ANSWER KEY BIO SOL Review 16 - DNA - RNA
... 10. (2005-43) Which of these is most responsible for carrying coded information from the nucleus? a. mRNA b. The ribosomes c. ATP d. The cell membrane 11. (2005-13) Tissue samples taken from the heart and stomach of a grasshopper would be expected to have the same — a. metabolic rates b. cell shape ...
... 10. (2005-43) Which of these is most responsible for carrying coded information from the nucleus? a. mRNA b. The ribosomes c. ATP d. The cell membrane 11. (2005-13) Tissue samples taken from the heart and stomach of a grasshopper would be expected to have the same — a. metabolic rates b. cell shape ...
BIO SOL Review 16
... 10. (2005-43) Which of these is most responsible for carrying coded information from the nucleus? a. mRNA b. The ribosomes c. ATP d. The cell membrane 11. (2005-13) Tissue samples taken from the heart and stomach of a grasshopper would be expected to have the same — a. metabolic rates b. cell shape ...
... 10. (2005-43) Which of these is most responsible for carrying coded information from the nucleus? a. mRNA b. The ribosomes c. ATP d. The cell membrane 11. (2005-13) Tissue samples taken from the heart and stomach of a grasshopper would be expected to have the same — a. metabolic rates b. cell shape ...
CH 20 DNA TECHNOLOGY - Ed W. Clark High School
... 3. stain gel then put under UV light 4. if banding patterns match, the same segment of DNA was placed into each well C. SOUTHERN BLOTTING 1. run a gel electrophoresis on samples to produce a smear of bands 2. place the gel in an alkaline solution with nitrocellulose paper on top and paper towels on ...
... 3. stain gel then put under UV light 4. if banding patterns match, the same segment of DNA was placed into each well C. SOUTHERN BLOTTING 1. run a gel electrophoresis on samples to produce a smear of bands 2. place the gel in an alkaline solution with nitrocellulose paper on top and paper towels on ...
What is Willy Wonka famous for?
... Who worked for him? • Oompa Loompas • They’re reaching retirement age! ...
... Who worked for him? • Oompa Loompas • They’re reaching retirement age! ...
DNA/RNA Worksheet TACGGCACCGTTAGGATT
... What sugar is present in DNA? _____________________________________________________ ...
... What sugar is present in DNA? _____________________________________________________ ...
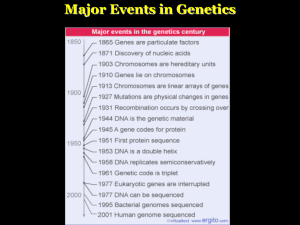
Major Events in Genetics
... A gene is a genetic sequence that codes for an RNA. In protein coding genes, the RNA codes for a protein. ...
... A gene is a genetic sequence that codes for an RNA. In protein coding genes, the RNA codes for a protein. ...
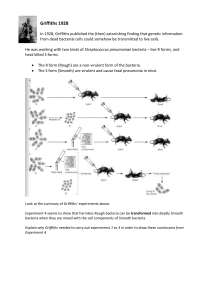
DNA experiments exercise
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
Exp 4 Lecture - Seattle Central College
... In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. • Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Genetic engineering involves inserting genes coding for new traits into a plasmid. • In this experiment, the pGLO plasmi ...
... In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. • Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Genetic engineering involves inserting genes coding for new traits into a plasmid. • In this experiment, the pGLO plasmi ...
Gene Technology
... Where do you “paste” the cut DNA? Vector- an agent used to carry the desired gene into another cell. Plasmid- type of vector; circular DNA molecule found in ...
... Where do you “paste” the cut DNA? Vector- an agent used to carry the desired gene into another cell. Plasmid- type of vector; circular DNA molecule found in ...
DNA - Angioma Alliance
... An inherited mutation will make a faulty protein in every cell where that protein is normally found. This will affect those parts of the body that contain the cells that make the faulty protein. ...
... An inherited mutation will make a faulty protein in every cell where that protein is normally found. This will affect those parts of the body that contain the cells that make the faulty protein. ...
Genetics 101 - People @ EECS at UC Berkeley
... • RNA polymerase (also called transcriptase) binds to DNA at promoter • RNA polymerase reads single strand of DNA and synthesizes corresponding single-stranded messenger RNA (mRNA) • RNA is similar to DNA • uses ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose • uses uracil (U) base instead of thymine ...
