3 Intro to Restriction Enzymes
... • So how does DNA get from one species to another? • Vector: something used to transfer DNA from one organism to another ...
... • So how does DNA get from one species to another? • Vector: something used to transfer DNA from one organism to another ...
Some abandoned Chinese patent applications
... mixture contains either Panax ginseng or P. quinquefolius. To generate reproducible RAPD fingerprints, high-quality genomic DNA is required. However, RAPD fingerprints have been shown to vary with ...
... mixture contains either Panax ginseng or P. quinquefolius. To generate reproducible RAPD fingerprints, high-quality genomic DNA is required. However, RAPD fingerprints have been shown to vary with ...
No Slide Title
... • Utilizes microbiological selection and screening procedures to isolate a gene that represents as little as 1 part in a million of the genetic material in an organism. ...
... • Utilizes microbiological selection and screening procedures to isolate a gene that represents as little as 1 part in a million of the genetic material in an organism. ...
GENETIC AND PHYSICAL MAPS OF GENE Bph
... gene Bph-10 which control the resistance to brown plant hopper (biotype 2+3). Advanced mapping population derived from a cross of IR31917-45-3-2 / IR54742 in which recurrent line is female parent, and IR54742 is a derivative line from Oryza officinalis, as a donor. Through bulked segregant and linka ...
... gene Bph-10 which control the resistance to brown plant hopper (biotype 2+3). Advanced mapping population derived from a cross of IR31917-45-3-2 / IR54742 in which recurrent line is female parent, and IR54742 is a derivative line from Oryza officinalis, as a donor. Through bulked segregant and linka ...
Transgenic_Organisms_Chocolate_Cherries
... do? You turn to biotechnology! By combining DNA that contains the desired trait with the organism’s DNA, scientists allow that organism to express that desired trait. Your Task: You must alter the DNA of a cherry tree so that it bears fruit that has a chocolate flavor. You have already isolated a ge ...
... do? You turn to biotechnology! By combining DNA that contains the desired trait with the organism’s DNA, scientists allow that organism to express that desired trait. Your Task: You must alter the DNA of a cherry tree so that it bears fruit that has a chocolate flavor. You have already isolated a ge ...
Linkage map - Cloudfront.net
... Since both DNA and vector were cleaved with same restriction enzyme, both ends will match ...
... Since both DNA and vector were cleaved with same restriction enzyme, both ends will match ...
BioSc 231 Exam 5 2003
... Multiple Choice. (2 points each) _____ For gene cloning, a geneticist digests DNA with ___ an enzyme that cleaves DNA at sequence-specific sites. A. DNA polymerase B. ligase C. restriction endonuclease D. sticky ends E. cDNA _____ Certain endonucleases cut DNA and leave DNA termini without overhangs ...
... Multiple Choice. (2 points each) _____ For gene cloning, a geneticist digests DNA with ___ an enzyme that cleaves DNA at sequence-specific sites. A. DNA polymerase B. ligase C. restriction endonuclease D. sticky ends E. cDNA _____ Certain endonucleases cut DNA and leave DNA termini without overhangs ...
CRACKING THE CODE OF LIFE QUESTIONS
... 1. What % of genes in a banana are found in us? 2. How many more genes do humans have than fruit flies? 3. How long did they predict it would take to decode the human genome? 4. What does Tay Sachs disease do to a babies’ brain? 5. Who does a child get the gene for Tay Sachs from? 6. What was slowin ...
... 1. What % of genes in a banana are found in us? 2. How many more genes do humans have than fruit flies? 3. How long did they predict it would take to decode the human genome? 4. What does Tay Sachs disease do to a babies’ brain? 5. Who does a child get the gene for Tay Sachs from? 6. What was slowin ...
Gene
... Genes close together on same chromosome tend to be inherited together and show linkage In 1936, hemophilia and color blindness found to be linked, both on X chromosome Difficult to map genes on autosomes, requires very large families with two specific genetic traits ...
... Genes close together on same chromosome tend to be inherited together and show linkage In 1936, hemophilia and color blindness found to be linked, both on X chromosome Difficult to map genes on autosomes, requires very large families with two specific genetic traits ...
Reproductive cloning
... – restriction enzymes bind to specific short sequences on the DNA and make a specific cut • the sequence is symmetrical • the cut generates DNA fragments that are “sticky” ...
... – restriction enzymes bind to specific short sequences on the DNA and make a specific cut • the sequence is symmetrical • the cut generates DNA fragments that are “sticky” ...
Concept 18.3. How get genetic variation in prokaryotes: • E. coli is
... - A prophage picks up a few adjacent genes as it leaves and transfers to a new host. - Transfer only of adjacent genes. ...
