
Linking Verbs
... Linking Verb test – Substitute “is” for singular subjects or “are” for plural subjects. If the sentence makes sense, then it is a linking verb. If it does not make sense, then it is an action verb. ...
... Linking Verb test – Substitute “is” for singular subjects or “are” for plural subjects. If the sentence makes sense, then it is a linking verb. If it does not make sense, then it is an action verb. ...
Verbal
... A verbal is sort of an off-duty verb that looks like a verb but functions as another part of speech in a sentence. o There are three types of verbals: gerunds, participles and infinitives. Gerunds are –ing verbs that function as nouns. o Example: Swimming is a good form of exercise. Participle ...
... A verbal is sort of an off-duty verb that looks like a verb but functions as another part of speech in a sentence. o There are three types of verbals: gerunds, participles and infinitives. Gerunds are –ing verbs that function as nouns. o Example: Swimming is a good form of exercise. Participle ...
Unit 1 Test: Study Guide PART I: Vocabulary PART II: Grammar and
... withhold self deliberately; refrain; desist Adjective deviating from normal; unusual; irregular Adjective sudden; unexpected; quickly changing AD (to, toward, or near) Part of Speech Definition Verb to change or modify so it’s suitable Adjective mentally or physically dependent on something Adjectiv ...
... withhold self deliberately; refrain; desist Adjective deviating from normal; unusual; irregular Adjective sudden; unexpected; quickly changing AD (to, toward, or near) Part of Speech Definition Verb to change or modify so it’s suitable Adjective mentally or physically dependent on something Adjectiv ...
Heading Glossary of grammatical terms
... an article or a pronoun has to ‘agree’ with the gender, number and (usually) case of the noun or pronoun it accompanies or replaces. ■ article There are two types of article in English and German: definite (the) and indefinite (a, an). However, in German the form of both definite and indefinite arti ...
... an article or a pronoun has to ‘agree’ with the gender, number and (usually) case of the noun or pronoun it accompanies or replaces. ■ article There are two types of article in English and German: definite (the) and indefinite (a, an). However, in German the form of both definite and indefinite arti ...
Absolute Brush Stroke
... Mind racing, anxiety overtaking, the diver peered once more at the specimen. (E. Stralka) I glanced at my clock, digits glowing fluorescent blue in the inky darkness of my room. (J. Coppolo) Jaws cracking, tongue curling, the kitten yawned tiredly, awaking from her nap. (T. Tesmer) ...
... Mind racing, anxiety overtaking, the diver peered once more at the specimen. (E. Stralka) I glanced at my clock, digits glowing fluorescent blue in the inky darkness of my room. (J. Coppolo) Jaws cracking, tongue curling, the kitten yawned tiredly, awaking from her nap. (T. Tesmer) ...
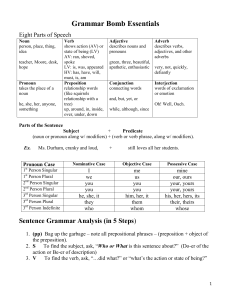
Eight parts of speech
... together and shows the relation between them. "My hand is on the table" shows relation between hand and table. Prepositions are so called because they are generally placed before the words whose connection or relation with other words they point out. Examples of common English Prepositions: above, a ...
... together and shows the relation between them. "My hand is on the table" shows relation between hand and table. Prepositions are so called because they are generally placed before the words whose connection or relation with other words they point out. Examples of common English Prepositions: above, a ...
Action Verb: Tells what the subject does. • Jeremy likes to run
... Subject: tells what or whom the sentence is ...
... Subject: tells what or whom the sentence is ...
sub inter super play er ing The ( poor / pour ) child was lost. She
... 12-13. (W4:17) A wider range of connectives is essential in order to vary sentence structure for effect and make your writing far more interesting. ...
... 12-13. (W4:17) A wider range of connectives is essential in order to vary sentence structure for effect and make your writing far more interesting. ...
