* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Activity Booklet – Task 1
Bicycle lighting wikipedia , lookup
Light pollution wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Doctor Light (Kimiyo Hoshi) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
Doctor Light (Arthur Light) wikipedia , lookup
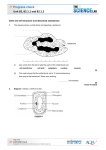
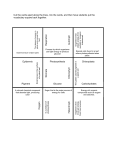
Acknowledgments The investigative tasks included in this Science Olympiad booklet are the result of a team effort and reflect the contributions of Ms Miriam Muscat, Mr Joseph Cutajar and Mr Michael Mercieca. Extended thanks to Mr Joe Bartolo (Senior Technical Officer) and his team of technicians for the excellent lab/equipment organisation and preparation. Much appreciation to Mr Robert Borg (Head of School) for hosting the event at St Theresa College Secondary School. Special thanks are due to Mr Joseph Cutajar for his technical support, design and compilation of the final booklet version. Table of Contents Acknowledgments....................................................................................................................................... 2 Instructions .................................................................................................................................................... 2 Overview .......................................................................................................................................................... 3 Why Light Matters .................................................................................................................................. 3 Task 1 ................................................................................................................................................................ 5 Space for Rough Work ............................................................................................................................ 13 Space for Rough Work ............................................................................................................................ 14 Space for Rough Work ............................................................................................................................ 15 Instructions 2 SAFETY FIRST – wearing a lab coat together with safety specs is mandatory at all times. The use of disposable gloves is also recommended. The lamp provided on your workstation is connected to a 240 V mains supply and can become very hot to touch. Proper caution is advised. You are asked to attempt all questions and write your answers clearly in the spaces provided. Any work scribbled on the ‘Rough Work’ space provided will not be considered. Each team is requested to clean the lab station adequately after handing in the script to the lab supervisor. It is important that all laboratory equipment is handled very carefully. In case of any breakages report immediately to the lab supervisor. You are also reminded of the necessity of good English and orderly presentation of your answers. Overview Why Light Matters From sunsets to rainbows, from the blues and greens of the ocean to the remarkable range of colours of plants and animals, our first experiences of light and colour are through what we see in the natural world. Photosynthesis Green plants, algae and some bacteria are able to produce the organic compounds that they need. Photosynthesis involves many chemical reactions during which sunlight energy is absorbed by chlorophyll pigments and converted into chemical energy. Photosynthesis is an essential process on which all animals depend. Think of adding a teaspoon of sugar in your coffee, eating a chicken burger or breathing oxygen in the air. All these actions depend directly or indirectly on plant material! Refraction A rainbow is a beautiful natural phenomenon that occurs when drops of rainwater meet sunlight. The multi-colour arch is produced by a fundamental process called refraction, or the “bending” of light. In optics, refraction is a phenomenon that often occurs when waves travel from a medium with a given refractive index to a medium with another at an oblique angle. A lens is a carefully moulded piece of transparent material that refracts light rays in such a way as to form an image. Lenses serve to refract light at each boundary. As a ray of light enters a lens, it is refracted, and as the same ray 3 of light exits the lens, it is refracted again. The net effect of the refraction of light at these two boundaries is a change in the direction of the light ray. Matter and Light The relationship between matter and light may not be obvious. However, matter and light are inextricably related to each other. Light is generated when enough energy is produced during a chemical reaction. Indeed, humans have used fires as a source of light. Courtesy of: commons.wikimedia.org The chemical reactions that produce light in different colours form the basis of the fireworks industry. Fireworks are popular within traditional local village feasts. However, they may be a source of pollution. 4 Task 1 “…Photosynthesis involves many chemical reactions during which sunlight energy is absorbed by chlorophyll pigments and converted into chemical energy.” 1) The plant provided in the lab is Syngonium podophyllum, commonly known as African Evergreen, Arrowhead Vine, Five Fingers and Goosefoot plant. This is a common, ornamental, indoor plant but is considered a weed in rainforests. The leaves vary in size, shape and colour depending on their position on the plant. Mature leaves are dark green with silvery-white veins. This plant reproduces vegetatively in the wild and is spread by cuttings in cultivation. Figure 1 Biology students wanted to investigate the leaf’s surface area able to carry out photosynthesis. a) Write the species name of this plant. ____________________________________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) b) Using the 1.0 cm grid overleaf, draw a scale diagram and calculate the surface area of a leaf from the plant provided. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) 5 6 c) Design an experiment to investigate whether the whole leaf’s surface area is able to carry out photosynthesis. Your report should include: i) a list of the steps for the procedure carried out and ONE reason for each step; _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ (8 marks) 7 ii) a labelled diagram of the set-up of your experiment; (2 marks) iii) TWO precautions taken during the investigation; _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ (2 marks) iv) a conclusion derived from your investigation and ONE reason for it. _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ (1, 1 mark) d) Syngonium podophyllum reproduces vegetatively or can be spread by cuttings. Name this type of reproduction. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) 8 2) Students constructed the apparatus shown below. A cork board was attached to a bicycle wheel mounted in a way to rotate clockwise by a motor at 1 revolution per minute. This slow rotation approximates a weightless environment for the seeds. Study the apparatus and then answer the questions that follow. motor rotating bicycle wheel broad bean seed pinned to damp cotton wool and cork based board a) On the diagram above, draw the growing shoots and roots after 10 days. Label the shoots and roots clearly. (2 marks) b) Name the hormone responsible for this growth. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) c) Name the apparatus used in the lab that works using the same concept shown in the diagram. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) d) On the diagram below, draw the growth response of the shoot and root if the bicycle wheel stops rotating. Label the shoot and root clearly. (1, 1 mark) 9 3) A biology teacher was interested in creating a bottle garden in the lab. She discussed with the students which bottle to use among a clear, brown or green glass bottle of equal thickness. a) Explain the importance of comparing glass bottles of equal thickness. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) b) The graph below shows the intensity of the light that is transmitted through the three differently coloured glass bottles. c) Name the glass bottle colour most suitable to use for the bottle garden. Give ONE reason for your answer. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ (1, 1 mark) 10 4) A tropical rain forest is a region of year-round warmth ranging from 20 − 34°C and an average rainfall of 125-660 cm. The following pictures show the different layers of a tropical rainforest and typical plants growing in this environment. Emergent layer Canopy layer Under canopy layer Forest floor a) Name the phylum to which the Crow’s Nest Fern belongs. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) b) Leaves in the canopy layer are smooth, oval shaped and pointed. Give ONE reason for this structure. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) 11 c) Some trees in the emergent layer have straight, thin trunks. They are shallow rooted and develop buttress roots. State how these types of roots can be helpful to the plant. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ (2 marks) d) Trees in the canopy layer do not branch out. State ONE reason for this. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) e) A leaf might take one year to decompose in a regular climate, but only six weeks to disappear in the rainforest floor. Name TWO abiotic factors that help accelerate the decomposition process. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ (2 marks) f) Epiphytes such as orchids and the Crow’s Nest Fern harvest their nutrients from the surrounding elements including air, rain and falling leaf litter. Explain why epiphytes are not parasites. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) g) The under canopy layer is mainly made up of tree trunks and small shrubs. Little air movements occur and there is high humidity in this layer. Cormiflori trees produce strong smelling flowers on their trunks. Explain the importance of this adaptation. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) Total Mark 12 35 Space for Rough Work 13 Space for Rough Work 14 Space for Rough Work 15