Lesson 3 - MrSimonPorter
... machining metals, drilling tiny holes in metals, production of CDs, reading and writing CDs, DVDs, etc. ...
... machining metals, drilling tiny holes in metals, production of CDs, reading and writing CDs, DVDs, etc. ...
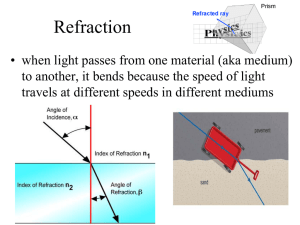
Refraction
... As starlight travels from space into the Earth’s atmosphere, the rays are refracted. Since the atmosphere is constantly changing, the amount of refraction also changes. ...
... As starlight travels from space into the Earth’s atmosphere, the rays are refracted. Since the atmosphere is constantly changing, the amount of refraction also changes. ...
P. LeClair
... occupied states, so photons of energy less than this gap cannot be absorbed (since that would involve promoting an electron to a forbidden state). Thus, insulators are transparent for photon energies less than their energy gap. Metals have no such gap, and can essentially absorb photons of any energ ...
... occupied states, so photons of energy less than this gap cannot be absorbed (since that would involve promoting an electron to a forbidden state). Thus, insulators are transparent for photon energies less than their energy gap. Metals have no such gap, and can essentially absorb photons of any energ ...
ppt - UCSB HEP
... • The sum of all charges in a closed system is constant • Thinking about the number of protons and electrons, this makes sense: If you keep the same number of protons and electrons, the total charge stays the same regardless of what else happens to these particles ...
... • The sum of all charges in a closed system is constant • Thinking about the number of protons and electrons, this makes sense: If you keep the same number of protons and electrons, the total charge stays the same regardless of what else happens to these particles ...
teacher`s notes - event title
... Electricity is a mysterious force. We can’t see it like we see the sun. We can’t hold it like we hold coal. We know when it is working, but it is hard to know exactly what it is. Before we can understand electricity we need to learn about atoms. An atom looks like the sun with the planets spinning a ...
... Electricity is a mysterious force. We can’t see it like we see the sun. We can’t hold it like we hold coal. We know when it is working, but it is hard to know exactly what it is. Before we can understand electricity we need to learn about atoms. An atom looks like the sun with the planets spinning a ...
Behavior of Light Waves
... • Waves can continue to change direction long after the original source of the energy has stopped. ...
... • Waves can continue to change direction long after the original source of the energy has stopped. ...
Periodic Properties of the Elements Effective Nuclear Charge, Zeff
... Effective Nuclear Charge, Zeff The splitting of the principle energy level into the s, p, d, and f energy sublevels is best explained by using the concept of “effective” nuclear charge, Zeff. An electron in a higher energy level is “screened” from seeing 100% (all the protons) of the nuclear charge ...
... Effective Nuclear Charge, Zeff The splitting of the principle energy level into the s, p, d, and f energy sublevels is best explained by using the concept of “effective” nuclear charge, Zeff. An electron in a higher energy level is “screened” from seeing 100% (all the protons) of the nuclear charge ...
Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts 8.1 Types of
... 3. Energy is given off (bond energy) when two atoms achieve greater stability together than apart D. Covalent Bonds 1. Electrons are shared by nuclei 2. Pure covalent (non-polar covalent) a. Electrons are shared evenly 3. Polar covalent bonds a. Electrons are shared unequally b. Atoms end up with fr ...
... 3. Energy is given off (bond energy) when two atoms achieve greater stability together than apart D. Covalent Bonds 1. Electrons are shared by nuclei 2. Pure covalent (non-polar covalent) a. Electrons are shared evenly 3. Polar covalent bonds a. Electrons are shared unequally b. Atoms end up with fr ...