Enzymes - Chautauqua Lake Central SD
... • Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction – each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job – enzymes are named for the reaction they help Oh, I get it! They end in -ase ...
... • Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction – each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job – enzymes are named for the reaction they help Oh, I get it! They end in -ase ...
Section 2 Types of Chemical Reactions
... • Begin by counting carbon atoms. • Carbon is already balanced in the equation. • Two additional hydrogen atoms are needed on the right side of the equation. • Now increase the oxygen atoms by placing the coefficient 2 in front of the molecular formula for oxygen. The correct chemical equation, or b ...
... • Begin by counting carbon atoms. • Carbon is already balanced in the equation. • Two additional hydrogen atoms are needed on the right side of the equation. • Now increase the oxygen atoms by placing the coefficient 2 in front of the molecular formula for oxygen. The correct chemical equation, or b ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... The random nature of molecular movement in liquids, despite molecules touching each other. The dynamic equilibria between solid-liquid and liquid-gas. Vapour pressure as the result of molecules colliding with the sides of the vessel. The alternating oppositely charged ions in 3 dimensions in ionic s ...
... The random nature of molecular movement in liquids, despite molecules touching each other. The dynamic equilibria between solid-liquid and liquid-gas. Vapour pressure as the result of molecules colliding with the sides of the vessel. The alternating oppositely charged ions in 3 dimensions in ionic s ...
Rxn Types
... Single Displacement Reactions Not all single displacement reactions that can be written actually happen. The metal or non-metal must be more active than the ion it is replacing. It will depend upon the element’s Activity as ...
... Single Displacement Reactions Not all single displacement reactions that can be written actually happen. The metal or non-metal must be more active than the ion it is replacing. It will depend upon the element’s Activity as ...
Chemistry 30 - SharpSchool
... 30-D1.4k define Kc to predict the extent of the reaction and write equilibrium law expressions for given chemical equations, using lowest whole-number coefficients 30-D1.3s write the equilibrium law expression for a given equation ...
... 30-D1.4k define Kc to predict the extent of the reaction and write equilibrium law expressions for given chemical equations, using lowest whole-number coefficients 30-D1.3s write the equilibrium law expression for a given equation ...
Chapter III: Matter - Norwell Public Schools
... As temperature and pressure change, substances change from one phase to another. ...
... As temperature and pressure change, substances change from one phase to another. ...
Unit 1 Atoms, Molecules and Stoichiometry
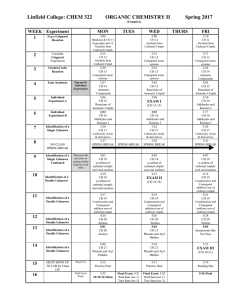
... In 1897, J. J. Thomson investigated the conductivity of electricity by gases at very low pressure. At ordinary pressures gases are electrical insulators, but when they are subjected to very high voltages at very low pressures (below 0.01 atm) they break down and conduct electricity. When Thomson app ...
... In 1897, J. J. Thomson investigated the conductivity of electricity by gases at very low pressure. At ordinary pressures gases are electrical insulators, but when they are subjected to very high voltages at very low pressures (below 0.01 atm) they break down and conduct electricity. When Thomson app ...
KIN1PP - Knockhardy
... A minimum amount of energy is required to overcome the ACTIVATION ENERGY (Ea). Only those reactants with energy equal to, or greater than, this value will react. ...
... A minimum amount of energy is required to overcome the ACTIVATION ENERGY (Ea). Only those reactants with energy equal to, or greater than, this value will react. ...
Unit 4 - cloudfront.net
... 4. The oxidation state of hydrogen when it is bonded to a non-metal is ______. When it is bonded to a metal its oxidation state is ______. (i.e. HCl = +1; LiH = -1) 5. Fluorine has an oxidation state of ______ in ALL its compounds. Other halogens can have ____________ oxidation states when bonded to ...
... 4. The oxidation state of hydrogen when it is bonded to a non-metal is ______. When it is bonded to a metal its oxidation state is ______. (i.e. HCl = +1; LiH = -1) 5. Fluorine has an oxidation state of ______ in ALL its compounds. Other halogens can have ____________ oxidation states when bonded to ...
