Grammar time! - Mrs. Penniston`s Class Website
... in front of the main verb. There can be more than one helping verb in a sentence. ...
... in front of the main verb. There can be more than one helping verb in a sentence. ...
Study Guide for Grammar Test 2
... Learn the term Predicate. It’s useful when we talk about commas. A predicate is the completer of a sentence. The subject names the "do-er" or "be-er" of the sentence; the predicate does the rest of the work. A simple predicate consists of only a verb, verb string, or compound verb: ...
... Learn the term Predicate. It’s useful when we talk about commas. A predicate is the completer of a sentence. The subject names the "do-er" or "be-er" of the sentence; the predicate does the rest of the work. A simple predicate consists of only a verb, verb string, or compound verb: ...
Glossary of Gramatical Terms
... A pronoun stands in place of a noun or a noun group. A pronoun refers to something that has been named and has already been written about. For example: the harbour is a popular place. It is mostly used by fishermen. Pronouns work only if they are not ambiguous (that is, there is a clear line of re ...
... A pronoun stands in place of a noun or a noun group. A pronoun refers to something that has been named and has already been written about. For example: the harbour is a popular place. It is mostly used by fishermen. Pronouns work only if they are not ambiguous (that is, there is a clear line of re ...
Action Verb Complements An ACTION VERB is a verb that shows
... whom? for whom? after the action verb. An IO must be a noun or a pronoun. Example: Sally gave her mother a check for rent. The DIRECT OBJECT answers the questions what? or whom? after the action verb. A DO must be a noun or a pronoun. Example: Jeff kicked the ball very hard. *Remember: No part of an ...
... whom? for whom? after the action verb. An IO must be a noun or a pronoun. Example: Sally gave her mother a check for rent. The DIRECT OBJECT answers the questions what? or whom? after the action verb. A DO must be a noun or a pronoun. Example: Jeff kicked the ball very hard. *Remember: No part of an ...
verb - School District of Cambridge
... linking verb – a verb that helps to make statement by serving as a link between two words - must be followed by a noun or pronoun that renames it or an adjective that describes it - most common ones are forms of “be” ex) I am hungry. She is the teacher. The school lunches taste funny. ...
... linking verb – a verb that helps to make statement by serving as a link between two words - must be followed by a noun or pronoun that renames it or an adjective that describes it - most common ones are forms of “be” ex) I am hungry. She is the teacher. The school lunches taste funny. ...
Parallelism - St. Cloud State University
... Boy Scouts learn cooking, canoeing, swimming, and how to make a rope. The last phrase is too heavy; it cannot balance the other –ing words. If we change the phrase to rope-making, it is balanced. A slightly different parallelism involves the common connectors either-or, neither-nor, not only-but als ...
... Boy Scouts learn cooking, canoeing, swimming, and how to make a rope. The last phrase is too heavy; it cannot balance the other –ing words. If we change the phrase to rope-making, it is balanced. A slightly different parallelism involves the common connectors either-or, neither-nor, not only-but als ...
Parts of Speech
... Parts of Speech Noun – person, place, thing, idea (mom, Wendy’s, school, love) Pronoun – takes place of a noun (he, she, it, you, his, I, my, our) Adjective – describes a noun (flat, gooey, soft, amazing) Verb – action (run, fly, dance, dream, want) or being (am, is, are) Adverb – tells how, when, o ...
... Parts of Speech Noun – person, place, thing, idea (mom, Wendy’s, school, love) Pronoun – takes place of a noun (he, she, it, you, his, I, my, our) Adjective – describes a noun (flat, gooey, soft, amazing) Verb – action (run, fly, dance, dream, want) or being (am, is, are) Adverb – tells how, when, o ...
Noun Functions
... 7. If the verb is linking, see if you have a word on the other side of the verb that renames the subject. If you do, that word is the predicate nominative. Example: Jim is a student in my 5th hour class. The linking verb is is. Jim = student, so student is the predicate nominative. 8. Finally, if no ...
... 7. If the verb is linking, see if you have a word on the other side of the verb that renames the subject. If you do, that word is the predicate nominative. Example: Jim is a student in my 5th hour class. The linking verb is is. Jim = student, so student is the predicate nominative. 8. Finally, if no ...
