LIF, human, recombinant
... commercial source. The bioactivity of ISOkine™ human LIF was determined by its ability to induce proliferation of TF-1cells in a dose dependent manner. The ED50 value for this effect is typically below 0.4 ng/ml corresponding to specific activity of >2.5 x 10e6 U/mg. Optimal concentration should be ...
... commercial source. The bioactivity of ISOkine™ human LIF was determined by its ability to induce proliferation of TF-1cells in a dose dependent manner. The ED50 value for this effect is typically below 0.4 ng/ml corresponding to specific activity of >2.5 x 10e6 U/mg. Optimal concentration should be ...
Protein For Athletes
... Protein requirements vary between athletes and sedentary individuals, but not by much. An upper limit of 1.7 grams/kilograms of protein per day meets the needs of even the hardest-training athletes, a 154-pound endurance athlete would need no more than 120 grams of protein per day. What are the Diff ...
... Protein requirements vary between athletes and sedentary individuals, but not by much. An upper limit of 1.7 grams/kilograms of protein per day meets the needs of even the hardest-training athletes, a 154-pound endurance athlete would need no more than 120 grams of protein per day. What are the Diff ...
Northern blot protocol for the detection of RNA in Neurospora Yi Liu
... a. Extract RNA from tissue powder 1. Harvest and grind the tissue with a mortar and pestle in liquid nitrogen. 2. Transfer powder (~200 mg) into a 1.5 ml eppendorf tube containing a mixture of 0.45 ml lysis buffer and 0.45 ml of phenol*: chloroform: IAA (25:24:1). Vertex briefly and mix on a rotator ...
... a. Extract RNA from tissue powder 1. Harvest and grind the tissue with a mortar and pestle in liquid nitrogen. 2. Transfer powder (~200 mg) into a 1.5 ml eppendorf tube containing a mixture of 0.45 ml lysis buffer and 0.45 ml of phenol*: chloroform: IAA (25:24:1). Vertex briefly and mix on a rotator ...
Chapter 3 Proteins:
... Protein Shape and Structure Levels of organization protein structure primary= aa seqeunce ► secondary= stretches of alpha helix, beta sheets ...
... Protein Shape and Structure Levels of organization protein structure primary= aa seqeunce ► secondary= stretches of alpha helix, beta sheets ...
Levels of Structural Organization Levels of Structural
... across plasma membranes • Exocytosis – moves substance from the cell interior to the extracellular space • Endocytosis – enables large particles and macromolecules to enter the cell • Receptor-mediated transport – uses clathrin-coated pits as the major mechanism for specific uptake of macromolecules ...
... across plasma membranes • Exocytosis – moves substance from the cell interior to the extracellular space • Endocytosis – enables large particles and macromolecules to enter the cell • Receptor-mediated transport – uses clathrin-coated pits as the major mechanism for specific uptake of macromolecules ...
2,3-BPG and the O 2
... longer than 50 aa peptides are first cleaved to smaller peptides with CNBr or enzymatically by trypsin/chymotrypsin (for overlap peptides) then the peptides are separated by chromatography and the peptide sequences are determined by Edman degradation; the order of the segments are determined by the ...
... longer than 50 aa peptides are first cleaved to smaller peptides with CNBr or enzymatically by trypsin/chymotrypsin (for overlap peptides) then the peptides are separated by chromatography and the peptide sequences are determined by Edman degradation; the order of the segments are determined by the ...
235 KB 3rd Aug 2015 Hemp Protein
... Four tablespoons (32g) of 43% Realhemp™ protein powder provides 125 calories, 14g of highly digestible quality protein, 9g of dietary fiber, and more than 25% of the Recommended Daily Intake (RDI) for B vitamins, iron, copper, folate, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus and zinc. Process: No heat or ch ...
... Four tablespoons (32g) of 43% Realhemp™ protein powder provides 125 calories, 14g of highly digestible quality protein, 9g of dietary fiber, and more than 25% of the Recommended Daily Intake (RDI) for B vitamins, iron, copper, folate, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus and zinc. Process: No heat or ch ...
Protein Synthesis - Quakertown Community School District
... Building Blocks of Proteins • Proteins are made of subunits called amino acids • These subunits are comprised of : – Amino group – Carboxyl group – R group is different for each amino acid ...
