (graphite) + O2 ® CO2 (g) After the completion of the reaction, the calorimeter temperature rises to 25.90 °C. The he ...
doc - Dartmouth College
... (a) Because acetic acid is present in excess, the maximum number of moles of aspirin that can be produced is limited by the number of moles of salicylic acid. The number of moles of salicylic acid = (6.22 g)/(138.12 g mol–1) = 0.045 mol. Thus, from the stoichiometry of the reaction, the maximum numb ...
... (a) Because acetic acid is present in excess, the maximum number of moles of aspirin that can be produced is limited by the number of moles of salicylic acid. The number of moles of salicylic acid = (6.22 g)/(138.12 g mol–1) = 0.045 mol. Thus, from the stoichiometry of the reaction, the maximum numb ...
Kitchen Chemistry Review
... Physical: Change in shape, size, state or amount Chemical: Change in chemical composition, new substance is made. ...
... Physical: Change in shape, size, state or amount Chemical: Change in chemical composition, new substance is made. ...
Stoichiometry and the Mole
... But it also goes beyond carbon. Previously we defined atomic and molecular masses as the number of atomic mass units per atom or molecule. Now we can do so in terms of grams. The atomic mass of an element is the number of grams in 1 mol of atoms of that element, while the molecular mass of a compound ...
... But it also goes beyond carbon. Previously we defined atomic and molecular masses as the number of atomic mass units per atom or molecule. Now we can do so in terms of grams. The atomic mass of an element is the number of grams in 1 mol of atoms of that element, while the molecular mass of a compound ...
Development of Novel Catalytic Asymmetric Reactions using
... aldol reaction.2 A detailed investigation of the above reaction mechanism revealed that water (or PdOH produced from 1) acted as a nucleophile on the silyl group, as shown in Scheme 4, and chiral Pd enolates (I) were generated as the key chemical intermediates through transmetallation. While the fin ...
... aldol reaction.2 A detailed investigation of the above reaction mechanism revealed that water (or PdOH produced from 1) acted as a nucleophile on the silyl group, as shown in Scheme 4, and chiral Pd enolates (I) were generated as the key chemical intermediates through transmetallation. While the fin ...
Class XI Chemistry Practics Paper
... .(a) Balance the following equation Fe2++Cr2O72- → Fe3++ Cr3+ (b) What is salt bridge. Write its application also Q25.(a) Give two properties of Water which are due to Hydrogen bonding. (b) Explain the Structure of H2O2. Q26.An org. compound contain 69% carbon and 4.8% Hydrogen, the remainder being ...
... .(a) Balance the following equation Fe2++Cr2O72- → Fe3++ Cr3+ (b) What is salt bridge. Write its application also Q25.(a) Give two properties of Water which are due to Hydrogen bonding. (b) Explain the Structure of H2O2. Q26.An org. compound contain 69% carbon and 4.8% Hydrogen, the remainder being ...
1st-Year-ch-wise-test
... (2) The filtration through filter paper is increased by using (a) sintered glass crucible (b) funnel of small stem (b) flutted filter paper (d) filter paper of greater porosity (3) A solvent chosen for crystallization should (a) not react chemically (b) react chemically (c) be expensive (d) dissolve ...
... (2) The filtration through filter paper is increased by using (a) sintered glass crucible (b) funnel of small stem (b) flutted filter paper (d) filter paper of greater porosity (3) A solvent chosen for crystallization should (a) not react chemically (b) react chemically (c) be expensive (d) dissolve ...
The Periodic Table of Elements and Atoms…
... their properties/characteristics. It works out that the atoms are in order of increasing atomic number (protons/electrons) as you move from left to right. The boxes are arranged into a grid of periods (Horizontal rows) and groups (Vertical ...
... their properties/characteristics. It works out that the atoms are in order of increasing atomic number (protons/electrons) as you move from left to right. The boxes are arranged into a grid of periods (Horizontal rows) and groups (Vertical ...
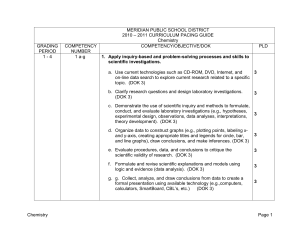
MERIDIAN PUBLIC SCHOOL DISTRICT
... b. Use the ideal gas laws to explain the relationships between volume, temperature, pressure, and quantity in moles. (DOK 2) ...
... b. Use the ideal gas laws to explain the relationships between volume, temperature, pressure, and quantity in moles. (DOK 2) ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.