REFERRING TO THE PAST, PRESENT AND FUTURE THROUGH
... WORDS WHICH, IN SOME SENSES, MAY BE CONSIDERED OPPOSITES OR EXTREMES. ...
... WORDS WHICH, IN SOME SENSES, MAY BE CONSIDERED OPPOSITES OR EXTREMES. ...
Practice Set #l--Diagram the following sentences looking
... C. Diagramming Prepositional Phrases. Prepositional phrases are frequently used to modify the subjects and verbs of sentences. A prepositional phrase must contain (a) a preposition, (b) the object of the preposition, and (c) any modifiers of the object. To diagram a prepositional phrase, the preposi ...
... C. Diagramming Prepositional Phrases. Prepositional phrases are frequently used to modify the subjects and verbs of sentences. A prepositional phrase must contain (a) a preposition, (b) the object of the preposition, and (c) any modifiers of the object. To diagram a prepositional phrase, the preposi ...
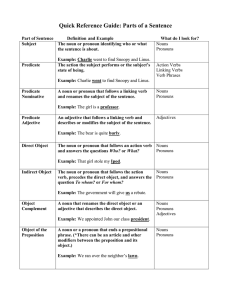
Part 2 Parts of Speech and Parts of a Sentence
... verb, precedes the direct object, and answers the question To whom? or For whom? ...
... verb, precedes the direct object, and answers the question To whom? or For whom? ...
can never oe ma prepOSltlOnalpnrase There and here are never the
... can never oe m a prepOSltlOnalpnrase There and here are never the subject of a sentence. The subject can be an "understood you": Bring me the remote control, please. (You bring it.) ...
... can never oe m a prepOSltlOnalpnrase There and here are never the subject of a sentence. The subject can be an "understood you": Bring me the remote control, please. (You bring it.) ...
Predicate Nominative/adjective Noun or pronoun following a linking
... helping verb—“is kicking” ...
... helping verb—“is kicking” ...
A noun is the word we use to identify a person, place, object or idea
... An adverb is used to modify a verb, an adjective or another adverb. It expresses in what manner, when, where, and how much. Examples of adverbs: The man spoke loudly. (modifies the verb spoke) ...
... An adverb is used to modify a verb, an adjective or another adverb. It expresses in what manner, when, where, and how much. Examples of adverbs: The man spoke loudly. (modifies the verb spoke) ...
writing punctuation handout
... words that form a single idea, or to divide a word at the end of a line. ...
... words that form a single idea, or to divide a word at the end of a line. ...
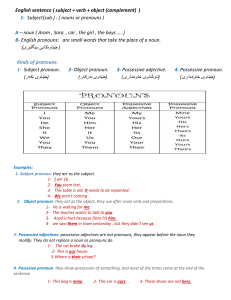
Subject(sub.) : ( nouns or pronouns )
... 2- Object pronoun: they act as the object, they use after main verb and prepositions. 1- He is waiting for me. 2- The teacher wants to talk to you. 3- Azad is hurt because Dara hit him. 4- we saw them in town yesterday , but they didn’t see us 3- Possessive adjectives: possessive adjectives are not ...
... 2- Object pronoun: they act as the object, they use after main verb and prepositions. 1- He is waiting for me. 2- The teacher wants to talk to you. 3- Azad is hurt because Dara hit him. 4- we saw them in town yesterday , but they didn’t see us 3- Possessive adjectives: possessive adjectives are not ...
Parts of Speech
... An article lets you know whether you are talking about something in particular or something in general. A, an, the *use an before a word starting with a vowel. I bought an orange at the store. We returned the movie to the store. ...
... An article lets you know whether you are talking about something in particular or something in general. A, an, the *use an before a word starting with a vowel. I bought an orange at the store. We returned the movie to the store. ...
parts_of_speech
... ADVERBS- What describes the verbs? (tells the when, where, or to what extent/ how much/ how often) Adverbs often end in “-ly.” PRONOUN- What takes the place of a noun? (They take the place of someone or something’s name: I, you, he, she, it, etc.) CONJUNCTIONS- What connects two or more things in ...