MBUPLOAD-5373-1
... ____10. This word is always followed by a noun or pronoun and shows relationships between other words often (but not always) relating to time or spatial relationships (space): A] Preposition b] complement c] direct object PART 1 answers: She wanted to go to the movies. ANSWERS 1. She Subject = Prono ...
... ____10. This word is always followed by a noun or pronoun and shows relationships between other words often (but not always) relating to time or spatial relationships (space): A] Preposition b] complement c] direct object PART 1 answers: She wanted to go to the movies. ANSWERS 1. She Subject = Prono ...
Subject-Verb Agreement
... A pronoun replaces a noun in a given sentence. There are various types of pronouns: subject (I, you, he, she, it, we, they), object pronouns (me, you, him, her, it, us, them), Possessive pronouns (mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, yours, theirs), Reflexive (myself, yourself, himself, herself, itsel ...
... A pronoun replaces a noun in a given sentence. There are various types of pronouns: subject (I, you, he, she, it, we, they), object pronouns (me, you, him, her, it, us, them), Possessive pronouns (mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, yours, theirs), Reflexive (myself, yourself, himself, herself, itsel ...
Nouns and Verbs
... • Linking verbs are most commonly different forms of the verb “to be.” am, are, is, was, were, be, being, been EXAMPLE: Laura is sweet. • In this sentence, the verb is LINKS the subject Laura to the idea that she is sweet. ...
... • Linking verbs are most commonly different forms of the verb “to be.” am, are, is, was, were, be, being, been EXAMPLE: Laura is sweet. • In this sentence, the verb is LINKS the subject Laura to the idea that she is sweet. ...
Parts of Speech
... Pronoun: a “replacement” noun, a word that serves as an ambassador for a noun. There are many different types of pronouns; the most common pronouns are “I”, “he”, or “she” (subject pronouns) and “me”, “him”, or “her” (object pronouns). Adjective: a word that modifies—describes or limits—a noun or pr ...
... Pronoun: a “replacement” noun, a word that serves as an ambassador for a noun. There are many different types of pronouns; the most common pronouns are “I”, “he”, or “she” (subject pronouns) and “me”, “him”, or “her” (object pronouns). Adjective: a word that modifies—describes or limits—a noun or pr ...
Stage 4 Check 11 – Answers - Tranmere Park Primary School
... 20-21. (W4:17,21) A comma is used after a fronted adverbial. It is also used to separate items in a list. It is not used before the last item which has ‘and’ in front of it. It tells the reader to pause, but not for as long as a full stop. ...
... 20-21. (W4:17,21) A comma is used after a fronted adverbial. It is also used to separate items in a list. It is not used before the last item which has ‘and’ in front of it. It tells the reader to pause, but not for as long as a full stop. ...
Verbals - Santa Ana College
... (As a noun) To give up in the middle of the game is unacceptable. (To give up is the subject of this sentence. It is an infinitive noun). (As an adjective) Do you have anything to do while you wait? (To do is an adjective because it is modifying the noun anything). (As an adverb) I will go with him ...
... (As a noun) To give up in the middle of the game is unacceptable. (To give up is the subject of this sentence. It is an infinitive noun). (As an adjective) Do you have anything to do while you wait? (To do is an adjective because it is modifying the noun anything). (As an adverb) I will go with him ...
sub pre anti dry er ing Don`t ( stair / stare ) at the lady. Shall I ( pour
... 10-11. (W4:17, 19) A noun phrase is a phrase with a noun as its head word. A noun with any sort of modifier is a noun phrase (the dog, the old house on the hill). A preposition usually goes in front of a noun and describes the position of something or the time or the way something happened ( under t ...
... 10-11. (W4:17, 19) A noun phrase is a phrase with a noun as its head word. A noun with any sort of modifier is a noun phrase (the dog, the old house on the hill). A preposition usually goes in front of a noun and describes the position of something or the time or the way something happened ( under t ...
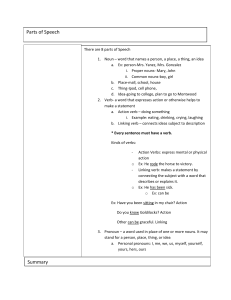
Parts of Speech Summary
... b. Linking verb – connects ideas subject to description * Every sentence must have a verb. Kinds of verbs: o ...