... - A prophage picks up a few adjacent genes as it leaves and transfers to a new host. - Transfer only of adjacent genes. ...
Biology Final Exam
... 5. What would be the complementary sequence of nucleotides for an mRNA molecule on the original DNA strand above? 6. In RNA, thymine is replaced by ________________. 7. What would be the amino acid sequence translated from the following mRNA sequence: CCAGUUAGG? 8. What is a point mutation? 9. The H ...
... 5. What would be the complementary sequence of nucleotides for an mRNA molecule on the original DNA strand above? 6. In RNA, thymine is replaced by ________________. 7. What would be the amino acid sequence translated from the following mRNA sequence: CCAGUUAGG? 8. What is a point mutation? 9. The H ...
three possibile models for replication
... 17) They can cause infected cells to produce toxins that lead to disease symptoms 18) Vaccines = harmless derivatives of viruses that stimulate the immune system to mount defenses against the actual pathogen (in the form of antibodies) … can be used to prevent certain viral illnesses Why are bacteri ...
... 17) They can cause infected cells to produce toxins that lead to disease symptoms 18) Vaccines = harmless derivatives of viruses that stimulate the immune system to mount defenses against the actual pathogen (in the form of antibodies) … can be used to prevent certain viral illnesses Why are bacteri ...
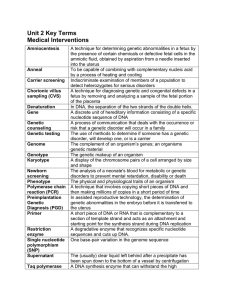
Unit 2 Terms
... A technique for determining genetic abnormalities in a fetus by the presence of certain chemicals or defective fetal cells in the amniotic fluid, obtained by aspiration from a needle inserted into the uterus To be capable of combining with complementary nucleic acid by a process of heating and cooli ...
... A technique for determining genetic abnormalities in a fetus by the presence of certain chemicals or defective fetal cells in the amniotic fluid, obtained by aspiration from a needle inserted into the uterus To be capable of combining with complementary nucleic acid by a process of heating and cooli ...
Chapter 12
... 4. What is the purpose of the “first stop” on the micropipettor? 5. What is the purpose of the “second stop?” 6. What is a restriction enzyme? 7. What is a plasmid? 8. Gel electrophoresis separates molecules based on what 2 properties? (Circle which property used in the Lab) 9. Why does DNA move tow ...
... 4. What is the purpose of the “first stop” on the micropipettor? 5. What is the purpose of the “second stop?” 6. What is a restriction enzyme? 7. What is a plasmid? 8. Gel electrophoresis separates molecules based on what 2 properties? (Circle which property used in the Lab) 9. Why does DNA move tow ...
Southern Blotting
... • Moreover, RFLP is a sequence of DNA that has a restriction site on each end with a "target" sequence in between. A target sequence is any segment of DNA that bind to a probe by forming complementary base pair. • RFLP can be used to detect certain deleterious diseases, such as, sickle cell anemia, ...
... • Moreover, RFLP is a sequence of DNA that has a restriction site on each end with a "target" sequence in between. A target sequence is any segment of DNA that bind to a probe by forming complementary base pair. • RFLP can be used to detect certain deleterious diseases, such as, sickle cell anemia, ...
Gene Therapy
... a mixture of DNA fragments is placed at one end of a gel and an electric current is run through the gel DNA molecules which are negatively charged move toward the positive end of the gel; the smaller the fragment of DNA the faster and farther it moves ...
... a mixture of DNA fragments is placed at one end of a gel and an electric current is run through the gel DNA molecules which are negatively charged move toward the positive end of the gel; the smaller the fragment of DNA the faster and farther it moves ...
Biology Test Chapters 13 Name and Honor Code: 1. The insertion of
... c. gene therapy d. genetic engineering 5. Organisms that are genetically engineered by inserting a gene from another organism are known as: a. clones b. autosomes c. vectors d. transgenic organisms 6. The process by which desired traits of certain plants & animals are selected and passed on to their ...
... c. gene therapy d. genetic engineering 5. Organisms that are genetically engineered by inserting a gene from another organism are known as: a. clones b. autosomes c. vectors d. transgenic organisms 6. The process by which desired traits of certain plants & animals are selected and passed on to their ...
View PDF
... - A prophage picks up a few adjacent genes as it leaves and transfers to a new host. - Transfer only of adjacent genes. ...
... - A prophage picks up a few adjacent genes as it leaves and transfers to a new host. - Transfer only of adjacent genes. ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.