* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parts of speech
Germanic strong verb wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
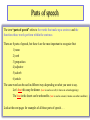
Parts of speech The term “parts of speech” refers to the words that make up a sentence and the functions those words perform within the sentence. There are 8 parts of speech, but these 6 are the most important to recognize first: 1) noun 2) verb 3) preposition 4) adjective 5) adverb 6) article The same word can be used in different ways depending on what you want to say. Let’s heat this soup for dinner. (heat is used as a verb; it shows an action happening) The heat in the desert can be unbearable. (heat is used as a noun; it names a weather condition) Look at the next pages for examples of all these parts of speech . . . Nouns A noun names something, just as your parents named you. • A noun answers the question: “What’s this?” or Who’s this?” Your name is a “proper noun.” ►Gladys, Bill, Ms. Smith, Aunt Mary, Frank Sinatra The name of just about everything else is a “common noun.” ►car, book, love, disgust, freedom, dog, insurance, police officer Verbs • A verb tells time—different tenses tell us when something happens, will happen, or has happened. ► I ran home. (yesterday, an hour ago) We are happy. (now, today) • A verb talks about an action or a state of being. ►Maria rides the bus to work. (action) Maria seems intelligent. (state) • There are verbs that have a linking or helping function. ►Bill is a doctor. (is links Bill with doctor) He is working hard these days. (is helps working to create a verb tense) • There are regular verbs that use -ed at the end to form a past tense, and irregular verbs that are all different in the past. • Modal verbs give extra meaning to a sentence. Can, must, may, might, could, should, and would are modal verbs. ► I played tennis. My brother swam in the pool. ►Tanya might go to the movies tonight, but she should stay home and do her homework. [The extra meanings are possibility (might) and advisability (should)] Prepositions • Prepositions tell where or when an action is taking place. They can also be used to add more information. • in, on, to, around, with, toward, through, of, for, from, across, by (and many more!) My sister is the girl with the long red hair who is standing next to the tall guy by the Coke machine. • Prepositions are followed by nouns or noun phrases, and we call them “prepositional phrases.” Look at all the important information added with prepositional phrases! with the long red hair next to the tall guy by the Coke machine “Modifying” words: adjectives and adverbs To modify means to alter or change, so adjectives and adverbs are used to affect the meaning of other parts of speech. • Adjectives modify nouns; they add a description to the noun and answer the question: “What kind?” • favorite things little girl tropical storm • Adverbs modify verbs; they describe actions and answer the questions: “How? How frequently?” • She spoke slowly. I often go dancing. Articles • Articles are used with nouns. • Articles are tricky in English! • For more information, see Articles, Lesson 1 and Articles, Lesson 2. the house, a cockroach, an egg, some chips