file
... custom baits of RNA probed following paired-end sequencing by HiSeq2500 (Illumina Inc.). The Guardant360 NGS panel targeted region was 78,000 base pairs (78 kbp) per sample and each base was sequenced at average raw coverage depth of 8,000X with minimum average base coverage of 3,000X.20 The failure ...
... custom baits of RNA probed following paired-end sequencing by HiSeq2500 (Illumina Inc.). The Guardant360 NGS panel targeted region was 78,000 base pairs (78 kbp) per sample and each base was sequenced at average raw coverage depth of 8,000X with minimum average base coverage of 3,000X.20 The failure ...
Genetic Engineering - University of Rhode Island
... finding ways to create new physiological and physical characteristics. To carry out this “gene splicing”, first the section of the DNA containing the gene must be isolated and then cut out. The sequence is then modified as needed. Then it is spliced into a different DNA segment or into a vector (org ...
... finding ways to create new physiological and physical characteristics. To carry out this “gene splicing”, first the section of the DNA containing the gene must be isolated and then cut out. The sequence is then modified as needed. Then it is spliced into a different DNA segment or into a vector (org ...
No Slide Title
... One out of ten Americans (11%) had no idea at all what DNA is. Based on everything you know, what is DNA? Would it be: ...
... One out of ten Americans (11%) had no idea at all what DNA is. Based on everything you know, what is DNA? Would it be: ...
Life Science Vocabulary.xlsx
... an organism that always produces an offspring with the same form of a trait as the purebred parent trait a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes allele the different forms of a gene Rosalind Franklin famous woman scientist who used x-rays to photograph DNA mo ...
... an organism that always produces an offspring with the same form of a trait as the purebred parent trait a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes allele the different forms of a gene Rosalind Franklin famous woman scientist who used x-rays to photograph DNA mo ...
Word Definition Synonym 1 DNA replication the
... an organism that always produces an offspring with the same form of a trait as the purebred parent trait a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes allele the different forms of a gene Rosalind Franklin famous woman scientist who used x-rays to photograph DNA mo ...
... an organism that always produces an offspring with the same form of a trait as the purebred parent trait a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes allele the different forms of a gene Rosalind Franklin famous woman scientist who used x-rays to photograph DNA mo ...
1methods
... purified from the feces as previously described 6. To generate DNA, the isolate was expanded in neonatal calves 1. DNA was purified from surface-sterilized oocysts 7, shotgun and BAC clones were constructed, and end sequences were generated as previously described 8. The analysis herein was performe ...
... purified from the feces as previously described 6. To generate DNA, the isolate was expanded in neonatal calves 1. DNA was purified from surface-sterilized oocysts 7, shotgun and BAC clones were constructed, and end sequences were generated as previously described 8. The analysis herein was performe ...
Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Chapter7
... kpb DNA fragments.There are alsoa variety of artificial chromosome vectors available including P1-derived artificial chromosomes (PACs) that carry up to 300 kpb fragments, bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) that carry fragments of 300 kpb and greater, and yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs, des ...
... kpb DNA fragments.There are alsoa variety of artificial chromosome vectors available including P1-derived artificial chromosomes (PACs) that carry up to 300 kpb fragments, bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) that carry fragments of 300 kpb and greater, and yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs, des ...
Biological Context
... Outcomes may not be black-andwhite since one trait can be affected by many genes or variants (polygenic or quantitative trait) ...
... Outcomes may not be black-andwhite since one trait can be affected by many genes or variants (polygenic or quantitative trait) ...
ASviewer: Visualizing the transcript structure and functional
... Summary: Alternative splicing (AS) produces diverse transcript structures by differential use of splice sites. Comparing the gene structure and functional domains of splice variants is an essential but nontrivial task with numerous gene predictions available publicly. We developed a novel viewer (AS ...
... Summary: Alternative splicing (AS) produces diverse transcript structures by differential use of splice sites. Comparing the gene structure and functional domains of splice variants is an essential but nontrivial task with numerous gene predictions available publicly. We developed a novel viewer (AS ...
name period ______ date
... 3. What is the name of the enzyme that breaks the nitrogen bases apart to get them ready for replication? 4. What is the name given to the point where replication starts on a DNA molecule? 5. How does the replicated daughter molecule of DNA compare to the parent molecule of DNA? 6. What would the co ...
