Review
... species in all phases must be equal to each other Processes move from a higher chemical potential to a lower one. Expression for the molar Gibbs free energy, the chemical potential, of a gas Calculation of the Equilibrium Constant from Gorxn or the reverse of this. Calculating the Temp dependence ...
... species in all phases must be equal to each other Processes move from a higher chemical potential to a lower one. Expression for the molar Gibbs free energy, the chemical potential, of a gas Calculation of the Equilibrium Constant from Gorxn or the reverse of this. Calculating the Temp dependence ...
No Slide Title
... If we now substitute into the expression for enthalpy, we get H = E + pV = (q - p V) + p V or (finally!) H = qp (p = constant) What does this mean? For a process carried out at constant pressure, q is a state function, and so no information is needed concerning path. This makes it far easier ...
... If we now substitute into the expression for enthalpy, we get H = E + pV = (q - p V) + p V or (finally!) H = qp (p = constant) What does this mean? For a process carried out at constant pressure, q is a state function, and so no information is needed concerning path. This makes it far easier ...
Chemical Reactions of Copper and Percent Recovery
... Following this final evaporation, you will obtain elemental copper – the same material used in the very first reaction. If you obtain the same amount that you started with, then you will have recovered 100 percent. This percent recovery is one of the most important laboratory calculations. This valu ...
... Following this final evaporation, you will obtain elemental copper – the same material used in the very first reaction. If you obtain the same amount that you started with, then you will have recovered 100 percent. This percent recovery is one of the most important laboratory calculations. This valu ...
Honors Chemistry Ms. K Pages 66
... 2. Sodium chloride always contains 39.34% Na and 60.66% Cl by mass. What law does this concept reflect? _______________________________________________ 3. Carbon and oxygen can combine to form carbon monoxide, CO, or carbon dioxide, CO2. What law does this concept reflect? __________________________ ...
... 2. Sodium chloride always contains 39.34% Na and 60.66% Cl by mass. What law does this concept reflect? _______________________________________________ 3. Carbon and oxygen can combine to form carbon monoxide, CO, or carbon dioxide, CO2. What law does this concept reflect? __________________________ ...
Unit 3.2 worksheet 4 atomic model of matter
... like a history of breathing. Like breathing, hypnosis is an. Current Unit. Unit 9: Chemical Bonding. Why and how do atoms combine to form compounds? In this unit, we will draw Lewis structures to describe bonding and. The Periodic Table by WebElements. The periodic table is an arrangment of the chem ...
... like a history of breathing. Like breathing, hypnosis is an. Current Unit. Unit 9: Chemical Bonding. Why and how do atoms combine to form compounds? In this unit, we will draw Lewis structures to describe bonding and. The Periodic Table by WebElements. The periodic table is an arrangment of the chem ...
2 - kcpe-kcse
... 3. The methane burned in oxygen and it reacted to give carbon dioxide and water. methane ...
... 3. The methane burned in oxygen and it reacted to give carbon dioxide and water. methane ...
Chapter 7: Solutions
... • In all precipitation reactions, the reactants are always aqueous. • Use the Solubility Rules Table to determine the phase of the “possible” products. • If a compound is water soluble, it remains dissolved and we write “(aq).” • If a compound is water insoluble, it precipitates as a solid and w ...
... • In all precipitation reactions, the reactants are always aqueous. • Use the Solubility Rules Table to determine the phase of the “possible” products. • If a compound is water soluble, it remains dissolved and we write “(aq).” • If a compound is water insoluble, it precipitates as a solid and w ...
Chapter 7: Thermochemistry
... the formation of one mole of the substance in the standard state from the reference forms of the elements in their standard state. The reference forms of the elements in all but few cases are the most stable forms of the elements under standard state. Because the formation of the most stable form of ...
... the formation of one mole of the substance in the standard state from the reference forms of the elements in their standard state. The reference forms of the elements in all but few cases are the most stable forms of the elements under standard state. Because the formation of the most stable form of ...
Chapter 7 - Faculty Web Pages
... 12 grams; its molar mass is 12 grams per mole. This leads to the conclusion: The molar mass of any substance in grams per mole is numerically equal to the atomic, molecular, or formula mass of that substance in atomic mass units. ...
... 12 grams; its molar mass is 12 grams per mole. This leads to the conclusion: The molar mass of any substance in grams per mole is numerically equal to the atomic, molecular, or formula mass of that substance in atomic mass units. ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... Note: This is an example of a disproportionation reaction - the same reactant (Cl2) undergoes both oxidation and reduction. 1. Simple redox reactions : a. Hydrogen displacement • e.g. Ca(s) + H2O Æ Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g) ...
... Note: This is an example of a disproportionation reaction - the same reactant (Cl2) undergoes both oxidation and reduction. 1. Simple redox reactions : a. Hydrogen displacement • e.g. Ca(s) + H2O Æ Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g) ...
0922085
... 8.2.2.7.2.3 of the Regulations annexed to ADN, the ADN Administrative Committee was required to prepare a catalogue of questions for the ADN examinations, decided that the item should be put on the agenda for future sessions, in order to enable lists of questions to be translated and adopted progres ...
