Guide to Chapter 17. Thermodynamics
... T/F a. All endothermic reactions are non-spontaneous. T/F b. When DH and DS are both positive, the reaction is non-spontaneous at all temperatures. T/F c. DS for vaporization is always positive. T/F d. DS for melting is always positive. T/F e. DH for vaporization is always positive. T/F f. If DH and ...
... T/F a. All endothermic reactions are non-spontaneous. T/F b. When DH and DS are both positive, the reaction is non-spontaneous at all temperatures. T/F c. DS for vaporization is always positive. T/F d. DS for melting is always positive. T/F e. DH for vaporization is always positive. T/F f. If DH and ...
File - Science with Mr. Louie
... In chemistry, we often use numbers that are either very large (1 mole = 602 200 000 000 000 000 000 000 atoms) or very small (the mass of an electron = 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 910 939 kg). Writing numbers with so many digits would be tedious and difficult. To make writing very larg ...
... In chemistry, we often use numbers that are either very large (1 mole = 602 200 000 000 000 000 000 000 atoms) or very small (the mass of an electron = 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 910 939 kg). Writing numbers with so many digits would be tedious and difficult. To make writing very larg ...
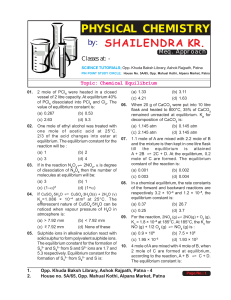
Chemical Equilibrium - Shailendra Kumar Chemistry
... CO(g) + Cl 2 (g) are simultaneously in equilibrium in a vessel at constant volume. If some CO is introduced into the vessel then at the new equilibrium the concentration of : (a) PCl5 is greater (b) PCl3 remains unchanged (c) PCl5 is less ...
... CO(g) + Cl 2 (g) are simultaneously in equilibrium in a vessel at constant volume. If some CO is introduced into the vessel then at the new equilibrium the concentration of : (a) PCl5 is greater (b) PCl3 remains unchanged (c) PCl5 is less ...
Chemistry II Aqueous Reactions and Solution Chemistry Chapter 4
... the anions are surrounded by the water molecules so that the hydrogen side of the molecule surrounds the anion. The cations are surrounded by the oxygen side of the water molecule. This configuration stabilizes the ions in ...
... the anions are surrounded by the water molecules so that the hydrogen side of the molecule surrounds the anion. The cations are surrounded by the oxygen side of the water molecule. This configuration stabilizes the ions in ...
5 pancakes 2 eggs
... that is used up during the reaction, i.e. limiting reactant. One bicycle needs 1 frame, 1 seat and 2 wheels, therefore not more than 3 bicycles can be made. The number of seats is the limiting part (reactant); one frame and two wheels are parts in excess; 3 bicycles is the yield. ...
... that is used up during the reaction, i.e. limiting reactant. One bicycle needs 1 frame, 1 seat and 2 wheels, therefore not more than 3 bicycles can be made. The number of seats is the limiting part (reactant); one frame and two wheels are parts in excess; 3 bicycles is the yield. ...
1 [Turn Over Section A For each question there are four possible
... No other combination of statements is used as a correct response. 36. Use of the Data Booklet is relevant to this question. When iron filings are added to nitric acid, a yellow solution and nitrogen dioxide gas are formed. On the addition of ammonium thiocyanate to the resultant solution, a bloodred ...
... No other combination of statements is used as a correct response. 36. Use of the Data Booklet is relevant to this question. When iron filings are added to nitric acid, a yellow solution and nitrogen dioxide gas are formed. On the addition of ammonium thiocyanate to the resultant solution, a bloodred ...
File
... Therefore enzymes are catalysts because they speed up biochemical reactions • We need enzymes for every process that happens in our bodies! e.g. Digesting food, replicating DNA ...
... Therefore enzymes are catalysts because they speed up biochemical reactions • We need enzymes for every process that happens in our bodies! e.g. Digesting food, replicating DNA ...
atom - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... The atomic theory /1 Dalton developed the first atomic theory in order to explain the law of conservation of mass, the law of definite and constant proportions and the law of multiple proportions. According to the first atomic theory, matter is made up of small atoms that cannot be created, divided ...
... The atomic theory /1 Dalton developed the first atomic theory in order to explain the law of conservation of mass, the law of definite and constant proportions and the law of multiple proportions. According to the first atomic theory, matter is made up of small atoms that cannot be created, divided ...
Common Student Misconceptions
... Compounds that do not contain OH– ions can also be bases. • Proton transfer between NH3 (a weak base) and water (a weak acid) is an example of an acid-base reaction. • Since there is a mixture of NH3, H2O, NH4+, and OH– in solution, we write NH3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇋ NH4+(aq) + OH–(aq) ...