... ADVERBS- What describes the verbs? (tells the when, where, or to what extent/ how much/ how often) Adverbs often end in “-ly.” PRONOUN- What takes the place of a noun? (They take the place of someone or something’s name: I, you, he, she, it, etc.) CONJUNCTIONS- What connects two or more things in ...
GMAS Crash Couse
... What a subject is doing; what is being done to it; state of being Verbs and subjects must agree in number ▪ 2 singular subjects joined by and: verb is plural ▪ 2 singular subjects connected by either… or, or neither… nor, the verb is singular ▪ 2 plural subjects connected by either… or, or neither ...
... What a subject is doing; what is being done to it; state of being Verbs and subjects must agree in number ▪ 2 singular subjects joined by and: verb is plural ▪ 2 singular subjects connected by either… or, or neither… nor, the verb is singular ▪ 2 plural subjects connected by either… or, or neither ...
Stay and write 2015 y1 [ ppt 5MB ]
... before a noun, to make the noun’s meaning more specific (i.e. to modify the noun), or after the verb be, as its complement. Adjectives cannot be modified by other adjectives. This distinguishes them from nouns, which can be. ...
... before a noun, to make the noun’s meaning more specific (i.e. to modify the noun), or after the verb be, as its complement. Adjectives cannot be modified by other adjectives. This distinguishes them from nouns, which can be. ...
Unit 2: Verbs, Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions and Interjections
... 2. Linking—a verb that connects a subject with a word that describes or identifies it; the verb does NOT show action • Forms of the verb “be” are the most common linking verbs Ex: He is a general. What two words does the linking verb connect?_____ ...
... 2. Linking—a verb that connects a subject with a word that describes or identifies it; the verb does NOT show action • Forms of the verb “be” are the most common linking verbs Ex: He is a general. What two words does the linking verb connect?_____ ...
for whom - Wikispaces
... A conjunction is a word used to join words or groups of words. Ex. And, but, or, nor, for, so, yet… Both girls and boys went to the park for a ...
... A conjunction is a word used to join words or groups of words. Ex. And, but, or, nor, for, so, yet… Both girls and boys went to the park for a ...
Chinese grammar
This article concerns Standard Chinese. For the grammars of other forms of Chinese, see their respective articles via links on Chinese language and varieties of Chinese.The grammar of Standard Chinese shares many features with other varieties of Chinese. The language almost entirely lacks inflection, so that words typically have only one grammatical form. Categories such as number (singular or plural) and verb tense are frequently not expressed by any grammatical means, although there are several particles that serve to express verbal aspect, and to some extent mood.The basic word order is subject–verb–object (SVO). Otherwise, Chinese is chiefly a head-last language, meaning that modifiers precede the words they modify – in a noun phrase, for example, the head noun comes last, and all modifiers, including relative clauses, come in front of it. (This phenomenon is more typically found in SOV languages like Turkish and Japanese.)Chinese frequently uses serial verb constructions, which involve two or more verbs or verb phrases in sequence. Chinese prepositions behave similarly to serialized verbs in some respects (several of the common prepositions can also be used as full verbs), and they are often referred to as coverbs. There are also location markers, placed after a noun, and hence often called postpositions; these are often used in combination with a coverb. Predicate adjectives are normally used without a copular verb (""to be""), and can thus be regarded as a type of verb.As in many east Asian languages, classifiers or measure words are required when using numerals (and sometimes other words such as demonstratives) with nouns. There are many different classifiers in the language, and each countable noun generally has a particular classifier associated with it. Informally, however, it is often acceptable to use the general classifier 个 [個] ge in place of other specific classifiers.Examples given in this article use simplified Chinese characters (with the traditional characters following in brackets if they differ) and standard pinyin Romanization.


















![Stay and write 2015 y1 [ ppt 5MB ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003100526_1-72287210420a6e1d2b6a1ef8c9b96048-300x300.png)

