C483 Final Exam Study Guide The final will be held in Morrison 007
... B. 100 point cumulative exam. This exam will cover major themes and integrated concepts for the course. It will be about 1/3 multiple choice, 1/3 short answer, and 1/3 problems taken from the list below. These questions will also serve as a good review for the major topics of the course. You are enc ...
... B. 100 point cumulative exam. This exam will cover major themes and integrated concepts for the course. It will be about 1/3 multiple choice, 1/3 short answer, and 1/3 problems taken from the list below. These questions will also serve as a good review for the major topics of the course. You are enc ...
This exam has 9 pages, including this one.
... Part C: Detailed Calculations - You must attempt all three questions. However, you have two choices within each question. C1: Do one of the following two questions (6 pts). i) A protein that is 20 amino acid residues in length folds into a stable structure. Assume that the protein forms all but one ...
... Part C: Detailed Calculations - You must attempt all three questions. However, you have two choices within each question. C1: Do one of the following two questions (6 pts). i) A protein that is 20 amino acid residues in length folds into a stable structure. Assume that the protein forms all but one ...
This exam has 9 pages, including this one.
... Part C: Detailed Calculations - You must attempt all three questions. However, you have two choices within each question. C1: Do one of the following two questions (6 pts). i) A protein that is 20 amino acid residues in length folds into a stable structure. Assume that the protein forms all but one ...
... Part C: Detailed Calculations - You must attempt all three questions. However, you have two choices within each question. C1: Do one of the following two questions (6 pts). i) A protein that is 20 amino acid residues in length folds into a stable structure. Assume that the protein forms all but one ...
Notes: Enzymes
... This disorder is named after a physician, Dr Bernard Sachs, who noted in 1887 that a number of children of Central and Eastern Europe (Ashkenazic) Jewish ancestry, who were born with no apparent problems, degenerated physically and mentally and died by the age of about four. The affected children we ...
... This disorder is named after a physician, Dr Bernard Sachs, who noted in 1887 that a number of children of Central and Eastern Europe (Ashkenazic) Jewish ancestry, who were born with no apparent problems, degenerated physically and mentally and died by the age of about four. The affected children we ...
div class="noscript">This application requires Javascript to be
... Ping-pong mechanism also called a double-displacement reaction is characterized by the change of the enzyme into an intermediate form when the first substrate to product reaction occurs. It is important to note the term intermediate indicating that this form is only temporary. At the end of the reac ...
... Ping-pong mechanism also called a double-displacement reaction is characterized by the change of the enzyme into an intermediate form when the first substrate to product reaction occurs. It is important to note the term intermediate indicating that this form is only temporary. At the end of the reac ...
Download PDF
... Student Learning Outcomes: 1. Students can describe the basic elements of amino acid, peptide, and protein structure. 2. Students can explain the common features of enzyme catalysts, and some of the basic methods used in studying enzyme function. 3. Students can outline the basic metabolic pathways ...
... Student Learning Outcomes: 1. Students can describe the basic elements of amino acid, peptide, and protein structure. 2. Students can explain the common features of enzyme catalysts, and some of the basic methods used in studying enzyme function. 3. Students can outline the basic metabolic pathways ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions ...
... re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions ...
Amino Acids and Dipeptides - Chemical Minds
... ii) Explain your answer in terms of the structure and functional groups present in the amino acids and in the dipeptide(s). ...
... ii) Explain your answer in terms of the structure and functional groups present in the amino acids and in the dipeptide(s). ...
Reading Guide
... dihydrofolate reductase? Why are these good targets for chemotherapy? 19. Amino acids are not completely catabolized in the liver. Rather, the nitrogen is removed through ________________ reactions, then the carbon skeletons are transformed into compounds such as ____________ and ____________ for fu ...
... dihydrofolate reductase? Why are these good targets for chemotherapy? 19. Amino acids are not completely catabolized in the liver. Rather, the nitrogen is removed through ________________ reactions, then the carbon skeletons are transformed into compounds such as ____________ and ____________ for fu ...
the molecular mechanism of photosynthetic glyceraldehyde
... GapB, the latter showing a similar behaviour to native AnBn isoform. Effects of the mutation on substrate affinity were minor if any. These results strongly support the participation of Glu362 to the catalytic mechanism of GAPDH, when the CTE is in the oxidized state. By comparying the crystal struc ...
... GapB, the latter showing a similar behaviour to native AnBn isoform. Effects of the mutation on substrate affinity were minor if any. These results strongly support the participation of Glu362 to the catalytic mechanism of GAPDH, when the CTE is in the oxidized state. By comparying the crystal struc ...
Chapter 5 (part 4) Enzyme Regulation
... • Vo vs [S] plots give sigmoidal curve for at least one substrate • Can remove allosteric site without ...
... • Vo vs [S] plots give sigmoidal curve for at least one substrate • Can remove allosteric site without ...
Revision PPT on enzymes File
... The shape of an enzyme is very important because it has a direct effect on how it catalyzes a reaction. Why do enzymes have different shapes? An enzyme’s shape is determined by the sequence of amino acids in its structure, and the bonds which form between the atoms of those molecules. ...
... The shape of an enzyme is very important because it has a direct effect on how it catalyzes a reaction. Why do enzymes have different shapes? An enzyme’s shape is determined by the sequence of amino acids in its structure, and the bonds which form between the atoms of those molecules. ...
amino acids
... The shape of an enzyme is very important because it has a direct effect on how it catalyzes a reaction. Why do enzymes have different shapes? An enzyme’s shape is determined by the sequence of amino acids in its structure, and the bonds which form between the atoms of those molecules. ...
... The shape of an enzyme is very important because it has a direct effect on how it catalyzes a reaction. Why do enzymes have different shapes? An enzyme’s shape is determined by the sequence of amino acids in its structure, and the bonds which form between the atoms of those molecules. ...
enzyme
... This class encompasses all enzymes that catalyze redox reactions reactions. The recommended name is dehydrogenase whenever possible, but reductase can also be used. Oxidase is used only when O2 is the acceptor for reduction. The systematic name is formed according to d ...
... This class encompasses all enzymes that catalyze redox reactions reactions. The recommended name is dehydrogenase whenever possible, but reductase can also be used. Oxidase is used only when O2 is the acceptor for reduction. The systematic name is formed according to d ...
Slide ()
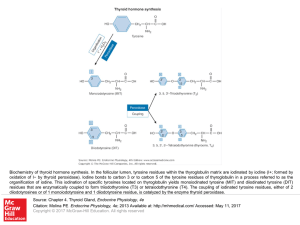
... Biochemistry of thyroid hormone synthesis. In the follicular lumen, tyrosine residues within the thyroglobulin matrix are iodinated by iodine (I+; formed by oxidation of I− by thyroid peroxidase). Iodine bonds to carbon 3 or to carbon 5 of the tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin in a process referred ...
... Biochemistry of thyroid hormone synthesis. In the follicular lumen, tyrosine residues within the thyroglobulin matrix are iodinated by iodine (I+; formed by oxidation of I− by thyroid peroxidase). Iodine bonds to carbon 3 or to carbon 5 of the tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin in a process referred ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.