Key terms for A level German
... Is the tense you would like to use e.g present, past, future, conditional, imperfect etc. ...
... Is the tense you would like to use e.g present, past, future, conditional, imperfect etc. ...
Suffixal Homophones
... can modify nouns or pronouns. It can sometimes stand alone, with the modified noun or pronoun implied. As verbals, participles can take an object. As verbals, participles can have tense (i.e., refer to past, present, or future) and voice (i.e., indicate that an agent is "actively" doing something or ...
... can modify nouns or pronouns. It can sometimes stand alone, with the modified noun or pronoun implied. As verbals, participles can take an object. As verbals, participles can have tense (i.e., refer to past, present, or future) and voice (i.e., indicate that an agent is "actively" doing something or ...
Subject Verb Agreement I
... 4. Doesn't is a contraction of does not and should be used only with a singular subject. Don't is a contraction of do not and should be used only with a plural subject. The exception to this rule appears in the case of the first person and second person pronouns I and you. With these pronouns, the ...
... 4. Doesn't is a contraction of does not and should be used only with a singular subject. Don't is a contraction of do not and should be used only with a plural subject. The exception to this rule appears in the case of the first person and second person pronouns I and you. With these pronouns, the ...
Grammar Study Guide
... Anyone without (his, their) homework will lose points. Each of the contenders took (his, their) turn in the ring. ...
... Anyone without (his, their) homework will lose points. Each of the contenders took (his, their) turn in the ring. ...
Writing for effectiveness - Trinity Classical School
... A modifier "dangles" when what it is supposed to modify is not part of the sentence. Before going on vacation, the bills need to be paid. After cutting the grass, the garden was weeded. ...
... A modifier "dangles" when what it is supposed to modify is not part of the sentence. Before going on vacation, the bills need to be paid. After cutting the grass, the garden was weeded. ...
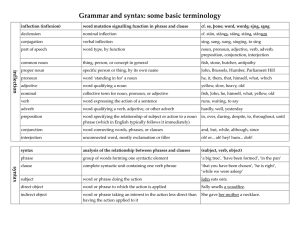
Grammar and syntax: some basic terminology
... word specifying the relationship of subject or action to a noun phrase (which in English typically follows it immediately) ...
... word specifying the relationship of subject or action to a noun phrase (which in English typically follows it immediately) ...
Transitive, Intransitive, and Linking Verbs
... The attorney revealed the bad news. The defendant could not provide an alibi. The jury deliberated the case for 48 minutes. The judge sentenced the man to five years in prison. ...
... The attorney revealed the bad news. The defendant could not provide an alibi. The jury deliberated the case for 48 minutes. The judge sentenced the man to five years in prison. ...
Chuprinski - English8room103
... Answers the questions how, where, when, in what, way, and to what extent Examples: Quickly Slowly Always ...
... Answers the questions how, where, when, in what, way, and to what extent Examples: Quickly Slowly Always ...
II. Subject and Predicate
... *** In your parse, give the complete clause and how it functions in the sentence. If it acts as an adjective or adverb, note that fact, and give which word the clause modifies. Example: What concerns us most is creeping inflation. what concerns us most—noun—subject. ***If the subordinate clause acts ...
... *** In your parse, give the complete clause and how it functions in the sentence. If it acts as an adjective or adverb, note that fact, and give which word the clause modifies. Example: What concerns us most is creeping inflation. what concerns us most—noun—subject. ***If the subordinate clause acts ...
Monday Notes n=common noun N=proper noun pos n=possessive
... tells How? (carefully) When? (quickly) Where? (northerly) To what extent? (very) not and never are always adverbs ...
... tells How? (carefully) When? (quickly) Where? (northerly) To what extent? (very) not and never are always adverbs ...
Action Verbs
... The house was struck by lightning. (passive) Lightning struck the house. (active –More interesting!) Passive voice is used in scientific writing to create an inductive, objective tone. Subjects were given small amounts of water during the experiment. ...
... The house was struck by lightning. (passive) Lightning struck the house. (active –More interesting!) Passive voice is used in scientific writing to create an inductive, objective tone. Subjects were given small amounts of water during the experiment. ...
HS4 – LOS USOS DIFERENTES DEL PRONOMBRE “SE” Perhaps
... Use Five: Accidental/Unplanned Occurrences – the “se” is used to express an accidental or unplanned occurrence. Many times it is used to remove the element of blame from the person who did the action so that (s)he does not have to claim responsibility. An indirect object pronoun will be used to refe ...
... Use Five: Accidental/Unplanned Occurrences – the “se” is used to express an accidental or unplanned occurrence. Many times it is used to remove the element of blame from the person who did the action so that (s)he does not have to claim responsibility. An indirect object pronoun will be used to refe ...
