H. Sodium Channel Blockers
... 1. Drug distributed to site of action 2. Protein binding 3. Blood brain barrier C. Metabolism 1. Liver 2. Hepatic First Pass Effect 3. Infants and Elderly have a decreased ability to metabolize drugs D. Excretion 1. Drugs eliminated from body primarily by kidneys but also intestines, lungs, and mamm ...
... 1. Drug distributed to site of action 2. Protein binding 3. Blood brain barrier C. Metabolism 1. Liver 2. Hepatic First Pass Effect 3. Infants and Elderly have a decreased ability to metabolize drugs D. Excretion 1. Drugs eliminated from body primarily by kidneys but also intestines, lungs, and mamm ...
JV Poster Barcelona 2012
... activity (a concomitant effect on the NMDA- and AMPA–receptors) against monofunctional drugs: the low-affinity NMDA receptor blocker memantine and the positive AMPA receptor modulator QQX. New bio-isosteric analogues of MK-801 (IPAC 1-5) were synthesized and designed to have bifunctional activity. L ...
... activity (a concomitant effect on the NMDA- and AMPA–receptors) against monofunctional drugs: the low-affinity NMDA receptor blocker memantine and the positive AMPA receptor modulator QQX. New bio-isosteric analogues of MK-801 (IPAC 1-5) were synthesized and designed to have bifunctional activity. L ...
Steps in synaptic transmission.
... Type (or types) of receptor through which the drug acts (alpha1, alpha2, beta1, etc) Normal response to activation of those receptors (agonist versus antagonist) What the drug in question does to receptor function ...
... Type (or types) of receptor through which the drug acts (alpha1, alpha2, beta1, etc) Normal response to activation of those receptors (agonist versus antagonist) What the drug in question does to receptor function ...
Protein Data Bank Advisory Committee
... • collects triglycerides from very low density or low density lipoproteins (VLDL or LDL) and exchanges them for cholesteryl esters from high density lipoproteins (and vice versa) • A long tunnel with two major binding sites. Docking studies suggest that it possible that torcetrapib binds to both of ...
... • collects triglycerides from very low density or low density lipoproteins (VLDL or LDL) and exchanges them for cholesteryl esters from high density lipoproteins (and vice versa) • A long tunnel with two major binding sites. Docking studies suggest that it possible that torcetrapib binds to both of ...
Preclinical evaluation of AVN-322, novel and highly selective 5
... displacement of radio-labeled [3H]LSD from 5-HT6R expressed in the cell membrane fraction; (B) dose-dependent inhibition of cAMP production induced by serotonin in HEK293 cells transfected with functional human 5-HT6R. In a cell-based functional assay AVN-322 was characterized as a weak 5-HT2BR anta ...
... displacement of radio-labeled [3H]LSD from 5-HT6R expressed in the cell membrane fraction; (B) dose-dependent inhibition of cAMP production induced by serotonin in HEK293 cells transfected with functional human 5-HT6R. In a cell-based functional assay AVN-322 was characterized as a weak 5-HT2BR anta ...
07 Adrenoceptor-antagonist
... Choice of a β-adrenoceptor antagonist drug • For some diseases (e.g., myocardial infarction, migraine, cirrhosis with varices, and congestive heart failure), it should not be assumed that all members of this class of drugs are interchangeable; the appropriate drug should be selected from those that ...
... Choice of a β-adrenoceptor antagonist drug • For some diseases (e.g., myocardial infarction, migraine, cirrhosis with varices, and congestive heart failure), it should not be assumed that all members of this class of drugs are interchangeable; the appropriate drug should be selected from those that ...
dental second assessment
... 11. Which of the following pairs of drugs is an example of physiological antagonism : a. Propranolol and isoprenaline . b. Atropine and acetyl choline. c. Protamine sulphate and heparin. d. Histamine and adrenaline. 12. Which of the following drugs acts by blocking sodium channels ? a. ASA. ...
... 11. Which of the following pairs of drugs is an example of physiological antagonism : a. Propranolol and isoprenaline . b. Atropine and acetyl choline. c. Protamine sulphate and heparin. d. Histamine and adrenaline. 12. Which of the following drugs acts by blocking sodium channels ? a. ASA. ...
TRICYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANTS
... Relate this to the clinical picture Advanced Treatment Options ...
... Relate this to the clinical picture Advanced Treatment Options ...
Adrenoceptor Blocking Agents
... They must be used very cautiously if at all in patients with reactive (asthma) airways. ...
... They must be used very cautiously if at all in patients with reactive (asthma) airways. ...
Document
... Design and synthesis of peptidomimetics Peptides are involved in a large number of biological processes. However they show severe limitations in terms of metabolic stability and druggability. The general idea is to replace peptides with peptidomimetics which show the same biolocigal activity but don ...
... Design and synthesis of peptidomimetics Peptides are involved in a large number of biological processes. However they show severe limitations in terms of metabolic stability and druggability. The general idea is to replace peptides with peptidomimetics which show the same biolocigal activity but don ...
Read more. - Griffin Discoveries
... The unique drug development platform consists of medicinal chemistry and molecular pharmacology tools that allow histamine receptors to be studied at an unprecedented level of details. No other company has these capabilities. 30% of all marketed drugs target GPCRs while histamine receptor drugs ...
... The unique drug development platform consists of medicinal chemistry and molecular pharmacology tools that allow histamine receptors to be studied at an unprecedented level of details. No other company has these capabilities. 30% of all marketed drugs target GPCRs while histamine receptor drugs ...
Slide 1
... and muscarinic receptors) depend on the G proteins that mediate their action on cells ...
... and muscarinic receptors) depend on the G proteins that mediate their action on cells ...
L2a.a transmitter201..