... Compounds that do not contain OH– ions can also be bases. • Proton transfer between NH3 (a weak base) and water (a weak acid) is an example of an acid-base reaction. • Since there is a mixture of NH3, H2O, NH4+, and OH– in solution, we write NH3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇋ NH4+(aq) + OH–(aq) ...
Acrobat () verson
... (a) Because acetic acid is present in excess, the maximum number of moles of aspirin that can be produced is limited by the number of moles of salicylic acid. The number of moles of salicylic acid = (6.22 g)/(138.12 g mol–1) = 0.045 mol. Thus, from the stoichiometry of the reaction, the maximum numb ...
... (a) Because acetic acid is present in excess, the maximum number of moles of aspirin that can be produced is limited by the number of moles of salicylic acid. The number of moles of salicylic acid = (6.22 g)/(138.12 g mol–1) = 0.045 mol. Thus, from the stoichiometry of the reaction, the maximum numb ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
The Mole
... • Precisely,1/12 the mass of an atom of carbon12. The carbon-12 (C-12) atom has six protons and six neutrons in its nucleus. • In imprecise terms, one AMU is the average of the proton rest mass and the neutron rest mass. This is approximately 1.67377 x 10 -27 kilogram (kg), or 1.67377 x 10 -24 gram ...
... • Precisely,1/12 the mass of an atom of carbon12. The carbon-12 (C-12) atom has six protons and six neutrons in its nucleus. • In imprecise terms, one AMU is the average of the proton rest mass and the neutron rest mass. This is approximately 1.67377 x 10 -27 kilogram (kg), or 1.67377 x 10 -24 gram ...
Chapter 7: Recent advances in enzyme technology
... enzyme-catalysed reactions. One major factor must first be addressed; the stability of the enzyme in these systems. A distinction should be drawn between the more water-soluble hydrophilic enzymes and the more hydrophobic enzymes often associated with lipid and membranes (e.g. lipases). The active i ...
... enzyme-catalysed reactions. One major factor must first be addressed; the stability of the enzyme in these systems. A distinction should be drawn between the more water-soluble hydrophilic enzymes and the more hydrophobic enzymes often associated with lipid and membranes (e.g. lipases). The active i ...
PRACTICE EXAM for FALL 2013 FINAL EXAM (Unit 6 + review) 1
... °C. What is the volume of the cold balloon? The pressure and amount of gas remain constant. b. A small gas cylinder contains 3.22 L of argon at 11.7 atm pressure. What is the volume of the gas at 1.05 atm? Assume temperature and amount of gas remain constant. c. 325 mL of air at room pressure (765 m ...
... °C. What is the volume of the cold balloon? The pressure and amount of gas remain constant. b. A small gas cylinder contains 3.22 L of argon at 11.7 atm pressure. What is the volume of the gas at 1.05 atm? Assume temperature and amount of gas remain constant. c. 325 mL of air at room pressure (765 m ...
1984 Advanced Placement Exam
... (D) The average kinetic energy of the hydrogen molecules is the same as the average kinetic energy of the oxygen molecules. (E) The average speed of the hydrogen molecules is the same as the average speed of the oxygen molecules. 51. Pi (π) bonding occurs in each of the following species EXCEPT (A) ...
... (D) The average kinetic energy of the hydrogen molecules is the same as the average kinetic energy of the oxygen molecules. (E) The average speed of the hydrogen molecules is the same as the average speed of the oxygen molecules. 51. Pi (π) bonding occurs in each of the following species EXCEPT (A) ...
Chemistry - Benton Park School
... a) How many moles of water are needed to react with 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? b) How many moles of glucose can you make from 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? c) How many moles of oxygen can you make from 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? ...
... a) How many moles of water are needed to react with 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? b) How many moles of glucose can you make from 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? c) How many moles of oxygen can you make from 0.03 moles of carbon dioxide? ...
Fall Final Rev 2014
... °C. What is the volume of the cold balloon? The pressure and amount of gas remain constant. b. A small gas cylinder contains 3.22 L of argon at 11.7 atm pressure. What is the volume of the gas at 1.05 atm? Assume temperature and amount of gas remain constant. c. 325 mL of air at room pressure (765 m ...
... °C. What is the volume of the cold balloon? The pressure and amount of gas remain constant. b. A small gas cylinder contains 3.22 L of argon at 11.7 atm pressure. What is the volume of the gas at 1.05 atm? Assume temperature and amount of gas remain constant. c. 325 mL of air at room pressure (765 m ...
POGIL - Basic Skills Supplement - The Mole-1
... In a molecule of water (H2O), for example, there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. When combining these two elements to make water, 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 atom of oxygen must be used from each element. One mole of each element includes a specific number of atoms (see above), but because of ...
... In a molecule of water (H2O), for example, there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. When combining these two elements to make water, 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 atom of oxygen must be used from each element. One mole of each element includes a specific number of atoms (see above), but because of ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.