Eight Parts of Speech
... Abstract nouns name ideas, qualities, or states (feelings). Singular nouns name one person, place, thing, or idea. Plural nouns name more than one person, place, thing, or idea. Collective nouns refer to a group of people or things. Compound nouns are made up of two or more words; they may be writte ...
... Abstract nouns name ideas, qualities, or states (feelings). Singular nouns name one person, place, thing, or idea. Plural nouns name more than one person, place, thing, or idea. Collective nouns refer to a group of people or things. Compound nouns are made up of two or more words; they may be writte ...
Parts of Speech Review
... Danced is still intransitive because “at the Prom” isn’t an object—it’s a prepositional phrase. ...
... Danced is still intransitive because “at the Prom” isn’t an object—it’s a prepositional phrase. ...
Subject Verb Agreement and Pronoun Agreement
... coach was overconfident. 2. Neither the Oregon coach nor the players were overconfident. ...
... coach was overconfident. 2. Neither the Oregon coach nor the players were overconfident. ...
The vast desert of linguistics…
... Grammar – the set of structural rules that controls the way language works. There are 3 aspects to grammar: word class, syntax and morphology • word class = define the roles that each word can play in a sentence • syntax = the set of rules that control where each word class can appear in a sentence ...
... Grammar – the set of structural rules that controls the way language works. There are 3 aspects to grammar: word class, syntax and morphology • word class = define the roles that each word can play in a sentence • syntax = the set of rules that control where each word class can appear in a sentence ...
Language Symbols Described
... approach (Project Read) uses a simple method to “frame” each word in a sentence with a shape. Nouns are underlined with a straight line Verbs use a horizontal zigzag line. Adverbs are framed with a triangle with where, when, how and why written on the side to show how the adverb phrase is used. Adje ...
... approach (Project Read) uses a simple method to “frame” each word in a sentence with a shape. Nouns are underlined with a straight line Verbs use a horizontal zigzag line. Adverbs are framed with a triangle with where, when, how and why written on the side to show how the adverb phrase is used. Adje ...
Step One Notes (Parts of Speech)
... shows relationship between a noun or pronoun and some other word in the sentence across, after, against, around, at, before, below, between, by, during, except, for, from, in, of, off, on, over, since, through, to, under, until, with, according to, because of, instead of, etc. We went to colle ...
... shows relationship between a noun or pronoun and some other word in the sentence across, after, against, around, at, before, below, between, by, during, except, for, from, in, of, off, on, over, since, through, to, under, until, with, according to, because of, instead of, etc. We went to colle ...
abstract
... imperfective (like pisat’ ‘write’), but can be perfective (like dat’ ‘give’). Prefixed verbs that do not have a secondary suffix are usually perfective (like na-pisat’ ‘write’), but can be imperfective (like pre-obladat’ ‘prevail’). Furthermore, sometimes one and the same verb has both perfective an ...
... imperfective (like pisat’ ‘write’), but can be perfective (like dat’ ‘give’). Prefixed verbs that do not have a secondary suffix are usually perfective (like na-pisat’ ‘write’), but can be imperfective (like pre-obladat’ ‘prevail’). Furthermore, sometimes one and the same verb has both perfective an ...
Parts of Speech Review (PowerPoint)
... Other Kinds of Pronouns • Reflexive Pronouns: reflects the subject of the sentence – there will always be at least one word between a reflexive pronoun and its antecedent. – Ex. Luke Skywalker made himself a lightsaber. ...
... Other Kinds of Pronouns • Reflexive Pronouns: reflects the subject of the sentence – there will always be at least one word between a reflexive pronoun and its antecedent. – Ex. Luke Skywalker made himself a lightsaber. ...
Statistical Natural Language Procesing: linguistic
... (e.g. ‘the’, ‘a’) and adjectives describe the properties of nouns (e.g. ‘red’, ‘long’, ‘intelligent’). Verbs are used to describe actions, activities and states (e.g. ‘have’, ‘threw’ , ‘walked’). Adverbs modify a verb in the same way as adjectives modify nouns (e.g. ‘often’, ‘heavily’). Prepositions ...
... (e.g. ‘the’, ‘a’) and adjectives describe the properties of nouns (e.g. ‘red’, ‘long’, ‘intelligent’). Verbs are used to describe actions, activities and states (e.g. ‘have’, ‘threw’ , ‘walked’). Adverbs modify a verb in the same way as adjectives modify nouns (e.g. ‘often’, ‘heavily’). Prepositions ...
nouns - Bastian10
... Refers to persons, places, or things in a more general way than a noun does. ...
... Refers to persons, places, or things in a more general way than a noun does. ...
The Sentence - Oakton Community College
... Be sure to distinguish between verbs and verbals. Verbals do not function as verbs anymore. You can see what they are by their position in the sentence. They may be nouns (subjects or objects) or even adjectives. To sing is a great joy. Singing is a great joy. (Subjects; hence, nouns). Mary loves to ...
... Be sure to distinguish between verbs and verbals. Verbals do not function as verbs anymore. You can see what they are by their position in the sentence. They may be nouns (subjects or objects) or even adjectives. To sing is a great joy. Singing is a great joy. (Subjects; hence, nouns). Mary loves to ...