... The same agent (e.g. glutamate, 5-HT (5hydroxytryptamine), acetylcholine) may act through both ligand-gated channels and Gprotein-coupled receptors. Many chemical mediators, including glutamate, nitric oxide and arachidonic acid metabolites, are produced by glia as well as neurons. Many other media ...
... The same agent (e.g. glutamate, 5-HT (5hydroxytryptamine), acetylcholine) may act through both ligand-gated channels and Gprotein-coupled receptors. Many chemical mediators, including glutamate, nitric oxide and arachidonic acid metabolites, are produced by glia as well as neurons. Many other media ...
Indexed Keywords
... destabilization should be translated in clinical practice. Systemic approaches are pursued to discover serum biomarkers that are applicable to define patients at risk for future cardiovascular events. Elevation in inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein, predicts outcomes of patients with a ...
... destabilization should be translated in clinical practice. Systemic approaches are pursued to discover serum biomarkers that are applicable to define patients at risk for future cardiovascular events. Elevation in inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein, predicts outcomes of patients with a ...
Memantine and Neuroprotection
... Zajaczkowski et al., 1997: in tonic activation of NMDA receptors, memantine can reverse deficits in synaptic plasticity, both at neuronal (LTP) and behavioural (learning) level Significant improvement in: cognitive processes, daily activities and self care (Ditzler, 1991; Görtelmeyer and Erbler, 199 ...
... Zajaczkowski et al., 1997: in tonic activation of NMDA receptors, memantine can reverse deficits in synaptic plasticity, both at neuronal (LTP) and behavioural (learning) level Significant improvement in: cognitive processes, daily activities and self care (Ditzler, 1991; Görtelmeyer and Erbler, 199 ...
Routes of Excretion
... 2. G-protein coupled receptors ◦ (metabotropic) ◦ 2nd messenger systems ◦ more than 50 G protein coupled receptors have been identified ◦ control many cellular processes ...
... 2. G-protein coupled receptors ◦ (metabotropic) ◦ 2nd messenger systems ◦ more than 50 G protein coupled receptors have been identified ◦ control many cellular processes ...
Kristen Ray - USD Biology
... First in a generation of SSRIs for treatment of major depressive disorder and anxiety disorders (OCD) ...
... First in a generation of SSRIs for treatment of major depressive disorder and anxiety disorders (OCD) ...
Slide () - Access Emergency Medicine
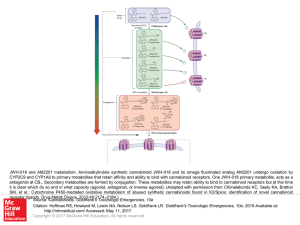
... JWH-018 and AM2201 metabolism. Aminoalkylindole synthetic cannabinoid JWH-018 and its omega fluorinated analog AM2201 undergo oxidation by CYP2C9 and CYP1A9 to primary metabolites that retain affinity and ability to bind with cannabinoid receptors. One JWH-018 primary metabolite, acts as a antagonis ...
... JWH-018 and AM2201 metabolism. Aminoalkylindole synthetic cannabinoid JWH-018 and its omega fluorinated analog AM2201 undergo oxidation by CYP2C9 and CYP1A9 to primary metabolites that retain affinity and ability to bind with cannabinoid receptors. One JWH-018 primary metabolite, acts as a antagonis ...
GKunz_EPCIS
... Opioid Analgesics • “Relative minor changes in the structure of an opioid can convert a drug that is primarily an agonist into one with antagonist actions at one or more types of opioid receptors. The most common such substitution is that of the large moiety (e.g., an ally or methylcyclopropyl group ...
... Opioid Analgesics • “Relative minor changes in the structure of an opioid can convert a drug that is primarily an agonist into one with antagonist actions at one or more types of opioid receptors. The most common such substitution is that of the large moiety (e.g., an ally or methylcyclopropyl group ...
Lecture 12, computers CORRECTED
... binding energies of docked ligands to this model binding site. ...
... binding energies of docked ligands to this model binding site. ...
Hormone Receptors on the Plasma Membrane
... [ligand] [receptor] kon = M-1 min-1 • koff = # of dissociation events/time (Rate of dissociation) = [ligand receptor] koff = min-1 • Binding occurs when ligand and receptor collide with the proper orientation and energy. • Interaction is reversible. • Rate of formation [L] + [R] or dissociation ...
... [ligand] [receptor] kon = M-1 min-1 • koff = # of dissociation events/time (Rate of dissociation) = [ligand receptor] koff = min-1 • Binding occurs when ligand and receptor collide with the proper orientation and energy. • Interaction is reversible. • Rate of formation [L] + [R] or dissociation ...
new-ff-Benzodiazepines-
... plasma proteins; the more nonpolar the drug, the greater the binding. They are also very effectively distributed to the brain. Compounds without 3-OH group have long half-lives and undergo conversion to the 3-hydroxyl compounds by hepatic oxidation. Compounds with 3-OH (oxazepam, lorazepam) are shor ...
... plasma proteins; the more nonpolar the drug, the greater the binding. They are also very effectively distributed to the brain. Compounds without 3-OH group have long half-lives and undergo conversion to the 3-hydroxyl compounds by hepatic oxidation. Compounds with 3-OH (oxazepam, lorazepam) are shor ...
Neurotransmitters
... Exists in as many as a third of all synapses. Drugs that boost GABA’s effects have a calming or relaxing effect. Reduced levels of GABA may play a role in emotional disorders in which anxiety is a core feature. ...
... Exists in as many as a third of all synapses. Drugs that boost GABA’s effects have a calming or relaxing effect. Reduced levels of GABA may play a role in emotional disorders in which anxiety is a core feature. ...