Biochemistry PPT - Madison County Schools
... Protein structure is key to their function Denature – a protein loses its shape (and consequently its function) when it is taken out of its natural range for factors such as temperature, pH, or salinity ...
... Protein structure is key to their function Denature – a protein loses its shape (and consequently its function) when it is taken out of its natural range for factors such as temperature, pH, or salinity ...
Introduction: As the building blocks of proteins, amino acids play a
... for glycine shown below, a simple amino acid has two dissociation steps corresponding to loss of H+ from the acidic carboxyl group at low pH followed by loss of H+ from the more basic amino group at high pH. The pKa value for each dissociable group of an amino acid can be determined from such a titr ...
... for glycine shown below, a simple amino acid has two dissociation steps corresponding to loss of H+ from the acidic carboxyl group at low pH followed by loss of H+ from the more basic amino group at high pH. The pKa value for each dissociable group of an amino acid can be determined from such a titr ...
100 Base Pair DNA Ladder
... Add 50 u1 ladder stock solution to 450ul ready-to-use loading buffer (containing 50ul 10X loading dye and 400 ul TE buffer). Vortex, mix well. Use 5 - 10 u1 of working solution per loading. The working solution may be stored at 4℃ for a few weeks. For long term storage, store at -20℃. Thaw the worki ...
... Add 50 u1 ladder stock solution to 450ul ready-to-use loading buffer (containing 50ul 10X loading dye and 400 ul TE buffer). Vortex, mix well. Use 5 - 10 u1 of working solution per loading. The working solution may be stored at 4℃ for a few weeks. For long term storage, store at -20℃. Thaw the worki ...
Document
... Scientific Advisory and mortar” in three U.S. companies to Board build non-redundant capacity. ...
... Scientific Advisory and mortar” in three U.S. companies to Board build non-redundant capacity. ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Made of two kinds of smaller molecules – glycerol and fatty acids (one glycerol to three fatty acids) – Dehydration synthesis hooks these up – 3 waters produced for every one triglyceride – ESTER linkages bond glycerol to the fatty acid tails – bond is between a hydroxyl group and a carboxyl group ...
... • Made of two kinds of smaller molecules – glycerol and fatty acids (one glycerol to three fatty acids) – Dehydration synthesis hooks these up – 3 waters produced for every one triglyceride – ESTER linkages bond glycerol to the fatty acid tails – bond is between a hydroxyl group and a carboxyl group ...
Lecture 6: Peptides
... – Get the protein of interest almost exclusively in one fraction – Get a significant amount of contaminants in a different fraction • Objective: To separate the protein of interest from a complex mixture of proteins (from tissues or recombinant organism) while maintaining biological function. • Biol ...
... – Get the protein of interest almost exclusively in one fraction – Get a significant amount of contaminants in a different fraction • Objective: To separate the protein of interest from a complex mixture of proteins (from tissues or recombinant organism) while maintaining biological function. • Biol ...
Purification and some properties of UDP
... 6MB (Figure 1). The column was washed with buffer D until no more protein emerged. Protein unspecifically bound was removed by a linear NaCl gradient (0–1 M in buffer D). Xylosyltransferase was eluted specifically with a solution of the peptide used as affinity ligand (0.1 mM in buffer E). Since the ...
... 6MB (Figure 1). The column was washed with buffer D until no more protein emerged. Protein unspecifically bound was removed by a linear NaCl gradient (0–1 M in buffer D). Xylosyltransferase was eluted specifically with a solution of the peptide used as affinity ligand (0.1 mM in buffer E). Since the ...
2.2 Prokaryotic Cells
... E.coli replicates about once every 40 minutes when incubated at 37o C. If however we increase the concentration of carbohydrate nutrients that the cell is supplied with then the division time can be reduced to 20 minutes. There is a suggestion here that an external signal (nutrient concentration) is ...
... E.coli replicates about once every 40 minutes when incubated at 37o C. If however we increase the concentration of carbohydrate nutrients that the cell is supplied with then the division time can be reduced to 20 minutes. There is a suggestion here that an external signal (nutrient concentration) is ...
