roman baths
... the tepidarium. The idea, as with a sauna, was for the sweat to get rid of the body's dirt. • After this a slave would rub olive oil into the visitor's skin and then scrap it off with a strigil. After this, the visitor would return to the tepidarium and then to frigidarium to cool down. Finally, he ...
... the tepidarium. The idea, as with a sauna, was for the sweat to get rid of the body's dirt. • After this a slave would rub olive oil into the visitor's skin and then scrap it off with a strigil. After this, the visitor would return to the tepidarium and then to frigidarium to cool down. Finally, he ...
History - Yaggyslatin
... Toss Up #2: Early on, Rome came into contact with this group of people who called cities such as Cerveteri, Caere, and Tarquinia home. Although the Romans wouldn’t really admit it, they were even ruled by two kings whose shared name gives away their nationality. Name this group of people from Etruri ...
... Toss Up #2: Early on, Rome came into contact with this group of people who called cities such as Cerveteri, Caere, and Tarquinia home. Although the Romans wouldn’t really admit it, they were even ruled by two kings whose shared name gives away their nationality. Name this group of people from Etruri ...
Civil Wars - Nipissing University Word
... of all the Latins those Italians who had not revolted ...
... of all the Latins those Italians who had not revolted ...
Book - sarahrswikispace
... Julius Caesar was the military and political leader of Rome who brought about the end of the Roman Republic and laid the foundations for the Roman Empire. Gaius Julius Caesar was born into one of the original patrician (upper-class) families of Rome. Although aristocratic, the family was of modest m ...
... Julius Caesar was the military and political leader of Rome who brought about the end of the Roman Republic and laid the foundations for the Roman Empire. Gaius Julius Caesar was born into one of the original patrician (upper-class) families of Rome. Although aristocratic, the family was of modest m ...
High School Literature 2.4
... The evil that men do lives after them; The good is oft interred with their bones; So let it be with Caesar. The noble Brutus Hath told you Caesar was ambitious: If it were so, it was a grievous fault, And grievously hath Caesar answer'd it. Here, under leave of Brutus and the rest-- For Brutus is an ...
... The evil that men do lives after them; The good is oft interred with their bones; So let it be with Caesar. The noble Brutus Hath told you Caesar was ambitious: If it were so, it was a grievous fault, And grievously hath Caesar answer'd it. Here, under leave of Brutus and the rest-- For Brutus is an ...
Week 7 in PowerPoint
... was deployed to besiege Masada, there to reduce the fortress by great works of engineering, including a huge ramp reaching the full height of the mountain • The entire three-year operation, and the very insignificance of its objective, must have made an ominous impression on all those in the East wh ...
... was deployed to besiege Masada, there to reduce the fortress by great works of engineering, including a huge ramp reaching the full height of the mountain • The entire three-year operation, and the very insignificance of its objective, must have made an ominous impression on all those in the East wh ...
Wednesday, Jan. 10
... was deployed to besiege Masada, there to reduce the fortress by great works of engineering, including a huge ramp reaching the full height of the mountain • The entire three-year operation, and the very insignificance of its objective, must have made an ominous impression on all those in the East wh ...
... was deployed to besiege Masada, there to reduce the fortress by great works of engineering, including a huge ramp reaching the full height of the mountain • The entire three-year operation, and the very insignificance of its objective, must have made an ominous impression on all those in the East wh ...
RRP Final Draft of Essay - 2011
... government and therefore became able to manipulate Rome’s decisions. But since the government focused on more than one person ruling at one time, it was a repetitive obstacle that blocked Caesar’s power. After successful events that pleased the Roman people he ultimately reached the title dictator, ...
... government and therefore became able to manipulate Rome’s decisions. But since the government focused on more than one person ruling at one time, it was a repetitive obstacle that blocked Caesar’s power. After successful events that pleased the Roman people he ultimately reached the title dictator, ...
Please note the embargo until 30 March 2017, 12:00 CET! Panem et
... scan of the ancient town of Carnuntum (east of Vienna, Austria) by using ground penetrating radar. This project has been undertaken on behalf of the county of Lower Austria. The scientists have revealed, without excavation, an entire city area next to the amphitheater, containing bakeries, taverns a ...
... scan of the ancient town of Carnuntum (east of Vienna, Austria) by using ground penetrating radar. This project has been undertaken on behalf of the county of Lower Austria. The scientists have revealed, without excavation, an entire city area next to the amphitheater, containing bakeries, taverns a ...
ROMAN NAMES
... When these praenomen were first used, they had a particular meaning that applied to the individual child. For example, Lucius meant “born by day”; Manius, “born in the morning.” The terms Quintus, Sextus, Decimus indicated the order of birth within a family—fifth, sixth, or tenth. The name Postumus ...
... When these praenomen were first used, they had a particular meaning that applied to the individual child. For example, Lucius meant “born by day”; Manius, “born in the morning.” The terms Quintus, Sextus, Decimus indicated the order of birth within a family—fifth, sixth, or tenth. The name Postumus ...
Ancient Empires Readings Greeks Romans Guptas
... The Greeks called themselves Hellenes. They had the same ethnic background, shared the same customs, and spoke the same basic language. However, their city-states preferred to remain independent. Nevertheless, they came together politically when threatened by an outside power—or when forced to by a ...
