PDF
... Red for verbs Blue for adjectives Green for nouns a) The man wore a tatty and worn raincoat. b) It was under the table that I found the fluffy rabbit. c) Before I could run the shiny red sports car stopped in front of me. 3. Write a sentence for each of these types of punctuation to show how they wo ...
... Red for verbs Blue for adjectives Green for nouns a) The man wore a tatty and worn raincoat. b) It was under the table that I found the fluffy rabbit. c) Before I could run the shiny red sports car stopped in front of me. 3. Write a sentence for each of these types of punctuation to show how they wo ...
English Help
... Appositives - a word or group of words that identifies or renames another word in a sentence. An appositive provides more information about a noun. Appositives are set off by commas. The sentence will still make sense is you leave the appositive out. ...
... Appositives - a word or group of words that identifies or renames another word in a sentence. An appositive provides more information about a noun. Appositives are set off by commas. The sentence will still make sense is you leave the appositive out. ...
Presentation
... A verb must agree with its subject in number (singular – one, plural – more than one) The number of the subject is not changed by intervening phrases or clauses (FLUFF) ...
... A verb must agree with its subject in number (singular – one, plural – more than one) The number of the subject is not changed by intervening phrases or clauses (FLUFF) ...
Prepositions - MultiMediaPortfolio
... Common Prepositions • Aboard, about, above, across, after, against, along, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, by, down, during, except, for, from, in, into, like, of, off, on, over, past, since, through, throughout, to, toward, under, underneath, until, up, ...
... Common Prepositions • Aboard, about, above, across, after, against, along, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, by, down, during, except, for, from, in, into, like, of, off, on, over, past, since, through, throughout, to, toward, under, underneath, until, up, ...
Parts of Speech - Rocky View Schools
... Look at this example: Sylvia looked everywhere for Sylvia is the antecedent of her. her sandals (her replaces Sylvia). Here is a bank of pronouns: myself, herself, itself, themselves, who, whom, whomever, whose, what, this, that, these, those, another, anyone, each, either, neither, no one, somebody ...
... Look at this example: Sylvia looked everywhere for Sylvia is the antecedent of her. her sandals (her replaces Sylvia). Here is a bank of pronouns: myself, herself, itself, themselves, who, whom, whomever, whose, what, this, that, these, those, another, anyone, each, either, neither, no one, somebody ...
Parts of Speech Review
... It may help you remember these conjunctions by recalling that they all have fewer than four letters. Also, remember the acronym FANBOYS: For-And-Nor-But-Or-Yet-So. Be careful of the words then and now; neither is a coordinating conjunction, so what we say about coordinating conjunctions' roles in a ...
... It may help you remember these conjunctions by recalling that they all have fewer than four letters. Also, remember the acronym FANBOYS: For-And-Nor-But-Or-Yet-So. Be careful of the words then and now; neither is a coordinating conjunction, so what we say about coordinating conjunctions' roles in a ...
Course/seminar content (provide complete description):
... apostrophe, simple intonation. Respectfull upper-case. Grammar: Nominal inflection (nouns and adjectives), irregular plurals, formation of feminines. Formatiion of adjectives; degree of adjectives. Determinate and indeterminate articles. Verbal inflection: present indicative, present progressive (st ...
... apostrophe, simple intonation. Respectfull upper-case. Grammar: Nominal inflection (nouns and adjectives), irregular plurals, formation of feminines. Formatiion of adjectives; degree of adjectives. Determinate and indeterminate articles. Verbal inflection: present indicative, present progressive (st ...
sub pre anti dry er ing Don`t ( stair / stare ) at the lady. Shall I ( pour
... Perfect modal form ( modal verb + have + past participle of the verb) NB modal verbs are a Stage 5 expectation. ...
... Perfect modal form ( modal verb + have + past participle of the verb) NB modal verbs are a Stage 5 expectation. ...
Foundations of Sanskrit Chapter 2 – Introduction to Grammar This
... Because all nouns are case marked, Sanskrit has free word order! Moving words around in a sentence is unlimited though the most common structure is subject-object-verb. Sanskrit also has less need of prepositions like with, by, of. The nouns and their suffixes are all on vocabulary sheet 1. This is ...
... Because all nouns are case marked, Sanskrit has free word order! Moving words around in a sentence is unlimited though the most common structure is subject-object-verb. Sanskrit also has less need of prepositions like with, by, of. The nouns and their suffixes are all on vocabulary sheet 1. This is ...
notes as word document
... 1. A NOUN NAMES A PERSON, PLACE, THING, OR IDEA. IT CAN BE PROPER OR COMMON, COLLECTIVE, CONCRETE, OR ABSTRACT, SINGULAR OR PLURAL. NOUNS HAVE PERSON (first, second, third), NUMBER (singular/plural), GENDER (masculine, feminine, neuter), AND CASE (nominative, possessive, objective). 2. A VERB IS A W ...
... 1. A NOUN NAMES A PERSON, PLACE, THING, OR IDEA. IT CAN BE PROPER OR COMMON, COLLECTIVE, CONCRETE, OR ABSTRACT, SINGULAR OR PLURAL. NOUNS HAVE PERSON (first, second, third), NUMBER (singular/plural), GENDER (masculine, feminine, neuter), AND CASE (nominative, possessive, objective). 2. A VERB IS A W ...
Adding Pronoun Constraints to a Grammar
... – only exception is ‘be’, which has a third form, ‘I am’ ...
... – only exception is ‘be’, which has a third form, ‘I am’ ...
review exercise - East Penn School District
... Roy is always hungry. Always is an adverb modifying an adjective Roy is almost always hungry. Almost is an adverb modifying another adverb, modifying an adjective 6. Preposition: word that shows a relationship of a noun or pronoun to some other word in the sentence. Ex: aboard, about, above, across, ...