6b. Thermodynamics
... • The reaction that occurs with minimum amount of activation energy and which will give products with the release of energy, that is more than what is required to initiate the reaction, ...
... • The reaction that occurs with minimum amount of activation energy and which will give products with the release of energy, that is more than what is required to initiate the reaction, ...
CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2
... It is thought that, in order for an enzyme to affect the rate of a reaction, the following events must take place. 1. The enzyme must form a temporary association with the substance or substances whose reaction rate it affects. These substances are known as substrates. 2. The association between en ...
... It is thought that, in order for an enzyme to affect the rate of a reaction, the following events must take place. 1. The enzyme must form a temporary association with the substance or substances whose reaction rate it affects. These substances are known as substrates. 2. The association between en ...
Isolation of a New Member of the $100 Protein Family: Amino Acid
... revealed that S100 is a member of a larger protein family that includes the cystic fibrosis antigen (6) also termed mrp-8 (44), the light chain of the cytoskeletal protein calpactin (8, 12, 18, 23), and predicted proteins derived from RNA abundantly expressed in fibroblasts (termed pEL98 [21], 18A2 ...
... revealed that S100 is a member of a larger protein family that includes the cystic fibrosis antigen (6) also termed mrp-8 (44), the light chain of the cytoskeletal protein calpactin (8, 12, 18, 23), and predicted proteins derived from RNA abundantly expressed in fibroblasts (termed pEL98 [21], 18A2 ...
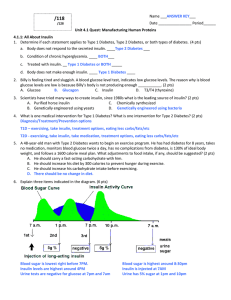
4_1 MI Quest_ ANSWER KEY - Kenwood Academy High School
... D. Equilibrium buffer 4.1.4: Protein Gel Electrophoresis 37. Protein electrophoresis differs from DNA electrophoresis because protein electrophoresis _______. (2 pts) A. Separates by length B. Separate by mass C. Separate by charge D. All of the above ...
... D. Equilibrium buffer 4.1.4: Protein Gel Electrophoresis 37. Protein electrophoresis differs from DNA electrophoresis because protein electrophoresis _______. (2 pts) A. Separates by length B. Separate by mass C. Separate by charge D. All of the above ...
Protein Modeling Challenge Science Olympiad Trial Event
... Challenge: Download the 1ZAA pdb file, create an image in RasMol, identify key structural features, and fold a Mini-Toober model (change to new zinc finger folding kit activities) ...
... Challenge: Download the 1ZAA pdb file, create an image in RasMol, identify key structural features, and fold a Mini-Toober model (change to new zinc finger folding kit activities) ...
Метод поиска SDP
... • A method for identification of amino acid residues that account for differences in protein functional specificity – Does not rely on the protein 3D structure – Automatically determines the number of significant positions – Considers substitutions according to the chemical properties of substituted ...
... • A method for identification of amino acid residues that account for differences in protein functional specificity – Does not rely on the protein 3D structure – Automatically determines the number of significant positions – Considers substitutions according to the chemical properties of substituted ...
PPT CH 18
... – Each amide H and carbonyl O is involved in H bonds locking the helix in place – Carbonyl O links to amide H 4 amino acids away – H bonds are parallel to the long axis of the helix – Helix is right-handed – Repeat distance or pitch is 5.4 angstroms – 3.6 amino acids per turn ...
... – Each amide H and carbonyl O is involved in H bonds locking the helix in place – Carbonyl O links to amide H 4 amino acids away – H bonds are parallel to the long axis of the helix – Helix is right-handed – Repeat distance or pitch is 5.4 angstroms – 3.6 amino acids per turn ...
tethering redox proteins to the outer membrane in Neisseria and
... outer membrane will limit its capacity for lateral movement, as it would need to move both the membrane anchor and the globular protein domain in a way that would avoid becoming tangled in the peptidoglycan. Furthermore, and more importantly for electron transfer, tethering may reduce the capacity f ...