... 8.2.2.7.2.3 of the Regulations annexed to ADN, the ADN Administrative Committee was required to prepare a catalogue of questions for the ADN examinations, decided that the item should be put on the agenda for future sessions, in order to enable lists of questions to be translated and adopted progres ...
Enzyme Activity
... Many are a lot lower, cold water fish will die at 30°C because their enzymes denature A few bacteria have enzymes very high temperatures up to 100°C Most enzymes however are fully denatured at 70°C ...
... Many are a lot lower, cold water fish will die at 30°C because their enzymes denature A few bacteria have enzymes very high temperatures up to 100°C Most enzymes however are fully denatured at 70°C ...
Solution - gearju.com
... 4. The oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 except when it is bonded to metals in binary compounds. In these cases, its oxidation number is –1. 5. Group IA metals are +1, IIA metals are +2 and fluorine is always –1. 6. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms in a molecule or ion is equal to ...
... 4. The oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 except when it is bonded to metals in binary compounds. In these cases, its oxidation number is –1. 5. Group IA metals are +1, IIA metals are +2 and fluorine is always –1. 6. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms in a molecule or ion is equal to ...
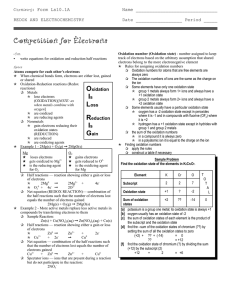
Competition for Electrons
... q Net equation — combination of the half reactions such that the number of electrons lost equals the number of electrons gained Cu2+ + Zn0 ! Zn2+ ...
... q Net equation — combination of the half reactions such that the number of electrons lost equals the number of electrons gained Cu2+ + Zn0 ! Zn2+ ...
School of Chemistry
... The pressure of CO2 inside the cabin of a submarine having a volume of 2.4 x 105 L is 7.9 x 10-3 atm at 312 K. A solution of LiOH of negligible volume is introduced into the cabin. Eventually the pressure of CO2 falls to 1.2 x 10-4 atm. How many grams of Li2CO3 forms according to the reaction: 2LiOH ...
... The pressure of CO2 inside the cabin of a submarine having a volume of 2.4 x 105 L is 7.9 x 10-3 atm at 312 K. A solution of LiOH of negligible volume is introduced into the cabin. Eventually the pressure of CO2 falls to 1.2 x 10-4 atm. How many grams of Li2CO3 forms according to the reaction: 2LiOH ...
Relative formula mass
... that can be extracted form its mineral. • Should: Be able to write balanced symbol equations. • Keywords: Atomic mass, relative formula mass, percentage composition, reactants and products. • Starter: What do these numbers mean ...
... that can be extracted form its mineral. • Should: Be able to write balanced symbol equations. • Keywords: Atomic mass, relative formula mass, percentage composition, reactants and products. • Starter: What do these numbers mean ...
8872 Chemistry H1 syllabus for 2016
... [the term relative formula mass or Mr will be used for ionic compounds] Candidates should be able to: (a) define the terms relative atomic, isotopic, molecular and formula masses, based on the 12C scale (b) define the term mole in terms of the Avogadro constant (c) calculate the relative atomic mass ...
... [the term relative formula mass or Mr will be used for ionic compounds] Candidates should be able to: (a) define the terms relative atomic, isotopic, molecular and formula masses, based on the 12C scale (b) define the term mole in terms of the Avogadro constant (c) calculate the relative atomic mass ...
Chemistry 30 Review of Basic Chemistry 20
... Round off to the least number of digits found in each of the individual numbers being ...
... Round off to the least number of digits found in each of the individual numbers being ...
Chemical Equilibrium – Le Chatelier`s Principle
... However, the value of Kc will depend on the ionic strength. All equilibrium constants depend on temperature and pressure (or volume). In this laboratory we will study Le Châtelier's Principle If a chemical system at equilibrium experiences a change in concentration, temperature, volume, or partial p ...
... However, the value of Kc will depend on the ionic strength. All equilibrium constants depend on temperature and pressure (or volume). In this laboratory we will study Le Châtelier's Principle If a chemical system at equilibrium experiences a change in concentration, temperature, volume, or partial p ...
ch17
... K therefore indicates the extent of a reaction, i.e., how far a reaction proceeds towards the products at a given temperature. A small value for K indicates that the reaction yields little product before reaching equilibrium. The reaction favors the reactants. ...
... K therefore indicates the extent of a reaction, i.e., how far a reaction proceeds towards the products at a given temperature. A small value for K indicates that the reaction yields little product before reaching equilibrium. The reaction favors the reactants. ...
CP Chemistry - Final Exam Review KEY
... The kinetic molecular theory assumes that there are no interactions between particles, no volume from the particles, there are perfectly elastic collisions, and the temperature is proportional to kinetic energy. Perform the following pressure conversions: a. 685 mm Hg to atm ...
... The kinetic molecular theory assumes that there are no interactions between particles, no volume from the particles, there are perfectly elastic collisions, and the temperature is proportional to kinetic energy. Perform the following pressure conversions: a. 685 mm Hg to atm ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.