](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014558250_1-e8033e1e03061302606be135a7c0b2f9-300x300.png)
Formula Sheet
... Proper length L0 = distance between two points for observer at rest with respect to them. Moving objects contract: L = L0/ɣ Moving masses increase: M = M0 * ɣ Mass-Energy Equivalence: E = M0c2 at rest, ɣM0c2 when moving Photoelectric Effect Photon Energy: E = hf = hc/λ, where h = Planck’s constant ( ...
... Proper length L0 = distance between two points for observer at rest with respect to them. Moving objects contract: L = L0/ɣ Moving masses increase: M = M0 * ɣ Mass-Energy Equivalence: E = M0c2 at rest, ɣM0c2 when moving Photoelectric Effect Photon Energy: E = hf = hc/λ, where h = Planck’s constant ( ...
ppt
... Oscillations are initiated by short voltage pulses The inductor and capacitor form the transmitter ...
... Oscillations are initiated by short voltage pulses The inductor and capacitor form the transmitter ...
January 2014: Mid-Year Proficiency Study Guide Chapter 1
... Example: When you add more force to your grocery cart it will accelerate if mass remains the same. a. Newton’s 3rd Law – law that states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction ...
... Example: When you add more force to your grocery cart it will accelerate if mass remains the same. a. Newton’s 3rd Law – law that states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction ...
P1 revision fact sheet
... Heat energy is transferred in one of 3 ways - conduction – vibrating particles pass on their energy to the particles next to them. The main form of heat transfer in solids - convection – particles with the most energy move from the hotter place to the cooler place and take their heat energy with the ...
... Heat energy is transferred in one of 3 ways - conduction – vibrating particles pass on their energy to the particles next to them. The main form of heat transfer in solids - convection – particles with the most energy move from the hotter place to the cooler place and take their heat energy with the ...
Chemistry (B) Final Exam Study Guide 1
... ____ 57. How do the energy differences between the higher energy levels of an atom compare with the energy differences between the lower energy levels of the atom? a. They are greater in magnitude than those between lower energy levels. b. They are smaller in magnitude than those between lower energ ...
... ____ 57. How do the energy differences between the higher energy levels of an atom compare with the energy differences between the lower energy levels of the atom? a. They are greater in magnitude than those between lower energy levels. b. They are smaller in magnitude than those between lower energ ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2013
... 1. Which idea of John Dalton is no longer considered part of the modern view of atoms? a. Atoms are extremely small. b. Atoms of the same element have identical masses. c. Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. d. Atoms of different elements can combine in different ratios to ...
... 1. Which idea of John Dalton is no longer considered part of the modern view of atoms? a. Atoms are extremely small. b. Atoms of the same element have identical masses. c. Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. d. Atoms of different elements can combine in different ratios to ...
Physics - Indus International School Bangalore
... (v) Lenses (converging and diverging) including characteristics of the images formed (using ray diagrams only); magnifying glass. (vi) Scattering of light ...
... (v) Lenses (converging and diverging) including characteristics of the images formed (using ray diagrams only); magnifying glass. (vi) Scattering of light ...
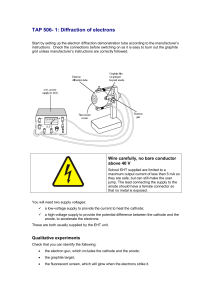
TAP 506- 1: Diffraction of electrons
... If the relationship is of the form d proportional to Vn, you can find the value of n by plotting a log-log graph. The gradient of the graph is equal to the value of n. ...
... If the relationship is of the form d proportional to Vn, you can find the value of n by plotting a log-log graph. The gradient of the graph is equal to the value of n. ...
Lecture 14 (Slides) September 27
... Probabalistic Description of Electrons • Classical physics suggests that we should be able (given enough information) to describe the behaviour of any body – changes in velocity, kinetic energy, potential energy and so on over time. Classical physics suggests that all energies are continuously vari ...
... Probabalistic Description of Electrons • Classical physics suggests that we should be able (given enough information) to describe the behaviour of any body – changes in velocity, kinetic energy, potential energy and so on over time. Classical physics suggests that all energies are continuously vari ...