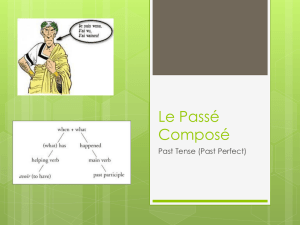
Document
... happened in the past (sometimes called the past perfect tense) It’s not the only French past tense It has 2 parts: helping (auxiliary) verb and a past participle. The helping verb for most verbs is avoir. You form the past participle of most –er verbs by replacing the –er with -é ...
... happened in the past (sometimes called the past perfect tense) It’s not the only French past tense It has 2 parts: helping (auxiliary) verb and a past participle. The helping verb for most verbs is avoir. You form the past participle of most –er verbs by replacing the –er with -é ...
(that) he went to school every day.
... • Teaching aims: • 1. Students can understand the difference between direct and indirect speech.. • 2. Students can learn how to transform direct speech into indirect speech. ...
... • Teaching aims: • 1. Students can understand the difference between direct and indirect speech.. • 2. Students can learn how to transform direct speech into indirect speech. ...
Station 1: ACTIVE VS. PASSIVE VOICE Copy the following
... Gerund: The –ing form of a verb that acts as a noun—functions as either the subject, direct object, or predicate nominative of a sentence. Ex: Walking is healthy. (“walking” comes from a verb but is acting as a noun—in this case the subject of the sentence.) Ex: I love walking. (“walking” is the ger ...
... Gerund: The –ing form of a verb that acts as a noun—functions as either the subject, direct object, or predicate nominative of a sentence. Ex: Walking is healthy. (“walking” comes from a verb but is acting as a noun—in this case the subject of the sentence.) Ex: I love walking. (“walking” is the ger ...
Five Basic Sentence Types
... dividing the predicate into phrases. If all the phrases except the main verb phrase are optional adverbial modifiers, then the verb is intransitive 2. If you can substitute a prototypical adverb (like here, then, or slowly) for the phrase, it is an adverbial phrase ...
... dividing the predicate into phrases. If all the phrases except the main verb phrase are optional adverbial modifiers, then the verb is intransitive 2. If you can substitute a prototypical adverb (like here, then, or slowly) for the phrase, it is an adverbial phrase ...
What`s the Subject
... 1. If one of them is a pronoun, it is always the subject. (Sometimes this pronoun is the “default/built-in” subject of the verb; i.e., a linking verb has only one explicit nominative substantive.) 2.a. If one is a proper noun (i.e., a name) and the other a common noun, it is the subject. 2.b. If one ...
... 1. If one of them is a pronoun, it is always the subject. (Sometimes this pronoun is the “default/built-in” subject of the verb; i.e., a linking verb has only one explicit nominative substantive.) 2.a. If one is a proper noun (i.e., a name) and the other a common noun, it is the subject. 2.b. If one ...
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs
... Key terms for transitive/intransitive verbs Direct objects are words that receive the action of the verb. Some verbs have direct objects and others do not. If the verb has a direct object, it is transitive. If it does not, it is intransitive. ...
... Key terms for transitive/intransitive verbs Direct objects are words that receive the action of the verb. Some verbs have direct objects and others do not. If the verb has a direct object, it is transitive. If it does not, it is intransitive. ...
File
... Needs to be the past tense of the verb. Can also end in –d, -en, -t, or –n. Examples: used, beaten, dealt, or seen. ...
... Needs to be the past tense of the verb. Can also end in –d, -en, -t, or –n. Examples: used, beaten, dealt, or seen. ...
Parts of Speech
... sentence. • Shows physical action, mental action, or a state of being. • passed, blasted, smile, thought, build, open, acting • Verbs are red. ...
... sentence. • Shows physical action, mental action, or a state of being. • passed, blasted, smile, thought, build, open, acting • Verbs are red. ...
Action verbs
... A word or a group of words. These word(s) complete the meaning of a verb. Example: Joey wants a puppy ...
... A word or a group of words. These word(s) complete the meaning of a verb. Example: Joey wants a puppy ...
to PDF lesson
... A Linking Verb links, or joins, the subject of a sentence (often a noun or pronoun) with a word or expression that identifies or describes the subject. ...
... A Linking Verb links, or joins, the subject of a sentence (often a noun or pronoun) with a word or expression that identifies or describes the subject. ...
lesson 12 - Biloxi Public Schools
... – My teacher, eating lunch at the park, ran into one of her students. • Again, complete sentences with our phrase used like an adjective, this time to describe “teacher”. ...
... – My teacher, eating lunch at the park, ran into one of her students. • Again, complete sentences with our phrase used like an adjective, this time to describe “teacher”. ...