Review Unit 8 Test (Chp 15,17)
... increases until it becomes the same as the reverse reaction rate at equilibrium. stays constant before and after equilibrium is reached. A is half true, but “decreases”, decreases to become a constant nonzero rate at equilibrium. not “increases.” decreases to become zero at equilibrium. Greater pres ...
... increases until it becomes the same as the reverse reaction rate at equilibrium. stays constant before and after equilibrium is reached. A is half true, but “decreases”, decreases to become a constant nonzero rate at equilibrium. not “increases.” decreases to become zero at equilibrium. Greater pres ...
Lecture syllabus - Linfield College
... explain it verbally to someone else in the course. If your listener grasps the concept easily from your explanation, you have proven that you understand it. If not, then most likely you need to work on clarifying your own grasp of it. It is also easy to discover whether or not you know a reaction or ...
... explain it verbally to someone else in the course. If your listener grasps the concept easily from your explanation, you have proven that you understand it. If not, then most likely you need to work on clarifying your own grasp of it. It is also easy to discover whether or not you know a reaction or ...
atoms. - Unicam
... experiments conducted between 1798 and 1804 on the elemental composition of water and copper carbonate. In 1806, Proust summarized his observations in what is now called Proust's Law. It stated that chemical compounds are formed of constant and defined ratios of elements, as determined by mass. For ...
... experiments conducted between 1798 and 1804 on the elemental composition of water and copper carbonate. In 1806, Proust summarized his observations in what is now called Proust's Law. It stated that chemical compounds are formed of constant and defined ratios of elements, as determined by mass. For ...
Chemistry 12 - Correspondence Studies
... reactant(s) in g; cp is the specific heat capacity of the water or dilute solution(s) of reactants in in J/g•°C; and ∆t is the change in temperature. The change in temperature is measured by finding the difference between the initial temperature of the system and the highest temperature reached duri ...
... reactant(s) in g; cp is the specific heat capacity of the water or dilute solution(s) of reactants in in J/g•°C; and ∆t is the change in temperature. The change in temperature is measured by finding the difference between the initial temperature of the system and the highest temperature reached duri ...
Document
... Sign Convention for w Recall from Chapter 6 that w = –PDV. When the system expands, DV is positive, so w is negative. The system does work on the surroundings, which decreases the internal energy of the system. When the system contracts, DV is negative, so w is positive. The surroundings do work on ...
... Sign Convention for w Recall from Chapter 6 that w = –PDV. When the system expands, DV is positive, so w is negative. The system does work on the surroundings, which decreases the internal energy of the system. When the system contracts, DV is negative, so w is positive. The surroundings do work on ...
No Slide Title - McMaster Chemistry
... STRONG ACIDS - react completely with water to form H3O+ (aq) HCl (aq) + H2O H3O+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) STRONG BASES - react completely with water to form OH- (aq) Li2O + H2O 2 Li+ (aq) + OH- (aq) Weak ACIDS/ weak BASES only react partially with water - an EQUILIBRIUM is formed : the conjugate ACID and ...
... STRONG ACIDS - react completely with water to form H3O+ (aq) HCl (aq) + H2O H3O+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) STRONG BASES - react completely with water to form OH- (aq) Li2O + H2O 2 Li+ (aq) + OH- (aq) Weak ACIDS/ weak BASES only react partially with water - an EQUILIBRIUM is formed : the conjugate ACID and ...
Lecture notes
... system then the energy of the system and its surroundings change. Within a chemical system the sum of all kinetic and potential energy, or total energy is called the internal energy, Eint or U. A system contains only internal enemy and not heat and work, which are the means for energy transfer betwe ...
... system then the energy of the system and its surroundings change. Within a chemical system the sum of all kinetic and potential energy, or total energy is called the internal energy, Eint or U. A system contains only internal enemy and not heat and work, which are the means for energy transfer betwe ...
AH 2015 incl MG
... Some zinc metal is added to a flask containing an acidified solution of the dioxovanadium(V) ion, VO2+(aq). The flask is stoppered with some cotton wool and gently swirled. The colour of the solution turns from yellow to blue. Further swirling turns the solution from blue to green. Finally, the flas ...
... Some zinc metal is added to a flask containing an acidified solution of the dioxovanadium(V) ion, VO2+(aq). The flask is stoppered with some cotton wool and gently swirled. The colour of the solution turns from yellow to blue. Further swirling turns the solution from blue to green. Finally, the flas ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.