... b. Linking verb – connects ideas subject to description * Every sentence must have a verb. Kinds of verbs: o ...
Parts of speech
... The term “parts of speech” refers to the words that make up a sentence and the functions those words perform within the sentence. There are 8 parts of speech, but these 6 are the most important to recognize first: 1) noun 2) verb 3) preposition 4) adjective 5) adverb 6) article The same word can be ...
... The term “parts of speech” refers to the words that make up a sentence and the functions those words perform within the sentence. There are 8 parts of speech, but these 6 are the most important to recognize first: 1) noun 2) verb 3) preposition 4) adjective 5) adverb 6) article The same word can be ...
PARTS OF SPEECH ADJECTIVE: Describes a noun or pronoun
... adverb). CONJUNCTION: A word that joins two or more elements. (See PARTS OF SPEECH) DIRECT OBJECT: the noun that receives the action of the verb. INDIRECT OBJECT: The noun that names the person or thing for whom or to whom the action of the verb is directed; cannot be present without a direct object ...
... adverb). CONJUNCTION: A word that joins two or more elements. (See PARTS OF SPEECH) DIRECT OBJECT: the noun that receives the action of the verb. INDIRECT OBJECT: The noun that names the person or thing for whom or to whom the action of the verb is directed; cannot be present without a direct object ...
Noun: A noun is a person, place, thing, quality, or act
... English: Noun: A noun is a person, place, thing, quality, or act. Examples: pencil, girl, supermarket, happiness Verb: Verbs are action or existence words that tell what nouns do. Examples: to fly, to run, to be, jump, lived Adjective: An adjective describes a noun. Examples: hairy, crazy, wonderful ...
... English: Noun: A noun is a person, place, thing, quality, or act. Examples: pencil, girl, supermarket, happiness Verb: Verbs are action or existence words that tell what nouns do. Examples: to fly, to run, to be, jump, lived Adjective: An adjective describes a noun. Examples: hairy, crazy, wonderful ...
Grammar 3 handout 2010
... or where something happened. Examples: slowly, intelligently, well, yesterday, tomorrow, here, everywhere, very 5. Pronoun: A pronoun is used instead of a noun, to avoid repeating the noun. Examples: I, you, he, she, it, we, they 6. Conjunction: A conjunction joins two words, phrases, clauses or sen ...
... or where something happened. Examples: slowly, intelligently, well, yesterday, tomorrow, here, everywhere, very 5. Pronoun: A pronoun is used instead of a noun, to avoid repeating the noun. Examples: I, you, he, she, it, we, they 6. Conjunction: A conjunction joins two words, phrases, clauses or sen ...
Chinese grammar
This article concerns Standard Chinese. For the grammars of other forms of Chinese, see their respective articles via links on Chinese language and varieties of Chinese.The grammar of Standard Chinese shares many features with other varieties of Chinese. The language almost entirely lacks inflection, so that words typically have only one grammatical form. Categories such as number (singular or plural) and verb tense are frequently not expressed by any grammatical means, although there are several particles that serve to express verbal aspect, and to some extent mood.The basic word order is subject–verb–object (SVO). Otherwise, Chinese is chiefly a head-last language, meaning that modifiers precede the words they modify – in a noun phrase, for example, the head noun comes last, and all modifiers, including relative clauses, come in front of it. (This phenomenon is more typically found in SOV languages like Turkish and Japanese.)Chinese frequently uses serial verb constructions, which involve two or more verbs or verb phrases in sequence. Chinese prepositions behave similarly to serialized verbs in some respects (several of the common prepositions can also be used as full verbs), and they are often referred to as coverbs. There are also location markers, placed after a noun, and hence often called postpositions; these are often used in combination with a coverb. Predicate adjectives are normally used without a copular verb (""to be""), and can thus be regarded as a type of verb.As in many east Asian languages, classifiers or measure words are required when using numerals (and sometimes other words such as demonstratives) with nouns. There are many different classifiers in the language, and each countable noun generally has a particular classifier associated with it. Informally, however, it is often acceptable to use the general classifier 个 [個] ge in place of other specific classifiers.Examples given in this article use simplified Chinese characters (with the traditional characters following in brackets if they differ) and standard pinyin Romanization.