hw3 - Piazza
... Due at the beginning of class on Thursday 9/19/13 Problem 1: Carrier Mobility – Dependence on Temperature Suppose you need to make a sensor for measuring the ambient outside temperature in Berkeley (10oC ≤ T ≤ 40oC) based on the change in resistance of a bar-shaped piece of silicon that is uniformly ...
... Due at the beginning of class on Thursday 9/19/13 Problem 1: Carrier Mobility – Dependence on Temperature Suppose you need to make a sensor for measuring the ambient outside temperature in Berkeley (10oC ≤ T ≤ 40oC) based on the change in resistance of a bar-shaped piece of silicon that is uniformly ...
1 In which way is the electric force similar to the gravitational force
... 5 A negatively charged object is brought close to the surface of a conductor, whose opposite side is then grounded. What is this process of charging called? A Charging by contact B Charging by induction C Charging by conduction D Charging by polarization ...
... 5 A negatively charged object is brought close to the surface of a conductor, whose opposite side is then grounded. What is this process of charging called? A Charging by contact B Charging by induction C Charging by conduction D Charging by polarization ...
File
... 3. Student Discussion: Why are these pictures examples of sound energy? Can these pictures be examples of any other forms of energy? ...
... 3. Student Discussion: Why are these pictures examples of sound energy? Can these pictures be examples of any other forms of energy? ...
Chapter 6 The Periodic Table
... Some nonmetals are gases (O, N, Cl); some are brittle solids (S); one is a fuming dark red liquid (Br) Notice the heavy, stair-step line? 3) Metalloids: border the line-2 sides • Properties are intermediate between metals and nonmetals ...
... Some nonmetals are gases (O, N, Cl); some are brittle solids (S); one is a fuming dark red liquid (Br) Notice the heavy, stair-step line? 3) Metalloids: border the line-2 sides • Properties are intermediate between metals and nonmetals ...
الشريحة 1
... electromagnetic spectrum and it includes the colors commonly observed (red, yellow, green, blue and violet). -The visible spectrum consists of electromagnetic radiation whose wavelengths range from 400 nm to nearly 800 nm ...
... electromagnetic spectrum and it includes the colors commonly observed (red, yellow, green, blue and violet). -The visible spectrum consists of electromagnetic radiation whose wavelengths range from 400 nm to nearly 800 nm ...
Phase Transitions of Dirac Electrons Observed in Bismuth
... diagnostic of the state of the electrons), Li and Checkelsky balanced a crystal of highpurity bismuth at the tip of a tiny gold cantilever, and measured the minute flexing of the cantilever as the magnetic field is changed. At low magnetic fields, the detected magnetic signal shows quantum oscillati ...
... diagnostic of the state of the electrons), Li and Checkelsky balanced a crystal of highpurity bismuth at the tip of a tiny gold cantilever, and measured the minute flexing of the cantilever as the magnetic field is changed. At low magnetic fields, the detected magnetic signal shows quantum oscillati ...
Energy and Energy Resources
... What is the mechanical energy of a goose standing on a rock that has 75 J of potential energy and 60 J of kinetic energy? 75 + 60 = _______________ ...
... What is the mechanical energy of a goose standing on a rock that has 75 J of potential energy and 60 J of kinetic energy? 75 + 60 = _______________ ...
Hearing
... How does it sound? • Frequency → Pitch → Note – Remember, frequency is a measure of how many waves pass by in a second – Pitch is how high or low a note sounds ...
... How does it sound? • Frequency → Pitch → Note – Remember, frequency is a measure of how many waves pass by in a second – Pitch is how high or low a note sounds ...
الشريحة 1
... electromagnetic spectrum and it includes the colors commonly observed (red, yellow, green, blue and violet). The visible spectrum consists of electromagnetic radiation whose wavelengths range from 400 nm to nearly 800 nm ...
... electromagnetic spectrum and it includes the colors commonly observed (red, yellow, green, blue and violet). The visible spectrum consists of electromagnetic radiation whose wavelengths range from 400 nm to nearly 800 nm ...
ELECTRON CLUSTERS - POSSIBLE DEUTERIUM FUSION CATALYSERS
... favour the fusion reaction d+d=He + γ, in a manner unknown to the author. The energy of a few MeV, e.g., 6 MeV, which is about the maximum which can result from a fusion act of two deuterons, could be transmitted not to the γ quantum, but to the whole EV, (which is a strongly coupled plasma as revea ...
... favour the fusion reaction d+d=He + γ, in a manner unknown to the author. The energy of a few MeV, e.g., 6 MeV, which is about the maximum which can result from a fusion act of two deuterons, could be transmitted not to the γ quantum, but to the whole EV, (which is a strongly coupled plasma as revea ...
Basic Atomic Theory, The Structure of Matter Atomic Structure
... nucleus and one or more electrons that travel in orbits around the nucleus, like satellites around the earth. The nucleus contains one or more positively charged particles called protons. The positive charge of a proton is ‘opposite’ to the negative charge of an electron, in the sense that the total ...
... nucleus and one or more electrons that travel in orbits around the nucleus, like satellites around the earth. The nucleus contains one or more positively charged particles called protons. The positive charge of a proton is ‘opposite’ to the negative charge of an electron, in the sense that the total ...
Atomic and Nuclear Physics
... • The existence of isotopes is evidence for the existence of neutrons because there is no other way to explain the mass difference of two isotopes of the same element. • By definition, two isotopes of the same element must have the same number of protons, which means the mass attributed to those pro ...
... • The existence of isotopes is evidence for the existence of neutrons because there is no other way to explain the mass difference of two isotopes of the same element. • By definition, two isotopes of the same element must have the same number of protons, which means the mass attributed to those pro ...
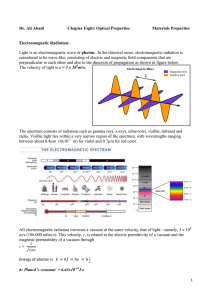
Dr. Ali Abadi Chapter Eight: Optical Properties Materials Properties
... Metals are opaque because the incident radiation having frequencies within the visible range excites electrons into unoccupied energy states above the Fermi energy, as demonstrated in Figure (a) below. Total absorption is within a very thin outer layer, usually less than 0.1 µm thus only metallic fi ...
... Metals are opaque because the incident radiation having frequencies within the visible range excites electrons into unoccupied energy states above the Fermi energy, as demonstrated in Figure (a) below. Total absorption is within a very thin outer layer, usually less than 0.1 µm thus only metallic fi ...