... The Greeks called themselves Hellenes. They had the same ethnic background, shared the same customs, and spoke the same basic language. However, their city-states preferred to remain independent. Nevertheless, they came together politically when threatened by an outside power—or when forced to by a ...
ROMANS ON DARTMOOR It is well known that the Romans had a
... it was stated ‘There is…no evidence at present for settled habitation on Dartmoor between about 400 BC and the period of the first Anglo-Saxon settlements about AD 700’, and the moor therefore remained ‘an uninhabited region for several hundred years’. Today this unlikely scenario has been radically ...
... it was stated ‘There is…no evidence at present for settled habitation on Dartmoor between about 400 BC and the period of the first Anglo-Saxon settlements about AD 700’, and the moor therefore remained ‘an uninhabited region for several hundred years’. Today this unlikely scenario has been radically ...
DaysWeeksMonthsYears..
... Scandinavian name for one of the gods of war. Tiu was related to another god known as 'Woden', also a god of war, and so we have 'Wednesday' (Woden's day). Thursday is named for 'Thor', the god of thunder. Friday is really named after Venus, the goddess of love, you'll find her in the French name fo ...
... Scandinavian name for one of the gods of war. Tiu was related to another god known as 'Woden', also a god of war, and so we have 'Wednesday' (Woden's day). Thursday is named for 'Thor', the god of thunder. Friday is really named after Venus, the goddess of love, you'll find her in the French name fo ...
MACIEJ JOŃCA, Głośne rzymskie procesy karne
... contributed to his dismissal of all the charges. An important feature of that case was probably the fact that a judge (proconsul Claudius Maximus) was a philosopher as well… It has to be said that the book is an incredible review of the Roman legal tradition and Roman intellectual formation. Althoug ...
... contributed to his dismissal of all the charges. An important feature of that case was probably the fact that a judge (proconsul Claudius Maximus) was a philosopher as well… It has to be said that the book is an incredible review of the Roman legal tradition and Roman intellectual formation. Althoug ...
Week 5 in PowerPoint - campo7.com
... passing of time) into a period of anarchy, up to the point when the failing democracy is replaced by monarchy; in turn monarchy will degenerate into tyranny, tyranny may give birth to democracy, etc. • Already some of the 15th century humanists, for example Leonardo Bruni, identified the decline of ...
... passing of time) into a period of anarchy, up to the point when the failing democracy is replaced by monarchy; in turn monarchy will degenerate into tyranny, tyranny may give birth to democracy, etc. • Already some of the 15th century humanists, for example Leonardo Bruni, identified the decline of ...
Introduction - Beck-Shop
... of Roman power in Italy. Thus, this book situates the critical policy decisions made by the ruling classes of various Italian cities, especially in the wake of Cannae, in the context of interstate behaviour and patterns of diplomacy between the communities of the peninsula stretching back to the eme ...
... of Roman power in Italy. Thus, this book situates the critical policy decisions made by the ruling classes of various Italian cities, especially in the wake of Cannae, in the context of interstate behaviour and patterns of diplomacy between the communities of the peninsula stretching back to the eme ...
Tuesday, Jan. 9
... passing of time) into a period of anarchy, up to the point when the failing democracy is replaced by monarchy; in turn monarchy will degenerate into tyranny, tyranny may give birth to democracy, etc. • Already some of the 15th century humanists, for example Leonardo Bruni, identified the decline of ...
... passing of time) into a period of anarchy, up to the point when the failing democracy is replaced by monarchy; in turn monarchy will degenerate into tyranny, tyranny may give birth to democracy, etc. • Already some of the 15th century humanists, for example Leonardo Bruni, identified the decline of ...
10 Dates in Church History
... ► 435 AD, Attila rises to power that began his westward conquest of Europe. ► As Europe fell, Attila became feared as the “Scourge of God.” ► 452 AD, Attila invades the peninsula of Italy and demands that Rome pay tribute in exchange for ...
... ► 435 AD, Attila rises to power that began his westward conquest of Europe. ► As Europe fell, Attila became feared as the “Scourge of God.” ► 452 AD, Attila invades the peninsula of Italy and demands that Rome pay tribute in exchange for ...
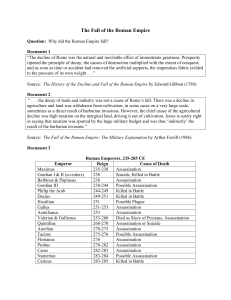
The Fall of the Roman Empire
... seem heavy since the soldiers rarely ever wore it. Therefore, they first asked the emperor to set aside the breastplates . . . and then the helmets. So our soldiers fought the Goths without any protection for chest and head and were often beaten by archers. Although there were many disasters, which ...
... seem heavy since the soldiers rarely ever wore it. Therefore, they first asked the emperor to set aside the breastplates . . . and then the helmets. So our soldiers fought the Goths without any protection for chest and head and were often beaten by archers. Although there were many disasters, which ...
A Tale of Two Cults: A Comparison of the Cults of Magna Mater and
... the “traditional” Roman pantheon, different cults and deities garnered remarkably different receptions from the official religious establishment of Rome. An example of two similar cults which were treated very differently can be found in a comparison of the cults of Magna Mater and Bacchus, two cult ...
... the “traditional” Roman pantheon, different cults and deities garnered remarkably different receptions from the official religious establishment of Rome. An example of two similar cults which were treated very differently can be found in a comparison of the cults of Magna Mater and Bacchus, two cult ...