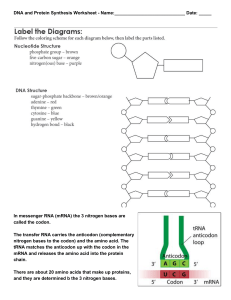
031607
... – High specificity and efficiency relative to inorganic catalysts, for example – Participate in reactions, but no net change – Lower the activation energy – Do not change equilibrium (get there faster) ...
... – High specificity and efficiency relative to inorganic catalysts, for example – Participate in reactions, but no net change – Lower the activation energy – Do not change equilibrium (get there faster) ...
CHEM523 Test 1
... THE QUESTIONS IN ORDER. Flip through the exam and answer the ones that you can answer immediately as soon as you identify them. 1) (10 points total) Draw the structures of and give the One and three letter abbreviations for: a) (6 points) The following three amino acids: i) A hydrophobic amino acid ...
... THE QUESTIONS IN ORDER. Flip through the exam and answer the ones that you can answer immediately as soon as you identify them. 1) (10 points total) Draw the structures of and give the One and three letter abbreviations for: a) (6 points) The following three amino acids: i) A hydrophobic amino acid ...
No Slide Title
... In proline, the side chain is connected to the backbone at two places: the C and the N. Therefore, it is not an amino acid, but an imino acid. Unless it is the N-terminal residue, proline does not have a backbone proton, and thus is not good for helices and strands. Due to the extra covalent bond, ...
... In proline, the side chain is connected to the backbone at two places: the C and the N. Therefore, it is not an amino acid, but an imino acid. Unless it is the N-terminal residue, proline does not have a backbone proton, and thus is not good for helices and strands. Due to the extra covalent bond, ...
24_Test - Ventura College
... Which of the following is not true of metal-ion catalysis? A. It can make a reaction center more susceptible to ...
... Which of the following is not true of metal-ion catalysis? A. It can make a reaction center more susceptible to ...
The 20 amino acids
... residue. Its side chain, R, is just a methyl group. Alanine likes to sit in an alpha helix, it doesn’t like beta strands very much, but it hates betaturns. If you want to mutate a residue, but you don’t have a good plan about what to replace it with, take alanine because it is a subset of all other ...
... residue. Its side chain, R, is just a methyl group. Alanine likes to sit in an alpha helix, it doesn’t like beta strands very much, but it hates betaturns. If you want to mutate a residue, but you don’t have a good plan about what to replace it with, take alanine because it is a subset of all other ...
26.3 Synthesis of Amino Acids
... • Only the pyridine-like, doubly bonded nitrogen in histidine is basic. • The pyrrole-like singly bonded nitrogen is nonbasic because its lone pair of electrons is part of the 6 electron aromatic imidazole ring (see Section 24.4). ...
... • Only the pyridine-like, doubly bonded nitrogen in histidine is basic. • The pyrrole-like singly bonded nitrogen is nonbasic because its lone pair of electrons is part of the 6 electron aromatic imidazole ring (see Section 24.4). ...
Coenzymes and cofactors Vitamins and minerals
... Coenzymes are organic carrier molecules. They are non-protein components of an enzyme that are required for the catalytic process to occur smoothly. They bind to the active sites of enzymes when the substrate molecules bind, and although they are not substrate molecules they participate in the catal ...
... Coenzymes are organic carrier molecules. They are non-protein components of an enzyme that are required for the catalytic process to occur smoothly. They bind to the active sites of enzymes when the substrate molecules bind, and although they are not substrate molecules they participate in the catal ...
Lecture 8
... process, and protein folding is a spontaneous process – When water molecules surround a nonpolar compound, they are restricted in the number of hydrogen bonds then can form which represents a lower entropy – By having the hydrophobic residues sequestered in the core of the folded protein, the water ...
