charge
... Example: Glass rubbed with silk becomes positive, rubber rubbed with fur becomes negative ...
... Example: Glass rubbed with silk becomes positive, rubber rubbed with fur becomes negative ...
PHYS 241-1
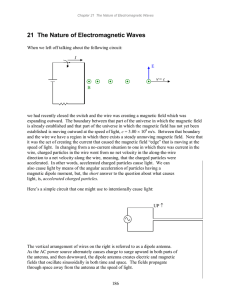
... Know what is meant by an electromagnetic plane wave. Know that for this wave, the electric and magnetic field vectors are in phase and that E B points in the direction of propagation of the wave. (See Figure 33-5.) Know that if this wave is traveling in the direction of the +x-axis, the magnitudes ...
... Know what is meant by an electromagnetic plane wave. Know that for this wave, the electric and magnetic field vectors are in phase and that E B points in the direction of propagation of the wave. (See Figure 33-5.) Know that if this wave is traveling in the direction of the +x-axis, the magnitudes ...
Chemistry - nyostrander.us
... 3. State the model that first included electrons as subatomic particles. [2] The Thomson model first included electrons (the negatively charged particles). _________________________________________________________________________ 4. State one conclusion about the internal structure of the atom that ...
... 3. State the model that first included electrons as subatomic particles. [2] The Thomson model first included electrons (the negatively charged particles). _________________________________________________________________________ 4. State one conclusion about the internal structure of the atom that ...
Experiments - Ohio State University
... Some Differences: experiment geometry data rate single purpose vs multi-purpose 880.A20 Winter 2002 ...
... Some Differences: experiment geometry data rate single purpose vs multi-purpose 880.A20 Winter 2002 ...
Name_______________________ Answers to Final Exam Study
... II. Atomic Structure, Matter and Nuclear Chemistry 9. Consider an element Ub that has two naturally occurring isotopes with the following percent abundances: the isotope with a mass number of 11.0 is 42.0% abundant; the isotope with a mass number of 18.0 is 58.0% abundant. What is the average atomic ...
... II. Atomic Structure, Matter and Nuclear Chemistry 9. Consider an element Ub that has two naturally occurring isotopes with the following percent abundances: the isotope with a mass number of 11.0 is 42.0% abundant; the isotope with a mass number of 18.0 is 58.0% abundant. What is the average atomic ...
The Basic Physics of Electricity and Magnetism
... current can flow through the coil, the iron will become magnetized. The magnetic field generated by the electrical current flowing through the wire causes all the small magnetic crystals contained within the iron to line up in the same direction, with north at one end and south at the other, and pro ...
... current can flow through the coil, the iron will become magnetized. The magnetic field generated by the electrical current flowing through the wire causes all the small magnetic crystals contained within the iron to line up in the same direction, with north at one end and south at the other, and pro ...
General revision
... ) Newton was able to explain reflection and refraction of light. ) Huygens set up the wave theory of light. ) Huygens was able to explain reflection and refraction of light. ) Huygens showed that a wave theory of light could also explain reflection and refraction. ) The wave theory of light was prop ...
... ) Newton was able to explain reflection and refraction of light. ) Huygens set up the wave theory of light. ) Huygens was able to explain reflection and refraction of light. ) Huygens showed that a wave theory of light could also explain reflection and refraction. ) The wave theory of light was prop ...
of light - Nutley Public Schools
... h. Refraction: The change in direction of a wave as it crosses the boundary between two media in which the wave travels at different speeds. i. Total internal reflection: The 100% reflection (with no transmission) of light that strikes the boundary between two media at an angle greater than the crit ...
... h. Refraction: The change in direction of a wave as it crosses the boundary between two media in which the wave travels at different speeds. i. Total internal reflection: The 100% reflection (with no transmission) of light that strikes the boundary between two media at an angle greater than the crit ...
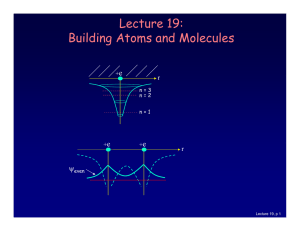
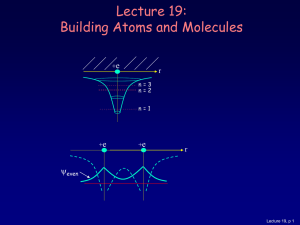
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
... For example, in a given atom they cannot have the same set of quantum numbers n, l, ml, ms. This means that each atomic orbital (n,l,ml) can hold 2 electrons: ms = ±½. ...
... For example, in a given atom they cannot have the same set of quantum numbers n, l, ml, ms. This means that each atomic orbital (n,l,ml) can hold 2 electrons: ms = ±½. ...
lecture 15 (zipped power point) (update: 2 Jan 03)
... This also means that this effect is difficult to observe in our macroscopic world (unless with the aid of some specially designed apparatus) The smallness of h in the relation = h/p makes wave characteristic of particles hard to be observed The statement that when h 0, becomes vanishingly smal ...
... This also means that this effect is difficult to observe in our macroscopic world (unless with the aid of some specially designed apparatus) The smallness of h in the relation = h/p makes wave characteristic of particles hard to be observed The statement that when h 0, becomes vanishingly smal ...