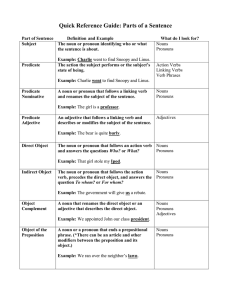
Parts of Speech and Parts of a Sentence
... • Sentences in the perfect tense include two events or actions, such as: I had finished my homework [event one] before my boyfriend arrived [event two]. For present perfect tense, another action is assumed, for example, the sentence: “I have studied for two hours” implies that I will do more study ...
... • Sentences in the perfect tense include two events or actions, such as: I had finished my homework [event one] before my boyfriend arrived [event two]. For present perfect tense, another action is assumed, for example, the sentence: “I have studied for two hours” implies that I will do more study ...
Parts of Speech
... Most important, match your pronouns with your related nouns and verbs. For example: A corporation need to rely on their employees to closely monitor their financial data so that they can maintain adequate controls over their expenditures. Wrong. A corporation is singular and requires singular pronou ...
... Most important, match your pronouns with your related nouns and verbs. For example: A corporation need to rely on their employees to closely monitor their financial data so that they can maintain adequate controls over their expenditures. Wrong. A corporation is singular and requires singular pronou ...
English Help
... Action Verbs . . . . . Words that tell about an action . He walked to school. Linking Verbs . . . . . Verbs that state that something is ; state-of-being She is pretty. Helping Verbs . . . . When a verb is made up of two or more words, the last word is the main verb. The other words are called helpi ...
... Action Verbs . . . . . Words that tell about an action . He walked to school. Linking Verbs . . . . . Verbs that state that something is ; state-of-being She is pretty. Helping Verbs . . . . When a verb is made up of two or more words, the last word is the main verb. The other words are called helpi ...
Definitions of grammar Definiciones de la gramática
... complete thought (subject, verb, object): Martha loves the city. Subject [sujeto]Generally, the person or thing that performs the action in a sentence. For example "New York grew rapidly." New York (who grew?) is the subject. Subjunctive Mood [modo subjuntivo].Verb tenses that indicate non-factual a ...
... complete thought (subject, verb, object): Martha loves the city. Subject [sujeto]Generally, the person or thing that performs the action in a sentence. For example "New York grew rapidly." New York (who grew?) is the subject. Subjunctive Mood [modo subjuntivo].Verb tenses that indicate non-factual a ...
Parts of Speech
... Pronoun – takes place of a noun (he, she, it, you, his, I, my, our) Adjective – describes a noun (flat, gooey, soft, amazing) Verb – action (run, fly, dance, dream, want) or being (am, is, are) Adverb – tells how, when, or where about a verb, adjective, or other adverb (slowly, loudly, carefully, to ...
... Pronoun – takes place of a noun (he, she, it, you, his, I, my, our) Adjective – describes a noun (flat, gooey, soft, amazing) Verb – action (run, fly, dance, dream, want) or being (am, is, are) Adverb – tells how, when, or where about a verb, adjective, or other adverb (slowly, loudly, carefully, to ...
Chapter 2 Folder 1 – The Accusative Case In Chapter 1 you learned
... object, you must have an action verb. Linking verbs (est, sunt) are never followed by direct objects. The direct object will answer who? or what? after the verb. e.g. Matthew hit the ball. What did he hit? The ball . . . . . .ball is the direct object. I love you! Whom do I love? You . . .. . .You i ...
... object, you must have an action verb. Linking verbs (est, sunt) are never followed by direct objects. The direct object will answer who? or what? after the verb. e.g. Matthew hit the ball. What did he hit? The ball . . . . . .ball is the direct object. I love you! Whom do I love? You . . .. . .You i ...
6th Grade Parts of Speech packet
... A common noun is a word that names a person, a place, or a thing. Singular nouns name one person, place, or thing. Plural nouns name more than one person, place, or thing. Add an –s to most nouns to make them plural. However, sometimes changing the word is necessary. For example, the plural form of ...
... A common noun is a word that names a person, a place, or a thing. Singular nouns name one person, place, or thing. Plural nouns name more than one person, place, or thing. Add an –s to most nouns to make them plural. However, sometimes changing the word is necessary. For example, the plural form of ...
Nouns, Pronouns, Verbs Review
... There are Demonstrative pronouns: this, that, these, those that point out a specific person, place, or thing Interrogative pronouns: who, whom, whose, which, and what that begin a question Relative pronouns: who, whom, whose, which that tell more about a noun or subject Indirect pronouns: anyo ...
... There are Demonstrative pronouns: this, that, these, those that point out a specific person, place, or thing Interrogative pronouns: who, whom, whose, which, and what that begin a question Relative pronouns: who, whom, whose, which that tell more about a noun or subject Indirect pronouns: anyo ...
Multi Sensory Grammar
... • Not and very are always adverbs. • Many adverbs end in –ly. • Adverbs answer the questions – How? When? Where? To what extent? • Adverbs are color coded purple and have a purple arrow going from them to the word that they modify. ...
... • Not and very are always adverbs. • Many adverbs end in –ly. • Adverbs answer the questions – How? When? Where? To what extent? • Adverbs are color coded purple and have a purple arrow going from them to the word that they modify. ...
Part 2 Parts of Speech and Parts of a Sentence
... verb, precedes the direct object, and answers the question To whom? or For whom? ...
... verb, precedes the direct object, and answers the question To whom? or For whom? ...