... process, and protein folding is a spontaneous process – When water molecules surround a nonpolar compound, they are restricted in the number of hydrogen bonds then can form which represents a lower entropy – By having the hydrophobic residues sequestered in the core of the folded protein, the water ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... Creatine kinase (CK) has three isozymes: CK-MM (skeletal muscle), CK-BB (brain), and CKMB (heart and skeletal muscle). CK-MB has a useful diagnostic window. It appears within 4–6 h of an MI, peaks at 24 h, and returns to baseline by 48–72 h. Today, in most clinical laboratories CK has been suppleme ...
... Creatine kinase (CK) has three isozymes: CK-MM (skeletal muscle), CK-BB (brain), and CKMB (heart and skeletal muscle). CK-MB has a useful diagnostic window. It appears within 4–6 h of an MI, peaks at 24 h, and returns to baseline by 48–72 h. Today, in most clinical laboratories CK has been suppleme ...
Mutating the second glutamate in the amidase active site
... in a different manner than it does in the wildtype enzyme. The result is that the double bond of the acrylamide rather than the amide carbonyl carbon is adjacent to the active site cysteine. This demonstrates the role of the hydrogen bond between E142 Oε2 and the substrate amino group in positioning ...
... in a different manner than it does in the wildtype enzyme. The result is that the double bond of the acrylamide rather than the amide carbonyl carbon is adjacent to the active site cysteine. This demonstrates the role of the hydrogen bond between E142 Oε2 and the substrate amino group in positioning ...
Document
... Conditions for Michaelis -Menten Two assumptions must be met for the MichaelisMenten equation • Steady state - the enzyme substrate complex ES is at a constant value. That is the ES is formed as fast as the enzyme releases the product. For this to happen the concentration of substrate has to be muc ...
... Conditions for Michaelis -Menten Two assumptions must be met for the MichaelisMenten equation • Steady state - the enzyme substrate complex ES is at a constant value. That is the ES is formed as fast as the enzyme releases the product. For this to happen the concentration of substrate has to be muc ...
HIV Protease (H1415) - Datasheet - Sigma
... Sigma-Aldrich, Inc. warrants that its products conform to the information contained in this and other Sigma-Aldrich publications. Purchaser must determine the suitability of the product(s) for their particular use. Additional terms and conditions may apply. Please see reverse side of the invoice or ...
... Sigma-Aldrich, Inc. warrants that its products conform to the information contained in this and other Sigma-Aldrich publications. Purchaser must determine the suitability of the product(s) for their particular use. Additional terms and conditions may apply. Please see reverse side of the invoice or ...
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
... The carbon backbones for amino acids come from glycolysis, the citric acid cycle and the pentose phosphate pathway. The L–stereochemistry is enforced by transamination of α–keto acids ...
... The carbon backbones for amino acids come from glycolysis, the citric acid cycle and the pentose phosphate pathway. The L–stereochemistry is enforced by transamination of α–keto acids ...
MC 2
... 1. Cohesion is the attractive force that water molecules exert on one another. Adhesion is the attractive force between water molecules and a surface. Both forces help explain capillary action, which is the ability of water molecules to rise up a narrow tube. Vascular plants, which include nearly al ...
... 1. Cohesion is the attractive force that water molecules exert on one another. Adhesion is the attractive force between water molecules and a surface. Both forces help explain capillary action, which is the ability of water molecules to rise up a narrow tube. Vascular plants, which include nearly al ...
+ Enzyme Inhibitors
... Lethal illness can be caused by the malfunction of just one type of enzyme out of the thousands of types present in our bodies. E.g., the disease phenylketonuria (PKU) results from a mutation of a single amino acid in the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, which catalyzes the first step in the degrad ...
... Lethal illness can be caused by the malfunction of just one type of enzyme out of the thousands of types present in our bodies. E.g., the disease phenylketonuria (PKU) results from a mutation of a single amino acid in the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, which catalyzes the first step in the degrad ...
Enzyme - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Enzymes aren’t used up • Enzymes are not changed by the reaction – used only temporarily – re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules – very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions substrate active site ...
... Enzymes aren’t used up • Enzymes are not changed by the reaction – used only temporarily – re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules – very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions substrate active site ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.