... • RNA polymerase (also called transcriptase) binds to DNA at promoter • RNA polymerase reads single strand of DNA and synthesizes corresponding single-stranded messenger RNA (mRNA) • RNA is similar to DNA • uses ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose • uses uracil (U) base instead of thymine ...
Biology Study Guide CH 12 Part I DNA-RNA
... 7. DNA is copied during a process called __________________. 8. DNA _____________ results in 2 DNA molecules, each consisting of one new strand & one original strand. 9. Be sure that you understand base pairing and can give the sequence of a complementary DNA strand. 10. Where is DNA located in a eu ...
... 7. DNA is copied during a process called __________________. 8. DNA _____________ results in 2 DNA molecules, each consisting of one new strand & one original strand. 9. Be sure that you understand base pairing and can give the sequence of a complementary DNA strand. 10. Where is DNA located in a eu ...
PCR - share1
... PCR: polymerase chain reaction -used to amplify DNA samples for fingerprinting, sequencing, or further genetic manipulation. - isolate segment of interest - warm to denature - cool to anneal primer - allow polymerase to proceed -“Taq” polymerase* - Each cycle doubles the DNA. DNA from as few as 20 ...
... PCR: polymerase chain reaction -used to amplify DNA samples for fingerprinting, sequencing, or further genetic manipulation. - isolate segment of interest - warm to denature - cool to anneal primer - allow polymerase to proceed -“Taq” polymerase* - Each cycle doubles the DNA. DNA from as few as 20 ...
Biology Spring Semester Final Exam Review
... 28. What do restriction enzymes do and why are they important for studying the human genome? 29. What is the Human Genome Project? Ch. 15 30. What is inbreeding and why can it be disadvantageous? 31. What is selective breeding of animals used for? 32. What happens to recombinant bacteria that contai ...
... 28. What do restriction enzymes do and why are they important for studying the human genome? 29. What is the Human Genome Project? Ch. 15 30. What is inbreeding and why can it be disadvantageous? 31. What is selective breeding of animals used for? 32. What happens to recombinant bacteria that contai ...
tggccatcgtaaggtgcgacc ggtagca
... Name: _____________________ DNA vs. Genes vs. Chromosomes Definitions 1. DNA is a nucleic acid that contains the sequence for all our traits. 2. Genes are sections of DNA that code for a particular trait. 3. Chromosomes are condensed DNA fibers, each containing several genes ...
... Name: _____________________ DNA vs. Genes vs. Chromosomes Definitions 1. DNA is a nucleic acid that contains the sequence for all our traits. 2. Genes are sections of DNA that code for a particular trait. 3. Chromosomes are condensed DNA fibers, each containing several genes ...
548475Review_guide_ch_5
... a. Inbreeding b. selective breeding c. DNA fingerprinting d. genetic engineering 5. An organism that has the same genes as the organism from which it was produced is called a a. clone ...
... a. Inbreeding b. selective breeding c. DNA fingerprinting d. genetic engineering 5. An organism that has the same genes as the organism from which it was produced is called a a. clone ...
Repeated DNA sequences - lecture 1
... Two of these (CAG and CCG) are involved in human genetic disease. In the genes that contain them, the copy number (n) of the repeat is variable. If n<40, there are no symptoms. But if n>50, symptoms of the disease start to show (these thresholds are slightly different in different diseases). In many ...
... Two of these (CAG and CCG) are involved in human genetic disease. In the genes that contain them, the copy number (n) of the repeat is variable. If n<40, there are no symptoms. But if n>50, symptoms of the disease start to show (these thresholds are slightly different in different diseases). In many ...
Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA
... -easy to find one that cuts your target DNA and cloning vector ...
... -easy to find one that cuts your target DNA and cloning vector ...
BICH/GENE 431 KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Chapter 22 – Model
... BICH/GENE 431 KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Chapter 22 – Model Organisms Reasons to use model organisms in molecular genetics research Bacteria and Bacteriophages (phages) - advantages: small genomes, single cell, grow fast, facile genetics, can grow large quantities for biochemical experiments - compare lyt ...
... BICH/GENE 431 KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Chapter 22 – Model Organisms Reasons to use model organisms in molecular genetics research Bacteria and Bacteriophages (phages) - advantages: small genomes, single cell, grow fast, facile genetics, can grow large quantities for biochemical experiments - compare lyt ...
Biotechnology Lab
... Competent cells • Transformation rate in normal cells is low • Transformation rate in competent cells is ...
... Competent cells • Transformation rate in normal cells is low • Transformation rate in competent cells is ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.