... outer membrane will limit its capacity for lateral movement, as it would need to move both the membrane anchor and the globular protein domain in a way that would avoid becoming tangled in the peptidoglycan. Furthermore, and more importantly for electron transfer, tethering may reduce the capacity f ...
Identification of NaHCO3 Stress Responsive Proteins in Dunaliella
... Data acquisition was performed with a Triple TOF 5600 System (AB SCIEX, Concord, ON) fitted with a Nanospray III source (AB SCIEX, Concord, ON) and a pulled quartz tip as the emitter (New Objectives, Woburn, MA). Data was acquired using 2.5 kV ion spray voltage, curtain gas of 30 psi, nebulizer gas ...
... Data acquisition was performed with a Triple TOF 5600 System (AB SCIEX, Concord, ON) fitted with a Nanospray III source (AB SCIEX, Concord, ON) and a pulled quartz tip as the emitter (New Objectives, Woburn, MA). Data was acquired using 2.5 kV ion spray voltage, curtain gas of 30 psi, nebulizer gas ...
Vipp1: a very important protein in plastids?!
... indicates a development in parallel to the emergence of the thylakoid membrane system and a connection to the evolution of oxygenic photosynthesis. However, proteins with significant similarities to Vipp1 have been identified in several non-photosynthetic bacteria (Fig. 1) in form of the phage shock ...
... indicates a development in parallel to the emergence of the thylakoid membrane system and a connection to the evolution of oxygenic photosynthesis. However, proteins with significant similarities to Vipp1 have been identified in several non-photosynthetic bacteria (Fig. 1) in form of the phage shock ...
StudyGuide_Biochemistry
... 6. How do plants get their carbohydrates? 7. What do plants do with those carbohydrates? 8. How do animals get their carbohydrates? 9. What happens to a complex carbohydrate after it is eaten? 10. What happens to any excess carbohydrates that we consume? 11. What are three functions of carbohydrates ...
... 6. How do plants get their carbohydrates? 7. What do plants do with those carbohydrates? 8. How do animals get their carbohydrates? 9. What happens to a complex carbohydrate after it is eaten? 10. What happens to any excess carbohydrates that we consume? 11. What are three functions of carbohydrates ...
Correct response
... 7. Monomers are bonded together by which of the following processes? a. hydrolysis b. non-hydration lysis c. ionic bonding d. dehydration synthesis 8. Which of the following lists correctly identifies the characteristic structures within an amino acid? a. ammonia - carbon group - side chain b. NH3 ...
... 7. Monomers are bonded together by which of the following processes? a. hydrolysis b. non-hydration lysis c. ionic bonding d. dehydration synthesis 8. Which of the following lists correctly identifies the characteristic structures within an amino acid? a. ammonia - carbon group - side chain b. NH3 ...
basic laboratory course 3
... on the ribosomes, it folds into a biologically active conformation. Thus, the threedimensional folding of a protein and its biological properties are directed by the sequence of amino acid residues along the polypeptide chain. Biochemists have identified three structural levels that define the thre ...
... on the ribosomes, it folds into a biologically active conformation. Thus, the threedimensional folding of a protein and its biological properties are directed by the sequence of amino acid residues along the polypeptide chain. Biochemists have identified three structural levels that define the thre ...
Western blot

The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot) is a widely used analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native proteins by 3-D structure or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide. The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein. The gel electrophoresis step is included in western blot analysis to resolve the issue of the cross-reactivity of antibodies.There are many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against tens of thousands of different proteins. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, although the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, immunogenetics and other molecular biology disciplines. A number of search engines, such as CiteAb, Antibodypedia, and SeekProducts, are available that can help researchers find suitable antibodies for use in western blotting.Other related techniques include dot blot analysis, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry where antibodies are used to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The method originated in the laboratory of Harry Towbin at the Friedrich Miescher Institute. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blot and was developed by George Stark at Stanford.