... 3. What is the name of the enzyme that breaks the nitrogen bases apart to get them ready for replication? 4. What is the name given to the point where replication starts on a DNA molecule? 5. How does the replicated daughter molecule of DNA compare to the parent molecule of DNA? 6. What would the co ...
Chapter 9: Gene Transfer, Genetic Engineering, and Genomics
... f. Explain the unique place of the virus in the process of bacterial transduction, and compare in detail generalized transduction and specialized transduction. g. Identify the decisive pieces of research that permitted scientists to develop the process of genetic engineering. h. Describe in detail t ...
... f. Explain the unique place of the virus in the process of bacterial transduction, and compare in detail generalized transduction and specialized transduction. g. Identify the decisive pieces of research that permitted scientists to develop the process of genetic engineering. h. Describe in detail t ...
LIFE: ITS CHARACTERISTICS AND STUDY Biology is the study of
... A letter in a textbook can be represented by 6 bits. An average book page contains about 3,000 characters 3,000 characters / page x 6 bits / character = 18,000 bits / page 6,000,000,000 / 18,000 = 333,333 pages This is approximately how much information is contained in every cell of a human being. ...
... A letter in a textbook can be represented by 6 bits. An average book page contains about 3,000 characters 3,000 characters / page x 6 bits / character = 18,000 bits / page 6,000,000,000 / 18,000 = 333,333 pages This is approximately how much information is contained in every cell of a human being. ...
Warheit#2
... with acoustic transmitters, and we defined survival as a fish’s detection at Strait of Juan de Fuca (JDF) acoustic detection array. We genotyped the fish using restriction-site associated DNA (RAD) sequences (RAD-seq). RAD-seq is a genome complexity reduction technique that generally produces 1000s ...
... with acoustic transmitters, and we defined survival as a fish’s detection at Strait of Juan de Fuca (JDF) acoustic detection array. We genotyped the fish using restriction-site associated DNA (RAD) sequences (RAD-seq). RAD-seq is a genome complexity reduction technique that generally produces 1000s ...
The Human Genome Project
... Analysis of RFLP variation in genomes was a vital tool in genome mapping and genetic disease analysis. If researchers were trying to initially determine the chromosomal location of a particular disease gene, they would analyze the DNA of members of a family afflicted by the disease, and look for RFL ...
... Analysis of RFLP variation in genomes was a vital tool in genome mapping and genetic disease analysis. If researchers were trying to initially determine the chromosomal location of a particular disease gene, they would analyze the DNA of members of a family afflicted by the disease, and look for RFL ...
Slide 1
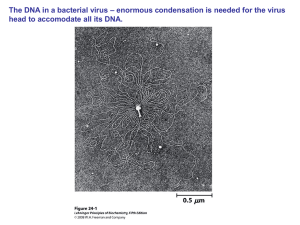
... The DNA in a bacterial virus – enormous condensation is needed for the virus head to accomodate all its DNA. ...
... The DNA in a bacterial virus – enormous condensation is needed for the virus head to accomodate all its DNA. ...
a@%,,$, 03%
... 17. Which enzyme is correctly matched with its function? (A) restriction enzyme: severs DNA at specific nucleotide sequences called restriction sites (B) restriction endonuclease: glues the two strands of DNA back together after replication (C) DNA ligase: cuts plasmid DNA in bacterial cells into o ...
... 17. Which enzyme is correctly matched with its function? (A) restriction enzyme: severs DNA at specific nucleotide sequences called restriction sites (B) restriction endonuclease: glues the two strands of DNA back together after replication (C) DNA ligase: cuts plasmid DNA in bacterial cells into o ...
PDF file of the lecture on "Gene Transfer"
... own transfer • ConjugaAon requires cell to cell contact between two cells of opposite ma4ng type (donor: F+ and recipient: F-‐) ...
... own transfer • ConjugaAon requires cell to cell contact between two cells of opposite ma4ng type (donor: F+ and recipient: F-‐) ...
Binary Ti vector plasmids
... plasmids resident in the A.t. Strain • The T-DNA , within which are the gene(s) to be transferred, is provided on the vector • Most binary Ti vectors replicate in both E. Coli and A.t. ...
... plasmids resident in the A.t. Strain • The T-DNA , within which are the gene(s) to be transferred, is provided on the vector • Most binary Ti vectors replicate in both E. Coli and A.t. ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.