... Roy is always hungry. Always is an adverb modifying an adjective Roy is almost always hungry. Almost is an adverb modifying another adverb, modifying an adjective 6. Preposition: word that shows a relationship of a noun or pronoun to some other word in the sentence. Ex: aboard, about, above, across, ...
Subject-Verb Agreement
... Subjects • Subject = who or what the sentence is about • Subjects can be – Singular = one person/thing – Plural = more than one person/thing ...
... Subjects • Subject = who or what the sentence is about • Subjects can be – Singular = one person/thing – Plural = more than one person/thing ...
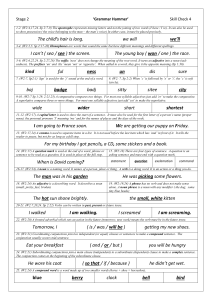
Stage 4 Check 1 - Tranmere Park Primary School
... count – counter) and to change the tense ( ie walk-walked-walking) ...
... count – counter) and to change the tense ( ie walk-walked-walking) ...
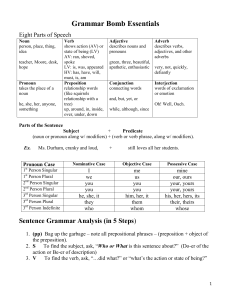
Grammar Bomb Essentials
... b. LV What word describes or renames the subject? PA Describes = adjective = Predicate Adjective PN Renames = noun = Predicate Nominative ...
... b. LV What word describes or renames the subject? PA Describes = adjective = Predicate Adjective PN Renames = noun = Predicate Nominative ...
Subject-Verb Agreement
... Subjects • Subject = who or what the sentence is about • Subjects come in two kinds – Singular = one person/thing – Plural = more than one ...
... Subjects • Subject = who or what the sentence is about • Subjects come in two kinds – Singular = one person/thing – Plural = more than one ...
Latin 101: How to Identify Grammatical Forms in Context
... Or, “What is the case of horā? Why is it in that case? horā is ablative of time* pronouns, including relative pronouns: case, number, gender, referent (=what it refers to) example: Quintus, quī ingeniosus erat, ludum in Venusiā nōn amat. quī: nom. sing. masc. referring to Quintus adjectives: case, n ...
... Or, “What is the case of horā? Why is it in that case? horā is ablative of time* pronouns, including relative pronouns: case, number, gender, referent (=what it refers to) example: Quintus, quī ingeniosus erat, ludum in Venusiā nōn amat. quī: nom. sing. masc. referring to Quintus adjectives: case, n ...
Unit I Review
... nominatives - other nouns that ‘equal’ (or are the same as) the subject, and that are in the predicate – known as predicate nominatives. Sentences that include ‘being verbs’ will have predicate nominatives. Predicate – The predicate is the verb and everything else in the sentence EXCEPT the subject. ...
... nominatives - other nouns that ‘equal’ (or are the same as) the subject, and that are in the predicate – known as predicate nominatives. Sentences that include ‘being verbs’ will have predicate nominatives. Predicate – The predicate is the verb and everything else in the sentence EXCEPT the subject. ...
16 Mar 09 - Pegasus @ UCF
... common and proper nouns – What are the rules for capitalizing a noun in English? count and noncount nouns – When do I use much/many, few/little? Why can’t I say much persons (In Spanish it’s "muchas personas")? Why do I say many cars but much/a lot of traffic (not many traffics)? singular and plural ...
... common and proper nouns – What are the rules for capitalizing a noun in English? count and noncount nouns – When do I use much/many, few/little? Why can’t I say much persons (In Spanish it’s "muchas personas")? Why do I say many cars but much/a lot of traffic (not many traffics)? singular and plural ...
7th Grade Grammar
... Common nouns that are part of a proper noun are capitalized. Small words that are part of a proper noun are not capitalized unless they are the first or last word. ...
... Common nouns that are part of a proper noun are capitalized. Small words that are part of a proper noun are not capitalized unless they are the first or last word. ...
Stage 2 Check 4 – Answers
... 5-6. (W2:6,22,24. Sp 2:27,28) The suffix ‘ness’ does not change the meaning of the root word. It turns an adjective into a noun (sadsadness). The prefixes ‘un’ and ‘dis’ mean ‘not’ or ‘opposite’. When added to a word, they give it the opposite meaning (Sp 1:30). ...
... 5-6. (W2:6,22,24. Sp 2:27,28) The suffix ‘ness’ does not change the meaning of the root word. It turns an adjective into a noun (sadsadness). The prefixes ‘un’ and ‘dis’ mean ‘not’ or ‘opposite’. When added to a word, they give it the opposite meaning (Sp 1:30). ...
Adjectives/Adverbs - Mrs. Moore`s 7th Grade English Class
... No one in our class had ever heard of the Buffalo soldiers. ...
... No one in our class had ever heard of the Buffalo soldiers. ...
First Grading Period Assessment Outline
... First Grading Period Assessment Preparation I. Vocabulary A. Spelling B. Definition C. Usage II. Parts of Speech A. Noun 1. Subject or object 2. Concrete or abstract B. Pronoun C. Verb 1. Active or passive 2. Auxiliary verbs 3. Linking or action D. Adjective 1. Which, what kind, how many, how much 2 ...
... First Grading Period Assessment Preparation I. Vocabulary A. Spelling B. Definition C. Usage II. Parts of Speech A. Noun 1. Subject or object 2. Concrete or abstract B. Pronoun C. Verb 1. Active or passive 2. Auxiliary verbs 3. Linking or action D. Adjective 1. Which, what kind, how many, how much 2 ...