... Building Blocks of Proteins • Proteins are made of subunits called amino acids • These subunits are comprised of : – Amino group – Carboxyl group – R group is different for each amino acid ...
CHEM523 Final Exam Possible
... hours to complete this exam. 1) Below are seven amino acids. Indicate all characteristics that apply to each amino acid by writing the appropriate letter(s) in the blanks provided. Note: Each entry may have more than one letter associated with it. Amino acid ...
... hours to complete this exam. 1) Below are seven amino acids. Indicate all characteristics that apply to each amino acid by writing the appropriate letter(s) in the blanks provided. Note: Each entry may have more than one letter associated with it. Amino acid ...
CHAPTER 14 Vesicular Traffic, Secretion, and Endocytosis
... Phagocytosis: take up whole cell or large particle. non selective actin mediated process, extension of the membrane. marcophage Ion containing protein Pinocytosis: small droplets of extracellular fluid and any material dissolved , nonspecifically Receptor-mediated endocytosis: specific receptor invo ...
... Phagocytosis: take up whole cell or large particle. non selective actin mediated process, extension of the membrane. marcophage Ion containing protein Pinocytosis: small droplets of extracellular fluid and any material dissolved , nonspecifically Receptor-mediated endocytosis: specific receptor invo ...
Exons and Introns
... 1.DNA In eukaryotes, the genome is divided into : •Non-coding areas... between genes. •Genes : Each gene is divided into several exons, separated by non coding sequences, •Introns (not coding) •Exons (coding) •Promoters, and regulation sequences. 2.RNA polymerases RNA polymerases are enzymes that wi ...
... 1.DNA In eukaryotes, the genome is divided into : •Non-coding areas... between genes. •Genes : Each gene is divided into several exons, separated by non coding sequences, •Introns (not coding) •Exons (coding) •Promoters, and regulation sequences. 2.RNA polymerases RNA polymerases are enzymes that wi ...
Oxidative Phosphorylation - Study in Universal Science College
... is responsible for the final combination of reducing equivalents with molecular oxygen. • It has a high affinity for O2 thus allowing the respiratory chain to function at its maximum. • This is the only irreversible reaction in the chain and hence provides direction to the movement of reducing equiv ...
... is responsible for the final combination of reducing equivalents with molecular oxygen. • It has a high affinity for O2 thus allowing the respiratory chain to function at its maximum. • This is the only irreversible reaction in the chain and hence provides direction to the movement of reducing equiv ...
Leukaemia Section t(11;14)(q23;q24) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Cytogenet. 1992 Jul 15;61(2):162-4 ...
... Cytogenet. 1992 Jul 15;61(2):162-4 ...
Rabbit anti-Estrogen Receptor-β
... A 19 amino acid synthetic peptide derived from the C-terminus of the human Estrogen Receptor-β protein. SPECIFICITY This antibody is specific for the human Estrogen Receptor -β protein (~53 kDa). Antibody reactivity was confirmed by Western blotting using recombinant human Estrogen Receptor-beta and ...
... A 19 amino acid synthetic peptide derived from the C-terminus of the human Estrogen Receptor-β protein. SPECIFICITY This antibody is specific for the human Estrogen Receptor -β protein (~53 kDa). Antibody reactivity was confirmed by Western blotting using recombinant human Estrogen Receptor-beta and ...
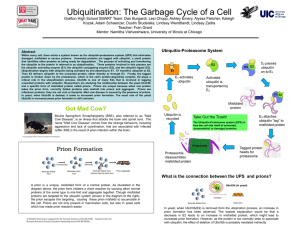
Poster
... the prion escapes this targeting, causing these prion misfolds to accumulate in the cell. Prions are not only present in mammalian cells, but also in yeast cells which has made prion research easier. ...
... the prion escapes this targeting, causing these prion misfolds to accumulate in the cell. Prions are not only present in mammalian cells, but also in yeast cells which has made prion research easier. ...
Protein Sequencing Submission Form
... A. If the peptide/protein is blocked, it will NOT be able to be sequenced, unless cleaved by enzyme(s) first. B. The only way to determine if the peptide/protein is blocked is to: 1. Conduct a tryptic digest apriori 2. Attempt to sequence, and see what happens ...
