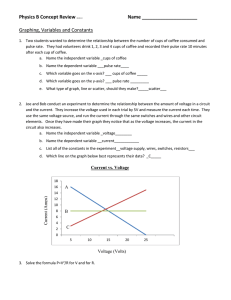
lecture17
... Example: A circular parallel-plate capacitor with plates 2.0cm in diameter is accumulating charge at the rate of 3.50 mC/s at some instant of time. What is the magnitude of the induced magnetic field at the distance r measured radially outward from the center of the plates? a) r=10.0 cm; b) r=1.0 c ...
... Example: A circular parallel-plate capacitor with plates 2.0cm in diameter is accumulating charge at the rate of 3.50 mC/s at some instant of time. What is the magnitude of the induced magnetic field at the distance r measured radially outward from the center of the plates? a) r=10.0 cm; b) r=1.0 c ...
energy of motion
... The pull of gravity is a force that might set an object (or a skier) in motion. The pull or push of a magnet is another force that can move objects. The force you exert with your legs or arms can set a ball in motion. ...
... The pull of gravity is a force that might set an object (or a skier) in motion. The pull or push of a magnet is another force that can move objects. The force you exert with your legs or arms can set a ball in motion. ...
Unit 6 Electromagnetic Waves
... – They can often observe parts of the IR and microwave spectrum from high elevations on Earth on clear days. – Planes can be turned into IR and Microwave observatories, since they often fly above much of the water vapor in Earth’s atmosphere. – Observations of UV, X- and Gamma rays must be done from ...
... – They can often observe parts of the IR and microwave spectrum from high elevations on Earth on clear days. – Planes can be turned into IR and Microwave observatories, since they often fly above much of the water vapor in Earth’s atmosphere. – Observations of UV, X- and Gamma rays must be done from ...
Work, KE, E - Rose
... dx/dt = vx, so we have Fx = m vx dvx/dx = d/dx(mvx2/2). Then Fxdx = d(mvx2/2). Finally, for the total work dW we have dW = Fxdx + Fydy + Fzdz = d(mvx2/2 + mvy2/2 + mvz2/2 ) = d(mv2/2) = dK. When we have only a conservative force acting, the work done by this force is the change in the kinetic energy ...
... dx/dt = vx, so we have Fx = m vx dvx/dx = d/dx(mvx2/2). Then Fxdx = d(mvx2/2). Finally, for the total work dW we have dW = Fxdx + Fydy + Fzdz = d(mvx2/2 + mvy2/2 + mvz2/2 ) = d(mv2/2) = dK. When we have only a conservative force acting, the work done by this force is the change in the kinetic energy ...
Document
... Oscillation time (period): duration of a single oscillation (“T”). Frequency: inverse of period (f). The wave propagates with a given velocity (“phase velocity”, “v” or “c”) Distance between points of identical phase: “wavelength” (λ) Phase difference (φ): difference (in time or space) between ident ...
... Oscillation time (period): duration of a single oscillation (“T”). Frequency: inverse of period (f). The wave propagates with a given velocity (“phase velocity”, “v” or “c”) Distance between points of identical phase: “wavelength” (λ) Phase difference (φ): difference (in time or space) between ident ...
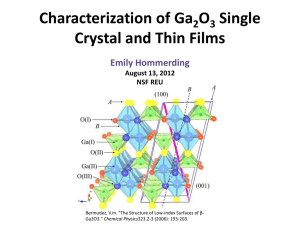
Characterization of Ga 2 0 3 Single Crystal and Thin Films
... Fadley, Charles S. "X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy: From Origins to Future Directions." Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment 601.1-2 (2009): ...
... Fadley, Charles S. "X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy: From Origins to Future Directions." Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment 601.1-2 (2009): ...
Basic Chemistry - Biology with Radjewski
... • They can attain stability by sharing electrons with other atoms (covalent bond) or by losing or gaining electrons (ionic bond) • The atoms are then bonded together into molecules. • Octet rule—atoms with at least two electron shells form stable molecules so they have eight electrons in their outer ...
... • They can attain stability by sharing electrons with other atoms (covalent bond) or by losing or gaining electrons (ionic bond) • The atoms are then bonded together into molecules. • Octet rule—atoms with at least two electron shells form stable molecules so they have eight electrons in their outer ...