... A. If the peptide/protein is blocked, it will NOT be able to be sequenced, unless cleaved by enzyme(s) first. B. The only way to determine if the peptide/protein is blocked is to: 1. Conduct a tryptic digest apriori 2. Attempt to sequence, and see what happens ...
Biomolecules are organic molecules built and used inside of cells
... Sequence of AA determines the _______________ of the protein (folded polypeptide) The shape of the protein determines its ___________________ in the cell – Every protein has a different job or function in your cells ...
... Sequence of AA determines the _______________ of the protein (folded polypeptide) The shape of the protein determines its ___________________ in the cell – Every protein has a different job or function in your cells ...
Protein Synthesis Test Review
... 3. What is another name for point mutation? __Substitution___________________________ 4. What is an insertion mutation? ___One or more bases is inserted into the genetic code.___ 5. What is a deletion mutation? ___ One or more bases is deleted from the genetic code. ____ 6. What do insertion and del ...
... 3. What is another name for point mutation? __Substitution___________________________ 4. What is an insertion mutation? ___One or more bases is inserted into the genetic code.___ 5. What is a deletion mutation? ___ One or more bases is deleted from the genetic code. ____ 6. What do insertion and del ...
Viral Ion Channels
... Viral ion channels are auxiliary proteins produced by viruses, including HIV and Influenza. The proteins are short polypeptides, with typically no more than 100 amino acids, which oligomerise in lipid bilayers to form bundles enclosing an ion-conducting pore. These molecules have attracted considera ...
... Viral ion channels are auxiliary proteins produced by viruses, including HIV and Influenza. The proteins are short polypeptides, with typically no more than 100 amino acids, which oligomerise in lipid bilayers to form bundles enclosing an ion-conducting pore. These molecules have attracted considera ...
SOMAmer® anti-Eukaryotic translation initiation factor
... Buffered SOMAmer reagent delivered at 10 μM in 5 mM HEPES, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8 ...
... Buffered SOMAmer reagent delivered at 10 μM in 5 mM HEPES, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8 ...
Complex carbohydrates
... The Necessities of Life Air is a mixture of several gases, including oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide. Most living things use oxygen in the chemical process that releases energy from food. Oxygen may come from the air or may be dissolved in water. Some insects like this spider have unique metho ...
... The Necessities of Life Air is a mixture of several gases, including oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide. Most living things use oxygen in the chemical process that releases energy from food. Oxygen may come from the air or may be dissolved in water. Some insects like this spider have unique metho ...
Computational biology in drug discovery
... Acylovir and related drugs are all nucleoside analogues/inhibitors whose patents will soon expire. Our protease inhibitor is a novel type of anti-herpes agent that may be used in combination therapy. ...
... Acylovir and related drugs are all nucleoside analogues/inhibitors whose patents will soon expire. Our protease inhibitor is a novel type of anti-herpes agent that may be used in combination therapy. ...
Protein Structure
... Proteins with 2 or more peptide chains or subunits Proteins with 2 or more peptide chains or subunits can be different or identical subunits loss of quaternary or tertiary (native) structure is called denaturation. Examples include - Heat – to unravel the folding by adding energy – eg. egg whites - ...
... Proteins with 2 or more peptide chains or subunits Proteins with 2 or more peptide chains or subunits can be different or identical subunits loss of quaternary or tertiary (native) structure is called denaturation. Examples include - Heat – to unravel the folding by adding energy – eg. egg whites - ...
Western blot

The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot) is a widely used analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native proteins by 3-D structure or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide. The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein. The gel electrophoresis step is included in western blot analysis to resolve the issue of the cross-reactivity of antibodies.There are many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against tens of thousands of different proteins. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, although the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, immunogenetics and other molecular biology disciplines. A number of search engines, such as CiteAb, Antibodypedia, and SeekProducts, are available that can help researchers find suitable antibodies for use in western blotting.Other related techniques include dot blot analysis, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry where antibodies are used to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The method originated in the laboratory of Harry Towbin at the Friedrich Miescher Institute. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blot and was developed by George Stark at Stanford.